![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epidemiology |
Bacteria – clostridium tetani Spores are neurotoxic Gram-positive and aerobic Pasillas (drumstick appearance on microscopy) Bacteria found in soil/animal faeces Can survive for years and are very hard to kill High mortality in neonates that contract it via the umbilical wound |
|
|
Pathophysiology |
Toxins travel from muscle to ganglioside Then by retrograde axonal transport to the CNS Exert a blocking affect on inhibitor neurones which causes contraction Mostly affects Gabba neurons which relay motoneuron action |
|
|
Clinical features |
Results in increased muscle tone Trismus/lockjaw Risus sardonicus Opisthotonus Rigidity/hypotonia, spasms, pain It can involve respiratory muscles and laryngeal muscles In second week there is also autonomic overactivity – labile BP, pyrexia, tachycardia |
|
|
Diagnosis |
Clinical Evidence of wound/source of contraction Lack of immunisation history WHO definition of confirmed neonatal tetanus – Illness in an infant who has normal ability in the first two days of life, but loses the ability between day 2 and 28 of life and becomes rigid or has spasms. Differential - strychnine poisoning |
|
|
Treatment |
Supportive care Hydration, nutritional support, benzodiazepines spasms spasms, magnesium sulphate/morphine for in autonomic instability, analgesias, environment (side room without stimulation/sudden noises that can trigger muscle spasms) Wound care including debridement if needed Metronidazole – prevent further toxin release Tetanus Ig ITU facilities - Autonomic instability Monitor for and treat complications Tetanus vaccine – three primary dose in babies six weeks and three booster doses |
|
|
Prevention |
Umbilical cord care Wound care Tetanus vaccine (maternal five dose regime started during pregnancy or high risk approach in an immunised populations of three doses) Neonatal tetanus surveillance is necessary to target elimination efforts |
|
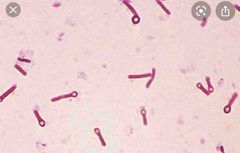
Front (Term) |
Clostridium tetani Drum stick appearance |
|

Front (Term) |
Risus sardonicus |
|
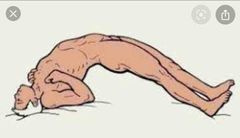
Front (Term) |
Opisthotonus |

