![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Layers of skin |
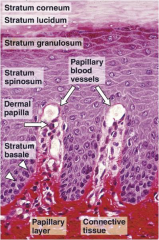
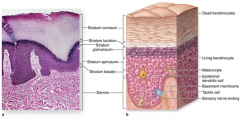
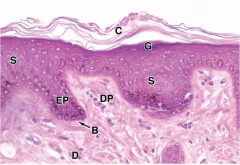
Epidermis - Stratum corner - stratum spinosum - stratum basale Dermis - papillary layer reticular layer Hypodermis superficial fascia |
|
|
Functions |
Protection - barrier against external environment Sensory - Receptors detect external environment Thermoregulatory - Regulates water loss & body temperature Metabolic - Synthesis of vitamin D3 Sexual signaling - pheromones, hair pigmentation |
|
|
Thick skin |
Stratum basale ( germinativum) - single row cells , anchored by hemidesomes , attach cells to basement membrane and connective tissue ( and desmosomes between cells) |
|
|
Epidermal layer |
Stratum spinosum ( prickle cells) - spines are sites of desmosomal attachment- tonofibrils, bundles of keratin filament...intermediate filament, and lamellar granules may be visible
|
|
|
Epidermal layer |
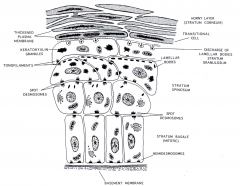
Stratum granulosum-flalttened cells with keratohyalin granules ( protein for soft keratin)- Lipid from lamellar granules, filled with glycolipid, released into intercellular spaces
|
|
|
Epidermal layer |
stratum lucidum - only in thick skin Thin, transparent with dead cells kerathohylin covered to eleidin |
|
|
epidermal layer |
stratum corneum - no nuclei or organelles, just flat scales attached by desmosomes, with waterproof lipid between cells |
|
|
Skin layers |
|
|
|
Epidermis Cell types |
Keratinocytes ( give rise to keratin ) make lamellar granules with glycolipids that are released into the extracellular space to make a water proof area. melanocytes ( pigment - producing ) Langerhans cells ( antigen - presenting ) Merkel cells ( epithelial tactile cells ) |
|
|
" thick vs. " thin " skin
|
Due to epidermal layer: think skin has an extra layer ( stratum lucidum ) |
|
|
Thick skin |
|
|
|
thin skin |
|
|
|
Epidermis keratinization and water barrier |
|
|
|
Melanocytes and langerhans cells |
Melanocytes ( skin pigmentation ) - produce melanin , protect against UV irradiation. Tyrosine > DOPA > melanin. Transferred to keratinocytes by " pigment donation " ( cytocrine secretion ) Langerhans cells - antigen - presenting cells - involved in delayed -type hypersensitivity reactions ( contact dermatitis) |
|
|
Melanin types |
Dark hair - Eumelanin Blonde or Red hair - Pheomelanin |
|
|
Langerhan cells |
present antigen and migrate into the dermis or dermal papilli in search of a lymphatic vessel. |
|
|
Dermis |
Papillary layer - dermal papillae -- projections into epidermis - fingerprints * primary epidermal ridges overlie primary dermal ridges , subdivided into secondary dermal ridges. Dermal papillae project here. Reticular layer - contains bundles of collagen, elastic fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages, adipocytes |
|
|
Cutaneous sensory receptors |
morphological classes - free nerve endings -encapsulated nerve endings * pacinian ( lamellate corpuscle , look like little onions. layers and layers around a nerve ending. Found deep into tissue) , Meisssner's ( tactile corpuscle, close to the surface. Fine sense of touch) , Ruffini's, Krauses's end bulb Functional classes : mechanoreceptors thermoreceptors nociceptors |

