![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Gravity? |

The mutually attractive force between massive objects. |
|
|
What are the four fundamental forces of nature? |
|
|
|
What is the Universal Law of Gravitation? Who created it? |
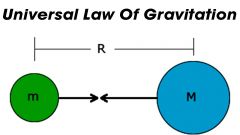
|
|
|
What is Orbit? |
The path taken by one object moving around another under the influence of their mutual gravitational or electric attraction.
|
|
|
What is Free Fall? |
The motion of an object when the only force acting on it is gravity. |
|
|
What is uniform of circular motion?
|
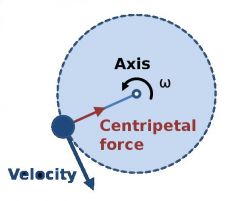
Motion in a circular path at a constant speed |
|
|
What is centripetal force?
Draw! |
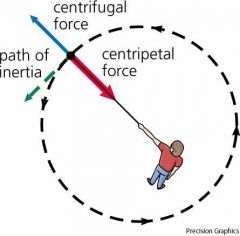
A force directed toward the center of a curvature of an object's curved path.
|
|
|
What is centrifugal force? Draw! |
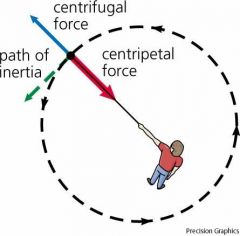
Force that acts outward on a body moving around a center, arises from bodies inertia. |
|
|
What is Circular Velocity?
|
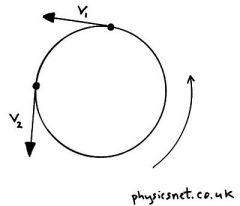
The orbital velocity needed to keep an object moving in a circular orbit.
|
|
|
What is a Satellite? |

Object in orbit around a more massive body.
|
|
|
What is Bound Orbit?
Velocity? |
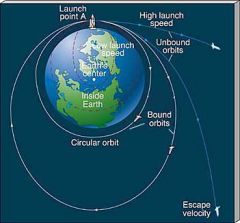
An orbit in which an object is gravitational bound to the body it is orbiting.
|
|
|
What is Escape Velocity? |
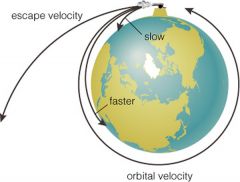
The minimum velocity needed for an object to achieve a parabolic trajectory and leave the gravitational grasp of another mass. |
|
|
What is Unbound Orbit? Velocity? |
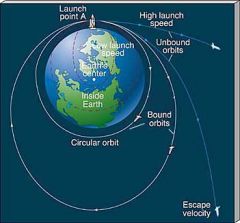
An orbit in which an object is no longer gravitational bound to the body it was orbiting.
|
|
|
What is the center of mass?
|

|
|
|
What is the Rouche limit?
|
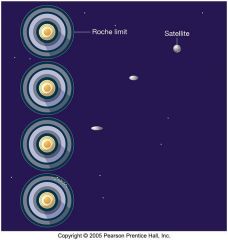
|
|
|
What is a Tide? |
The rising and falling of the surface of large bodies of water due to varying gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun. |
|
|
What are Tidal Forces? |
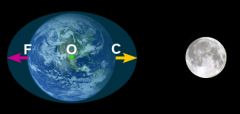
A force caused by the changing in the strength of gravity across an object. |
|
|
What is a Tidal Bulge? |
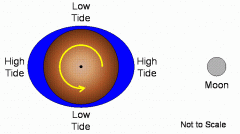
Distortion of a body resulting from tidal stresses.
|
|
|
What are Lunar Tides? |
Caused by the differential gravitational pull of the moon.
|
|
|
What are Solar Tides? |
Caused by the differential gravitational pull of the sun. |
|
|
What are Spring tides? When do they occur? Draw!! |
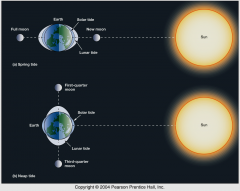
|
|
|
What are Neap Tides? When do they occur? Draw!! |
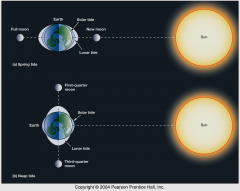
|

