![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
You are having difficulty locating the gallbladder in a patient with right upper quadrant pain. What anatomic landmark will help you identify the gallbladder fossa? |
- interlobar hepatic fissure |
|
|
In what anatomic variant is the fundus of the gallbladder folded over the body? |
- Phrygian cap |
|
|
A patient is referred from the emergency room to rule out acute cholecystitis. You think the gallbladder wall may be thickened. What is the normal diameter of the gallbladder wall? |
- < 3mm |
|
|
You are scanning the gallbladder and notice some smudgy echoes within it. You suspect the echoes are due to artifact. What is a common cause of artifactual echoes within the gallbladder? |
- reverberation - side lobes - slice thickness artifact
- all of the above |
|
|
You have a patient scheduled for gallbladder sonogram. What preparation is required? |
- the patient should be fasting for 8-12 hours prior to the study |
|
|
You have been requested to perform a gallbladder u/s to rule out cholelithiasis. What is cholilethiasis? |
- Gallstones |
|
|
You are scanning the gallbladder and notice that the wall abnormally thick. Which of the following is NOT a cause of gallbladder wall thickening? |
- Malignant ascites |
|
|
A referring physician has asked you about the accuracy of the gallbladder sonography. The diagnostic accuracy of the gallbladder sonography is: |
- > 90 % |
|
|
During gallbladder sonography, you notice echogenic foci whithin the gallbladder but do not detect distal acoustic shadowing. What changes below will improve the detectability of stone shadowing? |
- Increase transducer frequency, increase transducer focusing |
|
|
You are scanning a patient with a porcelain GB. What does this term mean? |
- The GB wall contains varying amounts of calcification |
|
|
Which of the following best describes the location of the distal CBD? |
- Posterior and slightly lateral to the panc head |
|
|
The patient you are scanning has eating breakfast prior to your study. What is the appearance of the GB in the postprandial state? |
- Contraction of the GB w/ difuse wall thickening |
|
|
A patient presents to the u/s department for a sonogram to rule out biliary obstruction. Which lab test would best indicate the presence of bile duct obstruction? |
- Serum direct bilirubin |
|
|
What is the most common cause of acute cholecystitis? |
- Calculous obstruction of GB nk or cystic duct |
|
|
Tenderness over the GB with probe pressure is termed: |
- Murphy's sign |
|
|
You are performing an abdominal u/s study and detect a dilated, nontender GB. What should you look for? |
- Mass in the head of the pancreas |
|
|
Which of the following is a symptom associated with acute cholecystitis? |
- Nausea - Vomiting - Epigastric pain - Rt upper quadrant pain -All of the above |
|
|
you are performing an u/s examination on a patient with acute cholecystitis. Complications of acute cholecystitis that you should look for include all of the following EXCEPT: |
- Pancreatic carcinoma |
|
|
You have been asked to rule out the presence of choledocholithiasis. What are you looking for? |
- Stones withing the CBD |
|
|
Identification of what anatomic structure would most help a sonographer locate a contracted GB? |
- Main lobar fissure |
|
|
The transverse diameter measurement of the Gb in a fasting patient measure 5.3 cm. This measurement is: |
- Consistent w/ a hydropic GB |
|
|
You are scanning a patient in ICU and notice low-level echoes w/in the GB consistent with sludge. The GB wall is thickened. Which statement below is true? |
- The patient has sludge most likely due to bile stasis. |
|
|
U/s images obtained on a 48-yr-old male show a comet-tailor V-shaped reverberation artifact originating form the anterior wall of the GB. This artifact most likely results from: |
- Adenomyomatosis |
|
|
You are performing an u/s study to rule out the presence of cholelithiasis. A small echogenic foci is seen in the posterior aspect of the GB fundus. How can you determine if this foci represents a polyp or a stone? |
- Shadowing is not present with polyps but is present with stones. |
|
|
What is the sonographic appearance of the lumen effective sludge w/in the GB? |
- An avscular mass with low-level echoes |
|
|
You are scanning a 34-yr-old multiparous women with symptoms of severe Rt. Upper quadrant pain, nausea, and vomiting. The GB is thick-walked w/ stones and an adjacent complex fluid collection is seen. This findings most likely represent: |
-Acute cholecystitis complicated by GB perforation |
|
|
You are scanning a 44-yr-old man with diabetes. He complains of severe epigastric pain radiating to the back, vomiting, chills and fever. U/s findings include a large GB w/ non dependent hyperechoic foci associated w/ ringdown artifacts. These findings are most consistent with: |
- Emphysematous cholecystitis |
|
|
Hypervascularity associated w/ acute cholecystitis is best evaluated w/ Doppler interrogation of what artery below? |
- Cystic artery |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a sign of acalculous cholecystitis? |
- cholelithiasis |
|
|
You are scanning a GB and notice posterior acoustic shadowing. You are unsure if the shadowing is due to bowel gas or gallstones. Which of the following would be helpful in making this distinction? |
- Roll the patient into a left lateral decubitus position |
|
|
You are imaging the GB in a TRV orientation and notice a long shadow at both edges. What is the etiology of this shadow? |
- Refraction artifact |
|
|
An u/s image obtained from the GB shows an irregular mass within the lumen which demonstrates hypervascularity by color Doppler imaging. Multiple stones are also seen within the GB lumen. These findings are most consistent with: |
- GB carcinoma |
|
|
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are associated with which of the following conditions? |
- Adenomyomatosis |
|
|
The best way to identify the intrahepatic biliary system is to image which structures below? |
- The intrahepatic biliary system cannot be detected sonographically |
|
|
A patient is referred for a follow-up abdominal sonogram. The previous u/s report indicates that pneumobilia was present. What is pneumobilia? |
- Air in the bile ducts |
|
|
You suspect intrahepatic bile duct dilatation in a patient with right upper quadrant pain and tenderness. How can you differentiate the dilated ducts from intrahepatic veins? |
- Dilated bile ducts demonstrate irregular, tortuous walls - Bile ducts will not demonstrate flow with color Doppler -A and C only |
|
|
What forms the common bile duct? |
- Junction of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct |
|
|
During u/s evaluation of the GB system, you notice thickening of the bile duct walls. This finding may be related to which of the following? |
- Sclerosing cholangitis - Pancreatitis - Choledocholithiasis - Cholangiocarcinoma
-All of the above
|
|
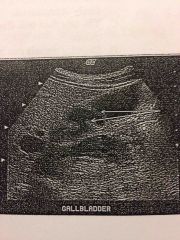
In this image of the GB, the arrows are pointing to: |
- Junctional folds |
|
|
You have been asked to perform an u/s to evaluate for biliary obstruction in a patient with a history of weight loss and midepigastric pain. You find both intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilation. The GB is hydropic. Which of the following conditions causing ductal dilation should you look for? |
- Choledocholithiasis - Pancreatic carcinoma - Chronic pancreatitis with stricture formation - All of the above |
|
|
Cystic dilation of the common bile duct is: |
- Choledochal cyst |
|
|
A 51-yr-old male is referred for abdominal u/s with abdominal liver function tests and jaundice. Which lab work would aid in differentiation of an intrahepatic versus extra hepatic cause of jaundice? |
- Serum bilirubin |
|
|
You are scanning at the area of the port hepatic in a patient with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Two large tubular structures are identified. How can you identify which structure is the duct and which is the hepatic artery? |
- Doppler signals can be elicited from the artery but not the bile duct. |
|
|
A patient presents for abdominal u/s with a history of jaundice, weight loss, and nausea. You detect dilation of the CBD at the level of the port hepatis but are unable to see the distal CBD due to overlying bowel gas. Which of the following would be most helpful in improving visualization of the CBD? |
- Roll the patient into a right posterior oblique position |
|
|
The most common anatomic variant of the GB is: |
- GB folds |
|
|
What is the most accurate test for acute cholecystitis? |
- Cholescintigraphy |
|
|
You are scanning a patient with a Porcelain GB. You must carefully evaluate the GB b/c these patients are at increase risk for: |
- GB carcinoma |
|
|
A patient is referred for GB u/s with a history of Rt. upper quadrant pain and nausea. You suspect the presence of a stone in the region of the GB nk, but are not sure. Which of the following would be helpful in confirming the presence of a stone? |
- Roll the patient into a Lt.: lateral decubitus pposition |
|
|
You have been asked to administer cholecystokinin to a patient. Which of the following do you expect to occur if the study is normal? |
- The GB will contract |
|
|
You are attempting to locate the common hepatic duct at the port hepatis. What is the most common anatomic relationship of the portal triad at the location? |
- The common duct is anterior to the hepatic artery and portal vein |
|
|
A patient is referred for u/s with jaundice, pain, nausea and vomiting and a history of cholecystectomy. Which of the following findings is most likely? |
- Choledocholithiasis |
|
|
You have detected a stone impacted in the distal CBD in a patient with jaundice and abdominal pain. You will tailor your exam to evaluate what complication of this condition? |
- Pancreatitis |
|
|
You are requested to perform an u.s evaluation of the GB and biliary tree on an elderly female with a small frame. Which of the following transducers is most suited to this task? |
- 5.0 MHz phased array |
|
|
A patientis referred for a abdominal u/s. You notice a yellow discoloration of the eyes and skin. This condition is called: |
- Jaundice |
|
|
You are asked to perform an u/s study on a patient with suspected cholangiocarcinoma. What associated findings should you look for? |
- Dilatation of the biliary tree |
|
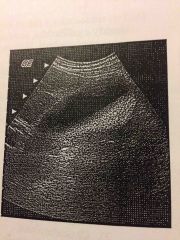
What is the etiology of the low-level echoes seen in the near field of this GB? |
-Reverberation artifact |
|
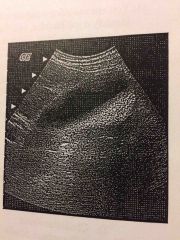
What is the etiology of the layered echoes seen in the posterior aspect of this GB? |
- Biliary sludge |
|
|
You are scanning a patient in the ER with severe nausea and abdominal pain. When you press with the transducer over the GB, the patient has increased pain. What did you do? |
- Elicited Homan's sign |
|
|
You are scanning a patient with sickle cell anemia and note the presence of gallstones and GB wall thickening. What else should you do to determine if acute cholecystitis is present? |
- Press with the u/s probe over the GB to determine if it is painful. - Look carefully to see if a gallstone is lodge in the GB nk. - Check for presence of pericholecystic fluid. - All of the above |
|
|
What is the purpose of obtaining images in the Lt. lateral decubitus position during ultrasonography of the GB? |
- Evaluate mobility of gallstones |
|
|
You are scanning a patient with symptoms of cholelithiasis. Although you cannot clearly identify a GB, you detect a bright band echoes with posterior shadowing in the Rt. upper quadrant. How can you determine if this represents a contracted GB filled with stones? |
- Connection of the shadowing echoes to the interlobar fissure confirms identification of the Gb - The wall-echo-shadow (WES) sign confirms identification of the GB - "Dirty" shadowing from bowel gas can be differentiated from "clear" shadowing from stones by the presence of ringdown artifact in the bowel gas shadow - All of the above |
|
|
A tumor that may be located in an intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile duct is known as: |
- Cholangiocarcinoma |
|
|
U/s images you obtained on an 81-yr-old man with acute Rt. upper quadrant pain show gallstones and bright echoes in the GB wall with ringdown artifacts. Which of the following inmost likely? |
- Emphysematous Cholecystitis |
|
|
You are scanning a 44-yr-old man with diabetes. He complains of severe epigastric pain radiating to the back, vomiting, chills and fever. U/s findings include a large GB w/ non dependent hyperechoic foci associated w/ ringdown artifacts. These findings are most consistent with: |
- Emphysematous cholecystitis |
|
|
Hypervascularity associated w/ acute cholecystitis is best evaluated w/ Doppler interrogation of what artery below? |
- Cystic artery |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a sign of acalculous cholecystitis? |
- cholelithiasis |
|
|
You are scanning a GB and notice posterior acoustic shadowing. You are unsure if the shadowing is due to bowel gas or gallstones. Which of the following would be helpful in making this distinction? |
- Roll the patient into a left lateral decubitus position |
|
|
You are imaging the GB in a TRV orientation and notice a long shadow at both edges. What is the etiology of this shadow? |
- Refraction artifact |

