![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atom |
Smallest particle of an element that retains the characteristics of that element. |
|
|
Element |
One of the more than 100 known substances that cannot be divided into simpler substances by chemical means. |
|
|
Molecule |
Smallest particle into which a substance can theoretically be divided and maintain its chemical properties, the chemical combinations two or more atoms. |
|
|
Conpounds |
The combination of two or more different elements to form a resulting product that is chemically different from the original ingredients. A compound must be chemically separated. |
|
|
Mixtures |
Two or more molecules or elements are grouped together, and each molecule maintains its chemical identity. A mixture can be physically separated . |
|
|
Nucleus |
Small, dense, positively charged mass located at the center of an atom. |
|
|
Proton |
Positively charged particle located in the nucleus |
|
|
Neutron |
Neutrally charged particle located in the nucleus |
|
|
Electron |
Negatively charged particle that revolves around the nucleus |
|
|
Atomic number |
1. Number of protons in the nucleus 2. Positive charge of a proton is the same magnitude as the negative charge of an electron. 3. Therefore, it may indicate the number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of s neutral atom. |
|
|
Shells |
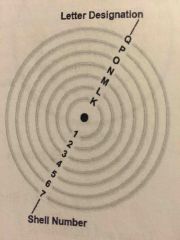
Using 2n^2=maximum number of electrons contained in shells one thru seven |
|
|
Valence |
A number that represents the extent to which an atom is able to combine directly with other atlms |
|
|
Valence Shell |
The outermost shell of an atom |
|
|
Valence Electrons |
Electrons that reside in the valence she'll of an atom |
|
|
Characteristic of Valence |
Maximum number of electrons that can fit into the valence she'll of any atom is eight |
|
|
Valence Differences- Conductors |
Substance that permit free motion of a large number of electrons |
|
|
Insulators |
1. Substances that contain no free electrons 2. Normally have five or more valence electrons |
|
|
Semiconducyors |
1. Substances that are neither good conductors note good insulators 2. Normally have four valence electrons |
|
|
Ionization |
The process by which an atom loses or gains electrons |
|
|
Negative Ion |
1. Atom that has more than its normal amount of electrons 2. Atom that acquires a negative charge |
|
|
Positive Ion |
1. Atom that had fewer than its normal number of electrons 2. Protons outnumber electrons 3. Atom that acquired a positive charge |
|
|
Kirchoff's Law |
The sum of the currents flowing to a given point in a circuit is equal to the sum of the currents flowing away from that point. |
|
|
Ohm's Law |
Current in a circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the circuits resistance |
|
|
Parallel Circuit |
A circuit in which the same voltage is applied to all branches and the current divided among the branches according to their resistances |
|
|
Series Circuit |
Circuit with only one path thru which current can flow |
|
|
Vector |
Directed line segment containing both magnitude(size) and direction |
|
|
Scalar |
In contrast to a vector is a quantity which had magnitude only. |
|
|
Radius Vector |
Revolves around an origin of the rectangular coordinate system |
|
|
Initial Side |
Is the original position of the radius vector |
|
|
Terminal Side |
Is the final position of the radius vector |
|
|
Reference Angle |
Smallest angle between the radius vectors terminal position and the x-axis |
|
|
In phase |
When two sine waves are exactly in step with each other, start at the same point, and reach their maximum and minimum value at the same time. |
|
|
Out of Phase |
When two sine waves of the same frequency are not exactly in step with each other |
|
|
Effective Voltage |
The value of AC voltage that will do the same amount of work as DC voltage |
|
|
Average Voltage |
The average of all instantaneous values on one alternation |
|
|
Phase Shift |
Is a displacement in both time and electrical degrees between two waveforms of the same frequency |

