![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Prone Position
|

Lying face down
|
|
|
Supine Positon
|

Lying ventral up
|
|
|
Another word for superior
|
Cranial
|
|
|
Another Word for inferior
|
caudal
|
|
|
The body cut right to left is
|
Median or midsagittal
|
|
|
The body cut ventral to dorsal
|
Coronal
|
|
|
The body cut superior to inferior
|
Transverse/horizontal
|
|
|
The body cut at an angle
|
Oblique
|
|
|
The body cut right to left like loaves of bread, all the ones off set from the middle
|
Parasagittal
|
|
|
Of the Upper Arm
|
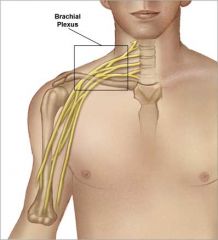
Brachial
|
|
|
Of the Clavical
|
Clavicular
|
|
|
Of the skin or near the skin
|
Cutaneous
|
|
|
Of the thigh
|
Femoral
|
|
|
Of the buttocks
|
Gluteal
|
|
|
Of the upper Pelvic Region
|
illiac
|
|
|
of the groin
|
Inguinal
|
|
|
Of the lower back
|
Lumbar
|
|
|
Of the front chest
|
Pectoral
|
|
|
Of the lowest area torso
|
Pelvic
|
|
|
Of the back of the knee
|
popliteal
|
|
|
Of the back of the knee
|
popliteal
|
|
|
of the ankle
|
tarsal
|
|
|
of the chest
|
thoracic
|
|
|
Of the back of the knee
|
popliteal
|
|
|
of the ankle
|
tarsal
|
|
|
of the chest
|
thoracic
|
|
|
Of the back of the knee
|
popliteal
|
|
|
of the ankle
|
tarsal
|
|
|
of the chest
|
thoracic
|
|
|
Proximal Epiphysis
Distal Epiphysis of the Humerus |

What is highlighted in the first box
What is higlighted in the second box |
|
|
Proximal Epiphysis
Distal Epiphysis of the Humerus |

What is highlighted in the first box
What is higlighted in the second box |
|
|
The line That separates the Epiphysis from the rest of the bone
|

Epiphyseal Lin
|
|
|
The tubular shaft that forms the long axis of a long bone.
|
Diaphysis
|
|
|
The center of the diaphysis that contains no bone tissue at all
|

The Medullary Cavity
|
|
|
The center of the diaphysis that contains no bone tissue at all
|
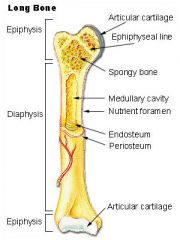
The Medullary Cavity
|
|
|
Fatty Bone/No role in blood cell formation. Lies in the open space in medullary cavity
|

Yellow Bone Marrow
|
|
|
Spongy Bone is called
|
Cancellous Bone
|
|
|
This covers the entire outer surface of the bone/with the exception of the ends on the epiphyses.
|
Periosteum
|
|
|
The hle in the wall of the diaphysis where the artery and vein run through to vascularize the bone
|

Nutrient Foramen
|
|
|
This type of joint in immovable, only slightly movable..Name Give me 1 examples
|
(FIBROUS)
Sutures, syndesmoses (connective tissue btw ulna and radius) gomphoses (tooth inserted into socket) |
|
|
The type of joint where the articulating bones are united by cartilage. 1 good example
|
Joint btw 1st rib and sternum
Inverterbral discs and pubic symphsis |
|
|
The most movable joints in the body, contain fluid filled joint cavitys. Most of the joints are of this class.
|
Synovial joints
|
|
|
(FunctionaI Classification)
Imovable articulation 3 examples |
Synarthroses
-Suture -Syndesmosis -Gompphosis |
|
|
(Functional Classification)
Slightly moveable joint 2 examples of |
Amphiarthroses
-Synchondrose-where hyaline cartilage unites bones-ribs to sternum -Symphyses-(Pubic symphis, and invertabral discs) |
|
|
(functional classication of joints)
Moveable joints 6 examples; |
diarthroses
1)Plane-Clavial to Scapula 2)Hinge-Knee 3)Pivot 4)Condyloid 5)Saddle 6)Ball and Socket |
|
|
Example of Synovial joint
Plane join |

Clavicle to scapula
|
|
|
Synovial joint hinge joint
|

Knee or elbow
|
|
|
Synovial joint (Pivot example)
|
axis
|
|
|
Any joint that connects via a condyle is what type of joint
|
(Synovial-Condyloid)
|
|
|
Articulating joint one with a convex side the other concave
|

Saddle joint
|
|
|
Synovial joint example of ball and socket
|

femur in the acetabulum
|
|
|
What 6 things distinguishes synovial joints from other joints?
|
1)Synovial Membrane
2)Synovial Cavity 3)Articular cartilage 4)Fibrous capsule 5)Tendone and ligaments to support externally 6)Ligaments to support bothe externally and internally |
|
|
What are Fibrous joints
|
Sutures (short fibers)
Gomphosis-The root of a tooth and its socket Syndesmosis-Slightly movable |
|
|
The tibiofibular articulation is what type of joint?
|

Fibrous
(Syndesmoses) |
|
|
The membrane between the between the radius and the ulna is what type of joint?
|
Fibrous-Synesmoses
|
|
|
The membrane between the between the radius and the ulna is what type of joint?
|
Fibrous-Synesmoses
|
|
|
What kind of joint is a suture
|
Fibrous
|
|
|
What type of joint unites bone ends/parts via collagenic fibers
|
Fibrous
|
|
|
What type of joint unites bone ends/ parts with cartilage
|
Cartilaginous
|
|
|
What are the 2 subcatagories of Cartlaginous joints
|
Synchondrosis (hyaline cartilage)
Symphysis (fibrocartilage) |
|
|
What type of joint in the immovable joint btw the the fist rib and the sternum
|
Synchondroses
|
|
|
Cartilaginous-Synchondroses
|
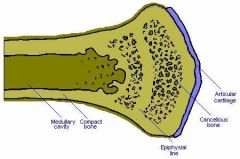
The epiphyseal plate is what type of joint
|
|
|
Inverterbral discs are what type of joints.
|
Cartilaginous/Symphyses
|
|
|
The pubic symphysis is what type of joint
|
symphyese
|
|
|
What are the 6 types of synovial joints
|
1)Plane
2)Hinge Joints 3)Pivot joint 4)Condyloid joints 5)Saddle Joints 6)Ball and Socket joints |
|
|
FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATION
(A joint that is immovable) |
Synarthroses
|
|
|
(FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATION)
A joint that is slightly movable |
Amphiarthroses
|
|
|
A small saclike dialation, (tooth socket)
|
Alveolus
|
|
|
A tube passage through bone that is an opening for veins, arteries or nerves
|
Canal
|
|
|
A slit shaped opening btw 2 bones
|
Fissure
|
|
|
A hole that goes through the bone that allows for the passage of blood vessels or nerves
|
Foramen
|
|
|
A shallow depression or cavity
|
Fossa
|
|
|
A flattened area of bone,
|
Lamina
|
|
|
A pipe shaped or tube like opening
|
meatus
|
|
|
A cavity withing a bone
|
sinus
|
|
|
A groove or deep depression btw 2 areas of the same bone
|
Sulcus
|
|
|
A small head on a bone
|
Capitulum
|
|
|
A rounded prominence at the end of a bone
|
Condyle
|
|
|
A condyle above another condyle
|
epicondyle
|
|
|
A round projection beyond the head of the bone
|
Head
|
|
|
A round projections beyond the neck of the bone
|
Head
|
|
|
A process shaped like a small hamerhead,
|
Malleolus
|
|
|
the head of the bone
|
Olecranon
|
|
|
a projection from, or a bump on a bone
|
process
|
|
|
A process shaped like a pulley
|
Trochlea
|
|
|
a rough, bony ride,
|
crest
|
|
|
A prominent ridge along the diaphyses of a bone
|
line
|
|
|
A sharp projection
|
spine
|
|
|
A large, roughed raised or enlarged area of a bone
|
troochanter
|
|
|
A rounded enlargment, but smaller and smoother than a trochanter
|
tubercle
|
|
|
A rough enlarged area
|
tuberosity
|
|
|
How many bones are in the axial skeleton
|
80
|
|
|
How many bones are in the appendicular skeleton
|
126
|
|
|
What provides the framework to which the upper limbs attack, and is made up of the scapula and clavical
|
The pectoral girdle
|
|
|
What provides the framework to which the lower limbs attack and is made up of the 2 coxal bones.
|
The pelvic girdle
|
|
|
The acromion is posterior to the what process
|
coracoid
|

