![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Reactant |
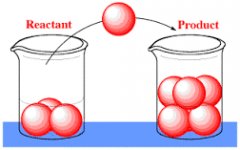
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction |
|
|
product |
an article or substance that is manufactured or refined for sale. |
|
|
catalyst |
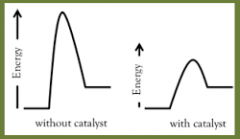
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. |
|
|
Inhibitor |
a : an agent that slows or interferes with a chemical action as substance that reduces or suppresses the activity of another substance |
|
|
Rate of Reaction |
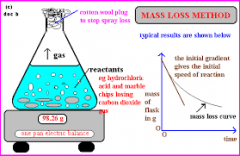
the speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds. It is often expressed in terms of either the concentration (amount per unit volume) of a product that is formed in a unit of time or the concentration of a reactant that is consumed in a unit of time. |
|
|
chemical- reaction |
a process that involves rearrangement of the molecular or ionic structure of a substance, as opposed to a change in physical form or a nuclear reaction. |
|
|
Decomposition |
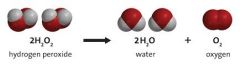
Chemical decomposition, analysis or breakdown is the separation of a chemical compound into elements or simpler compounds. It is sometimes defined as the exact opposite of a chemical synthesis. Chemical decomposition is often an undesired chemical reaction. |
|
|
precipitation |
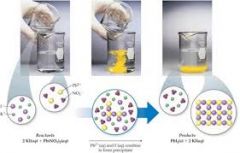
A precipitation reaction refers to the formation of an insoluble salt when two solutions containing soluble salts are combined. The insoluble salt that falls out of solution is known as the precipitate, hence the reaction's name. Precipitation reactions can help determine the presence of various ions in solution. |
|
|
synthesis- reaction |
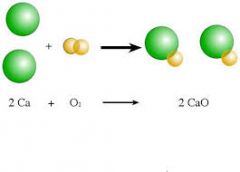
A synthesis reaction or direct combination reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex product. The reactants may be elements or compounds. The product is always a compound. |
|
|
single -Displacement |
A single replacement reaction, also known as a substitution reaction, is a type of chemical reaction where one element replaces another element in a compound. |
|
|
double - displacement |
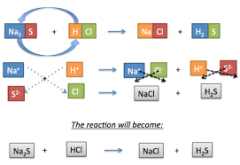
A double displacement reaction, also known as a double replacement reaction or metathesis, is a type of chemical reaction where two compounds react, and the positive ions (cation) and the negative ions (anion) of the two reactants switch places, forming two new compounds or products |
|
|
exothermic - reaction |
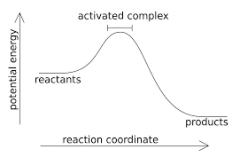
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy by light or heat. It is the opposite of an endothermic reaction. Expressed in a chemical equation: reactants → products + energy. |
|
|
endothermic - reaction |
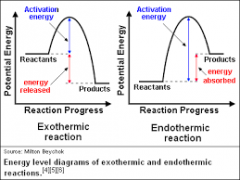
The term endothermic process describes a process or reaction in which the system absorbs energy from its surroundings; usually, but not always, in the form of heat. ... The opposite of an endothermic process is an exothermic process, one that releases, "gives out" energy in the form of (usually, but not always) heat. |
|
|
chemical - equation |
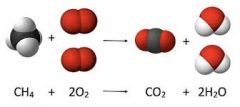
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and formulae, wherein the reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side. |
|
|
conservation of mass |

a principle stating that mass cannot be created or destroyed. |

