![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hotspots |
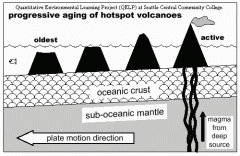
A weak area in the Earth's crust that allows lava to seep through and form volcanoes and islands. As the plate moves the hotspot stays in the same place to create chain islands. |
|
|
Volcanoes |
Volcanoes mostly occur at plate boundaries. An can be related to divergent plates or a subduction zone. |
|
|
Earthquakes |
Earthquakes are measured on a Richter scale ending at nine. They are created by tectonic plates slide past each other causing stress and allowing the rocks to deform. Earthquakes can be created by transform boundaries or sudden faults. |
|
|
Epicentre and focus |
Epicentre is the point on the Earth's surface hits. It is directly above the focus. Focus is the point inside the Earth where the earthquake begins. |
|
|
P waves Primary waves |
A type of seismic wave that compresses and expands the ground. It is the first to arrive at an Earthquake |
|
|
S waves Secondary waves |
A type of seismic wave that moves the Earth side to side and up and down. |
|
|
L waves Surface waves |
Produces motion in the upper crust (up and down, side to side, back and forth). Travel more slowly than P and S waves but are much more destructive. |
|
|
Rift valley |
A rift valley is created by two continental plates diverging. |
|
|
Fold mountains |
Fold mountains are formed when plates are put under so much pressure they fold and bend. This is why large mountains such as the Himalayas have Sedimentary rocks on the top of them. |
|
|
Rift valleys |
A rift valley forms where the Earth’s crust, or outermost layer, is spreading or splitting apart. This kind of valley is often narrow, with steep sides and a flat floor. |

