![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Arteriosclerosis |
Loss of elasticity in the walls of the blood vessels |
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis |
Accumulation of fat deposits inside of arteries, making them more narrow |
|
|
|
Axilla |
Armpit |
|
|
|
Body temperature |
The amount of heat in the body that is balance between the amount of heat produced and amount lost by the body |
|
|
|
Cheyne-stokes |
A pattern of breathing in which respirations gradually increase in rate and depth and then become shallow and slow, breathing may stop for 10 to 20 seconds |
|
|
|
Congestive heart failure (CHF) |
The inability of the heart to pump an adequate quantity of blood |
|
|
|
Emphysema |
Respiratory condition in which the elasticity of the alveoli is lost, resulting in difficulty breathing. |
|
|
|
Heart attack/ myocardial infarction (MI) |
A blockage or clot and occuring in an artery in the heart, resulting in chest pain due to tissue damage |
|
|
|
Hypertension |
High blood pressure |
|
|
|
Hypotension |
Low blood pressure |
|
|
|
Pneumonia |
Inflammation of the lungs with fluid accumulation in the affected alveoli |
|
|
|
Pulse |
The beat of the heart felt at an artery as a wave of blood passes through the artery (about 10 millileters per pulse) |
|
|
|
Pulse rate |
The number of heartbeats or pulse pulses felt in one minute |
|
|
|
Respiration |
Act of breathing in and out of the lungs (inhalation/exhalation) |
|
|
|
Orthostatic hypotension |
A sudden drop in blood pressure when the resident moves from lying to sitting or standing position, resulting in fainting |
|
|
|
Tuberculosis |
An infection, primarily of the lung, from microbacterium tuberculosis |
|
|
|
Vital signs |
Temperature, pulse, respirations, and blood pressure. |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
A) organs 1)heart 2)blood vessel 3)blood |
|
|
|
What is the function of the cardiovascular system? |
1) carries nutrients and oxygen to the cells 2)removes waste products from cells |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |

Heart |
|
|
|
aging process (cardiovascular) |
1)Decreased ability of the heart to act as a pump 2)pulse rate decreases 3) decreased ability of the cardiovascular system to respond to position changes or increased demand for blood supply. 4) narrowing of blood vessels and loss of elasticity in vessel walls, which results in poor circulation in elevated blood pressure(BP) |
|
|
|
Related health problems (cardiovascular) |
1) hypertension 2) heart attack/myocardial infarction 3) congestive heart failure 4) need for a pacemaker |
|
|
|
Nursing care (cardiovascular) |
1) report abnormal pulse or BP to the charge nurse 2) encourage resident to change positions slowly to avoid a sudden drop in BP, resulting in fainting 3) a resident with hiccups may have a loose pacemaker wire, report to charge nurse 4) report changes in skin color or temperature 5) observe for shortness of breath or swelling of legs and feet that could indicate CHF 6) immediately report to charge nurse any complaints of chest pain, left arm or jaw pain, difficulty breathing, perspiration, or changing rate of Rhythm. These may be signs of heart attack, backache in women may also be a sign of a heart attack. |
|
|
|
Respiratory systems |

|
|
|
|
Respiratory system |
A) organs 1) nose 2) mouth 3) esophagus 4) pharynx 5) larynx 6) trachea 7) bronchi 8) lungs 9) bronchioles 10) alveoli |
|
|
|
Functions of the respiratory system? |
1)provides oxygen to cells 2)removes carbon dioxide from cells |
|
|
|
Aging process (respiratory) |
1) loss of elasticity in lungs, lungs to not expand and contract as well 2) chest muscle weakness results in shallow breathing and less effective cough |
|
|
|
Related health problems (respiratory) |
1)emphysema 2)pneumonia 3)lung cancer 4)tuberculosis |
|
|
|
Nursing care (respiratory) |
1) allow frequent rest periods for president become short of breath with exertion or ADLS 2) Elevate HOB to make breathing easier at night 3) report any changes in Resident color or respiratory rate to the charge nurse |
|
|
|
Hypothermia |
When the temperature of the body is below the individuals normal range |
|
|
|
Pulse range for an elderly adult |
Between 50 and 100 beats per minute |
|
|
|
How long do you take a pulse? |
1 full minute |
|
|
|
Regular rhythm |
Pulse is felt in a pattern with the same time interval occurring between Beats |
|
|
|
Irregular rhythm |
Note when the beats are unevenly spaced or beats are skipped |
|
|
|
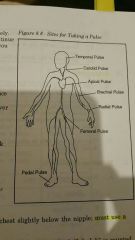
Temporal pulse |
1) located on each side of face 2) the beat of the heart is felt over the temporal artery. |

|
|
|
Carotid pulse |
1) located on the side of the neck 2) not a preferred method for elderly. CAUTION: may stop circulation to the brain. |

|
|
|
Apical pulse |
1) most accurate reading 2) located on the left side of the chest slightly below the nipple; MUST USE A STETHOSCOPE 3) the heartbeat normally sounds like "lub-dub". Each "lub-dub" is counted as one beat 4) use if radial pulse is difficult to take |

|
|
|
Brachial pulse |
1) located at the bend of the elbow |
|
|
|
Radial pulse |
1) most common and convenient site 2) pulse is located on the underside of the wrist near the residence them. It can be felt by placing the first three fingers of one hand against the radial artery. Do not take the pulse with your thumb. |

|
|
|
Femoral pulse |
1)located near the groin area |

|
|
|
What is the pulse site acronym? |
The. (temporal) Caring. (Carotid) Assistant. (Apical) Bathes. (Brachial) Really. (Radial) Fraile. (Femoral) People. (Pedal) |
|
|
|
Pedal pulse |
1) located on the top of each foot 2l the beat of the heart is felt over the dorsalis pedis artery |

|
|
|
Respirations |
1) one respiration includes breathing in and breathing out. It just Rises up on inhalation and falls during exhilation. 2) respiratory rate is the number of respirations in one minute. The normal range for an adult is between 14 and 20. Report to charge nurse with respirations do not fall within this range. There is no difference in the respiratory range for an older adult. |
|
|
|
What is the respiratory rate? |
Between 14 and 20 |
|
|
|
Chart for vitals |

|
|
|
|
What is the oral temperature? |
95.oo- 98.6 |
|
|
|
What is the rectal temperature? |
96.00- 99.6 |
|
|
|
What is the axillary temperature? |
94.00- 97.6 |
|
|
|
What is the pulse rate? |
50- 100 |
|
|
|
List (3) types of thermometers |
1) oral 2) rectal 3) electronic |
|
|
|
List (3) visiting that would indicate NOT to take a temperature by the ORAL route. |
1) has been smoking 2) is unconscious 3) is recieving oxygen |
|

