![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does co-dominance? |
One allele is not dominant over its partner. Both alleles are expressed in the phenotype. i.e. ABO blood type. |
|
|
A father has blood type A, and the moth had blood type B. Can the child have O blood? |
Yes. Punnett square.
.....A.....O B..AB...BO O..AO..OO |
|
|
What is incomplete dominance? |
An allele is not fully dominant over its partner. Both are expressed showing a phenotype in between the two conditions. Blending of traits. |
|
|
What is pleiotropy? |
One gene influences many traits. i.e. Albinism. |
|
|
What is epistasis? |
Trait determined by multiple genes. One gene controls expression of another. |
|
|
What is continuous variation? |
Continuous variation is variation that has no limit on the value that can occur within a population. A line graph is used to represent continuous variation. i.e. Height, eye color. |
|
|
What are Environmental Influences? |
Gene expression determined by the environment. i.e. Color of fur is determined by temperature on a Siamese cat. |
|
|
What is a Karyotype? What can this show? |
A diagnostic instrument that reveals abnormalities in chromosomes. It can show missing or extra chromosomes. |
|
|
What is nondisjunction? |
Chromosomes do not separate correctly. Results in aneupolidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes). |
|
|
What is Down Syndrome? |
Also called Trisomy 21. - Characteristic facial features, short stature; hearts defects; susceptible to respiratory infections, leukemia, and Alzheimer's; and a varying degree of mental retardation. |
|
|
What are some common disorders that result from abnormal chromosomes (aneupolidy)? |
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Turner's Syndrome Kinefelter's Syndrome |
|
|
What is autosomal recessive? |
Autosomal recessive is where a trait can only be passed if two recessive genes are present (i.e. "rr"). |
|
|
What does an autosomal recessive pedigree look like? |
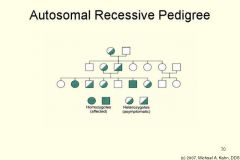
|
|
|
What is autosomal dominant? |
Autosomal dominant is where the trait that is passed to the next generation is a dominant trait. Thus, the child will inherit the trait if they are heterozygous (Rr) or homozygous dominant (RR). |
|
|
What does an autosomal dominant pedigree look like? |
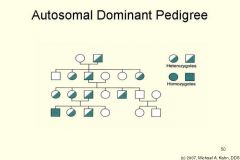
|
|
|
What is sex-linked inheritance? |
due to the fact that women have two X chromosomes, they have less of a possibility of being given traits that are sex-linked. This is because even if one of their alleles is recessive for, say, color blindness, they still have another the chance that the other will be dominant and they will have normal vision.
X(h)X(H)
Whereas males: X(h)y |
|
|
What are some traits that are considered to be sex-linked? |
Hemophilia, Red-Green Colorblindness, Duchene's Muscular Dystrophy are all on the X chromosome.
Testis are on the Y chromosome. |
|
|
A woman is heterozygoes for hemophilia, and the man she married does not have the disease. Can they have a child with hemophilia? What is the probability that they will have a child with hemophilia? |
..........X(H)..........X(h) X(H)...X(H)X(H)..X(H)X(h) y........X(H)y........X(h)y
Yes, they can have a son with hemophilia. It is a 25% chance. |
|
|
What us X Chromosome Inactivation? |
One of the two X chromosomes is inactivated during development. |
|
|
What is a Barr Body? |
Highly condensed. Genes are inaccessible. |
|
|
Which X chromosome is inactivated in X Chromosome Inactivation? |
The XIST gene shuts down the chromosome that transcribed it. |
|
|
What is the role of X Chromosome Inactivation in cat color? |
X(B) = Orange fur X(b) - Black fur.
If a cat has X(B) X(b) then it will be calico or tortoiseshell. A male can only be calico/tortoise shell if it is XXY. |
|
|
What represents a female in a pedigree? What represents a male? |
Female = circle. Male = square. |
|
|
What indicates an afflicted person in a pedigree? What about a healthy person? |
A solid circle/square represents an afflicted person. An empty one represents a healthy person. |
|
|
How is a carrier represented in a pedigree? |
As a half shaded circle/square. |

