![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How long are typical single covalent bonds? |
1.54 Angstrom |
|
|
What is the typical bond length of hydrogen bonds? |
2.9 Angstrom Salt bridges can be both hydrogen bonding and non-hydrogen bonding, thus length ranges from 2.6-3.5 But we'll just say hydrogen bonds are shorter, so 2.9 |
|
|
What formula capitulates the 2nd law of thermodynamics? |
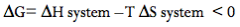
|
|
|
What is the henderson Hasselbalch equation? |
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]) |
|
|
What is the ratio of acceptor/donor when pH = 4 and pKa = 5? |
1:10 |
|
|
What is the ratio of acceptor/donor when pH = 7 and pKa = 5? |
100:1 |
|
|
When pKa - pH > 0, is there more acid or base? Aka, when pKa > pH, is there more acid or base? |
Base! Protonated Form |
|
|
When pKa - pH < 0, is there more acid or base? Aka, when pKa < pH, is there more acid or base? |
Acid! Deprotonated Form |
|
|
What amino acids are negatively charged at physiological pH? |
Glutamate (E) and Aspartate (D) |
|
|
What amino acids are positively charged at physiological pH? |
Arginine (R) and Lysine (K) and SOMETIMES Histidine (H) |
|
|
Are most amino acids L or R stereochemically? |
Only L amino acids constitute proteins |
|
|
What does E6V mean? And in what disease is this substitution found? |
The 6th glutamate is replaced with a valine. This is sickle cell anemia |
|
|
Why does bringing a positive charge into proximity or ionizable groups decrease pKa while a negative charge increases it? |
A positive charge would increase the likelihood of donating a H+ ion because it would stabilize the resulting negative charge, thus lower pKa |
|
|
Why does burying a positively charged ionizable group in a hydrophobic environment decrease pKa while pKa increases for negatively charged ionizable groups? |
Postively charged groups will do their best to act nonpolar (Chargeless) because like dissolves like, so that means that rather than more like a base and less like an acid so that the -OH can remain neutral |
|
|
Phi is the rotation about the ___ bond |
N-C Bond |
|
|
Psi is the rotation about the ___ bond |
C - C=O bond |
|
|
Where is the disfavored region of a ramachandram plot? |
Quadrant 4 near {90, -90} |
|
|
Where are beta sheets found in a ramachadran plot? |
Quadrant 2 between -180 to -60 phi and ~0 to 180 psi |
|
|
Where are right handed alpha helices found in a ramachadran plot? |
Horizontal sliver in quadrant 3 From -180 to -60 phi and -70 to -50 psi |
|
|
Where are left handed alpha helices found in a ramachadran plot? |
Vertical sliver in quadrant 1 From 55 to 65 phi and ~0 to 80 psi |
|
|
What is the x-axis of a ramachadran plot? |
Rotation about the N-C bond, phi values |
|
|
What is the y-axis of a ramachadran plot? |
Rotation about the C - C=O, psi values |
|
|
What is the major stabalizing form of secondary structure? |
Hydrogen bonding between -C=O and H-N- in the backbone |
|
|
Are alpha helices mostly right or left handed? |
Almost exclusively right handed |
|
|
How many residues are there per turn in an alpha helix? |
3.6 residues |
|
|
How large is the rise per turn in an alpha helix? |
5.4 angstrom |
|
|
CO and NH form hydrogen bonds with amino acids ___ residues ahead in sequence |
4 |
|
|
Why is it unfavorable to have Serine, Aspartate, or Asparagine residues in alpha helices? |
S, D, and N disrupt alpha helices because their side chains compete for hydrogen bonds with the backbone atoms |
|
|
How does Threonine, Valine, and Isoleucine disrupt an alpha helix? |
Steric clashes |
|
|
How does the hydrogen bonding scheme of parallel and antiparallel bonding differ in beta sheets? |
Antiparallel sheets hydrogen bond 1 amino acid on strand A to 1 amino acids on strand B Parallel sheets hydrogen bond 1 amino acid on strand A to 2 different amino acids on strand B |
|
|
What type of bonding stabilizes the 3* structure of proteins? |
Hydrophobic and van der waals interactions |
|
|
Where would you expect to find sulfur bridges in cells? |
Extracellular proteins, bacterial periplasms, ER, and Golgi because they are all oxidative envrionment which is needed for bond formation |
|
|
What about the cytosol makes it an unfit environment for sulfur bridges to form? |
Cytosol is a reductive environment which would convert a cystine bridge to 2 cysteine residues |
|
|
What are common hydrogen bond donors found in proteins? What makes it a donor rather than an acceptor? |
-OH, -NH3+, and -NH- Donors have the H and are usually more electron deficient
|
|
|
What are hydrogen bond acceptors found in proteins? |
Lone electrons such as C=O and NH2 electrons |
|
|
What is the typical length of a salt bridge aka electrostatic interaction? |
3 angstoms |
|
|
What is the typical bond length of a van der waals interaction? |
3.6 angstom ranges from 2.5-4.6 |
|
|
Sort bonds from Strongest to weakest (Covalent, van der waals, hydrogen, and electrostatic) |
Covalent > Electrostatic > Hydrogen > Van der waals |
|
|
What does levinthal's paradox teach us about protein folding? |
There's an enormous difference between predicted and actual folding time which tells us that protein folding is not random guess and check ---> Cumulative selection |
|
|
What are the 4 ways to denature a protein? |
1) Acid/Base treatment 2) Heat 3) Detergents 4) Reducing agents |
|
|
What 2 hydrogen-bond disrupting compounds do we commonly use to denature a protein? |
Urea and Guanidinium Chloride |
|
|
How do organic solvents denature proteins? |
Lower dielectric constant, increase electrostatic interactions, and weakens hydrophobic effect within the protein |
|
|
What detergent do we commonly use to denature proteins and how does it do it? |
SDS works by binding to nonpolar core of protein and destabilizing native structure |
|
|
What structural level is most effected by heating a protein and why? |
Tertiary structure because heat effects long range interaction first |
|
|
How does Rosetta software predict protein structure? |
Rosetta simulates protein folding process to predict structure |
|
|
Does 1 peptide sequence always equal 1 structural paradigm? If so, how? |
No, there needs to be states with diminished stability, flexible regions, and a new binding surface that is revealed upon alternate folding thus expanding biological function |
|
|
How do we prevent pathogenic misfolding of proteins? |
Molecular chaperones, UPR, and quality control processes |
|
|
Is the proteome of nucleosome larger? |
Proteome due to the post-translational modification possible and the existence of quarternary structures |
|
|
What is the formula for a change in entropy of the surroundings? |
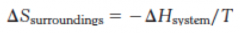
|
|
|
Derive the Henderson-Hasslebach from Equilibrium constant for the deprotonation of an acid |
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA] --> log(Ka) = log [H+] + log([A-]/[HA]) --> -pKa = -pH + log([A-]/[HA]) --> pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]) |
|
|
What compound do we commonly use to reduce disulfide bridges? |
Beta-mercaptoethanol |
|
|
What are the standard state conditions of a delta G naught |
pH=7 and 25*C |
|
|
What is the formula for free energy and equilibriums? |
delta G naught = -RT ln(k) |
|
|
Order bonds from shortest to longest {covalent, hydrogen, van der waals, electrostatic aka salt bridge} |
Covalent < Electrostatic < Hydrogen < Van der Waals |

