![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Entamoeba histolytica causes what disease |
amebic dysentery |
|
|
Giardia lamblia causes what disease |
giardiasis |
|
|
Balantidium coli |
diarrhea |
|
|
Cryptosporidium sp. causes what disease |
cryptosporidiosis |
|
|
Naegleria fowleri causes what disease |
encephalitis |
|
|
What tests are used to detect E. coli besides IMViC? |
MPN, Pour plate, Membrane Filter, and Agar dip slide method |
|
|
What are the IMViC tests? |
Indole, Methyl red, Vogues Proskauer, Citrate |
|
|
What is fecal pollution? |
Pollution from human sewage |
|
|
What is environmental? |
Coliforms from animals naturally in the river |
|
|
What is the standard for municipal drinking water? |
1 coliform/100mL |
|
|
What is the standard for shell fishing? |
70 coliforms/100mL |
|
|
What is the standard for recreational water? |
1000 coliforms/100mL |
|
|
What is Drinking Water Treatment Lvl 1? |
Disinfection Only. 0-50 coliforms/100mL |
|
|
What is Drinking Water Treatment Lvl 2? |
Conventional methods (coagulation, filtration, and disinfection). 50-5000 coliforms/100mL |
|
|
What is Drinking Water Treatment Lvl 3? |
Extensive methods. 5000-50,000 coliforms/100mL |
|
|
What is Drinking Water Treatment Lvl 4? |
Unacceptable. >50,000 coliforms/100mL |
|
|
What tests are used for Fecal Streptococci? |
MPN, Pour Plate, Membrane filter, FC/FS ration (Fecal coliform/Fecal strep) |
|
|
What tests are used for Clostridium perfringens? |
MPN, Blood agar results, Nagler's reaction, Plate count |
|
|
What tests are used for Staphyloccus aureus? |
Spread plate, petrifilm, membrane filter, coagulase, DNase |
|
|
What tests are used for Pseudomonas aeruginosa? |
Asparagine broth, Acetamide broth, Cetrimide agar |
|
|
What is the legend of the origin of BOD testing? |
Sewage was dumped in English river and took 5 days to reach the ocean. |
|
|
What are natural sources of BOD? |
Bogs, swamps, leaves, and vegetation |
|
|
What are human sources of BOD? |
pulp and paper mills, meat-packing plants, food processing industries, and wastewater treatment plants |
|
|
What are nonpoint inputs of BOD? |
Runoff from urban areas, agricultural areas, and feedlots |
|
|
What does BOD measure? |
Biodegradable organic and inorganic compounds in water |
|
|
What is the standard incubation time for BOD? |
5 days at 20 degrees C. |
|
|
What is Ultimate BOD? |
20 days is considered the time for a complete biochemical oxidation of organic matter in a water sample |
|
|
What can give an artificially low BOD? |
Algal effect, low PH, low # of bacteria, and chlorine |
|
|
What can give an artifically high BOD? |
Nitrification effect (NH3>NO3) |
|
|
How is COD (Chemical oxygen demand) different than BOD? |
Uses strong oxidation agent to break down sample. Value usually 1.25x BOD. Not accurate if sample contains chlorine. |
|
|
What is the primary treatment at a sewage treatment plant and its purpose? |
Settling tank to let fats float, solids sink, and liquid goes to secondary treatment. |
|
|
What are the secondarytreatments at a sewage treatment plant and its purpose? |
Biological breakdown of liquids aerobically. Trickling filter, waste water trickled over biofilm of rocks and plastic. Activated sludge, air pumped into large tank of liquid. |
|
|
What is the tertiarytreatment at a sewage treatment plant and its purpose? |
To provide a final treatment to raise effluent quality. Filtration, lagooning, constructed wetlands, and/or nutrient removal (Phosporous/Nitrogen) |
|
|
What is disinfection's purpose at a sewage treatment plant? |
To substantially reduce the number of microbes in the wastewater before discharge into the environment. |
|
|
What are the parts of the disinfection process at a sewage treatment plant? |
Chlorination is the most common. UV light damages genetic material. Ozone is very unstable and oxidizes most organic material. |
|
|
What is anaerobic digestion? |
Sludge treatment of domestic sewage in septic tanks |
|
|
What is aerobic digestion? |
Sludge treatment where a jet aerator is used to aerate water, sewage, sludge, manure, leachate, etc. |
|
|
What is composting? |
Mixing the sludge with sawdust, straw, or wood chips. |
|
|
What is incineration? |
Sludge treatment where you burn the slude and vaporize residual water. |
|
|
What is the flowchart of sewage treatment plant? |
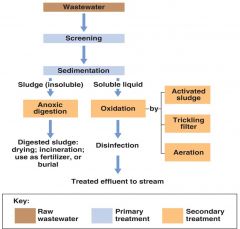
|
|
|
What is the flowchart of water treatment plant? |

|
|
|
What is the purpose of screening at a water treatment plant? |
To catch solids as water passes through to rest of plant. |
|
|
What is the purpose of coagulation at a water treatment plant? |
Raw, untreated water is mixed with chemicals forming sticky globs that attach to bacteria and other impurities. Coagulants like aluminum sulfate, ferrous sulfate, and polymer. |
|
|
What is the purpose of filteringat a water treatment plant? |
Water is pumped through beds of sand and gravel and the remaining particles are screened out. |
|
|
What is the purpose of permanganateat a water treatment plant? |
Oxidizes ferrous iron and manganese. |
|
|
What is the purpose of limingat a water treatment plant? |
Softens water by reducing Ca, Mg, and bacteria |
|
|
What is the purpose of Copper Sulfateat a water treatment plant? |
Removes algae, but cannot be used with lime. |
|
|
What is the purpose of carbon filterat a water treatment plant? |
Removes tastes and odors. |
|
|
What are mineral soils? |
Derivedfrom rock weathering and other inorganic materials |
|
|
What are organic soils? |
Derivedfrom sedimentation in bogs and marshes |
|
|
What are igneous rocks? |
Made from solidification of lava, such as granite. |
|
|
What are sedimentary rocks? |
Madefrom deposits and consolidation ofweathered products of other rocks, such as limestone. |
|
|
What are metamorphic rocks? |
Igneousor sedimentary rock subjected to high temperature and pressure, such as marble. |
|
|
What is the O horizon in a soil profile? |
Layer of undecomposed plant materials. |
|
|
What is the A horizon in a soil profile? |
Surface soil (high in organic matter, dark in color, used for agriculture. High in microbial activity) |
|
|
What is the Bhorizon in a soil profile? |
Subsoil (minerals and so on leached from surface soil. Little organic matter, less microbial activity than A horizon) |
|
|
What is the Chorizon in a soil profile? |
Soil base (develops directly from underlying bedrock, very little microbial activity) |
|
|
What is a bacteria found in soil? |
Pseudomonas |
|
|
What is an actinomycete found in soil? |
Streptomyces |
|
|
What is a myxobacteriafound in soil? |
Myxococcus |
|
|
What is a cyanobacteriafound in soil? |
Schizothrix |
|
|
What is a moldfound in soil? |
Penicillium |
|
|
What is an algaefound in soil? |
Green algae |
|
|
What is a yeastfound in soil? |
Cryptococcus |
|
|
What are the 3 main types of soil? |
Sandy soil, clay soil, silt soil |

