![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Image receptor (IR) exposure |
One of the 2 photographic properties that comprise visibility of detail. In digital imaging it is the critical quality factor to assess and comparable to density in the film / screen environment |
|
|
|
Brightness |
The concept of density as it is displayed on a softcopy monitor for digital imagesNot the same as density images imagesNot the same as density Not the same as density |
|
|
|
Window level |
The digital processing that produces changes in density / brightness Describes digital post-processing that produces changes in brightness, so it is appropriate to use when controlling the display of an image |
|
|
|
IR exposure and contrast |
What are the two photographic properties that allow detail to be seen on radiographic images |
|
|
|
IR exposure |
The term density was replaced when using digital with the term _____, because film is no longer the primary image receptor |
|
|
|
Exposure Indicator (EI) values |
With digital imaging, the key to a visible image is having the correct IR exposure, which is best evaluated using the |
|
|
|
Overexposed image |
The IRS has received too many photons and, as a result, has recorded too much information Black |
|
|
|
Underexposed image |
Has not received the information and is not capable of being manipulated to reveal details that were never recorded using digital post processing White |
|
|
|
Digital post processing |
Can eliminate the excess information of an overexposed image and reveal details within the range of human visual ability, producing a visually acceptable image |
|
|
|
Quantum mottle/noise |
In radiography, a speckled, snowy looking, non-uniform ___ caused by an insignificant number of X-ray photons striking the radiographic image receptor during an exposure. The _____ is corrected by increasing mAs |
|
|
|
Quantum noise |
A lack of significant incoming data to process an image. Also known as quantum mottle Can be corrected by increasing mAs |
|
|
|
System noise |
Electronic components within the digital image receptor can also add noise to the image, known as |
|
|
|
Ambient noise |
background radiation also contributes to image noise and results in |
|
|
|
Film screen systems |
With ______, mAs was considered to be the controlling factor for IR exposure. With digital systems, this is no longer true |
|
|
|
Influencing factors affecting IR exposure |
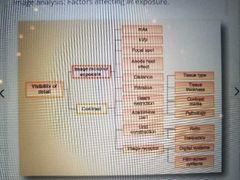
|
|
|
|
Linear, non-linear |
Digital receptor have a ___ response to exposure while film has a ____ |
|
|
|
30% |
Minimum percent change in mAs for Visible density change |
|
|
|
Doubles or halfs |
The general rule of thumb for mAs changes is to make adjustments in increments of |
A repeated image that is underexposed at 10 mAs should be repeated at 20, 40, or 80 mAs, depending on the circumstances |
|
|
Repeating |
Less than 30% change in mAs seldom justifies.. |
|
|
|
KVp |
Controls average energy of X-ray photons at anode Target Affects production of scatter radiation |
|
|
|
IR exposure and film density |
Both the quantity and quality of the X-ray beam will vary significantly with changes in kVp. As a result, kVp has a tremendous impact on |
|
|
|
15% rule |
is used as a guide to maintain the same IR exposure when kilovoltage changes.This increase in kilovoltage causes a doubling of exposure to the IR. This increase in kilovoltage causes a doubling of exposure to the IR. This increase in kilovoltage causes a doubling of exposure to the IR. |
|
|
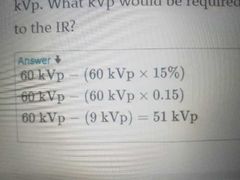
15% rule |
A radiograph of the elbow is produced using a 4 mAs at 60 kVp. What kVp would be required to halve the exposure to the IR? |
|
|
|
kVp |
Can influence the shape of the histogram |
|
|
|
KVp change |
_______ is not recommended to control image noise |
|
|
|
4-5% , 10-12% |
A change in IR exposure can usually be detected with a
__ to __% change in kvp in lower ranges (30-50 kVp)
and
__ to __% change in higher ranges (90-130 kvp) |
|
|
|
Contrast |
Significant changes in kVp can impact |
|
|
|
mAs |
Primary influencing factor to IR exposure |
|
|
|
Total exposure to the image receptor |
Image quality is a function of |
|
|
|
Quantum noise |
Is the largest contributor to total noise |
|
|
|
mAs |
Is Primary IR exposure controlling factor Directly proportional to exposure Marginal noise on image generally requires a 30% increase in exposure |
|
|
|
Focal spot size |
Larger _____ utilize a greater incident electron stream then smaller ones.
Will not affect density / IR exposure in properly calibrated equipment.
Blooming results from high mAs selection.
Proper calibration on a regular basis keeps focal spot issues controlled.
Calibrated systems with continued blooming, may warrant x-ray Tube replacement |
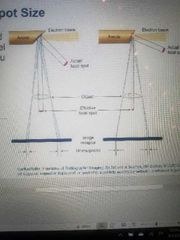
|
|
|
Anode heel effect |
Alters the intensity of radiation, and therefore the IR exposure, between the anode and cathode ends of the X-ray tube. |
|
|
|
Anode heel effect |
Alters intensity of beam across cathode anode access.
IR exposure up to 45% greater at cathode side of beam
Always place thicker side of body part on cathode side |
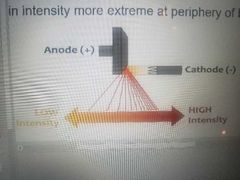
|
|
|
Anode Heel Effect |
More pronounced with wider collimation. This effect is minimized by collimating the beam and eliminating as much of the intensity difference at the periphery as possible |
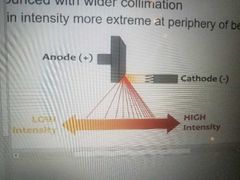
|
|
|
Exposure maintenance formula (distance) |
To maintain IR exposure, mAs (or an influencer) must be changed to compensate for the exposure changeThis formula is used because mAs must increase when distance increases, and vice versa in order to maintain ion exposure This formula is used because mAs must increase when distance increases, and vice versa in order to maintain ion exposure This formula is used because mAs must increase when distance increases, and vice versa in order to maintain ion exposure This formula is used because mAs must increase when distance increases, and vice versa in order to maintain ion exposure This formula is used because mAs must increase when distance increases, and vice versa in order to maintain ion exposure This formula is used because mAs must increase when distance increases, and vice versa in order to maintain ion exposure |
|
|
|
Inverse Square law (Distance) |
SID altars the intensity of the beam reaching the IR, according to this law. The law states that the intensity exposure varies inversely with the square of the distance. For example, as distance increases, radiation intensity and IR exposure decrease |
|
|
|
OID (distance) |
Has an effect on IR exposure. The air gap technique uses an increased OID to prevent scatter radiation from reaching the IR. By increasing OID using the air gap technique, scatter that would normally strike the IR will miss the receptor, causing a decrease in IR exposure |
|
|
|
Filtration |
Has the ability to alter beam intensity affect IR exposure. IR exposure decreases when this increases Increased _____ increases average energy of beam but reduces intensity of beam (quantity) |
|
|
|
Beam restriction (collimation) |
Reducing the primary beam field size reduces the total number of photons available. This reduces the amount of scatter radiation and therefore reduces the overall IR exposure Reduces scatter and secondary radiation (remnant) striking IR Dramatic changes in this require mAs compensation |
|
|
|
Decreases IR exposure |
Increased beam restriction does what to IR exposure |
|
|
|
Anatomical part |
The amount of attenuation is dependent on the thickness and type of the tissue being imaged. Tissue type is affected by the atomic number and density of tissue The use of contrast media will alter the atomic number and affect IR exposure. Pathologically can alter tissue thickness and or type, affecting IR exposure Inverse relationship between IR exposure and part thickness tissue density As tissue thickness, average atomic number of the tissue, and / or tissue density increases, IR exposure decreases |
|
|
|
Pathology |
Can have either an additive or destructive effect. Additive conditions (radioplaque) decrease IR exposure. Destructive conditions (radiolucent) increase IR exposure |
|
|
|
Grids |
_____ absorb scatter, which would otherwise be exposure to the IR and density to the film. The more efficient the ______, the less will be the IR exposure. _____ with high ratios, low frequencies, and dense interspace material, moving grids, and improperly used grids, all reduce IR exposure _____ with high ratios, low frequencies, and dense interspace material, moving grids, and improperly used grids, all reduce IR exposure |
|
|
|
Image receptors |

|
|
|
|
Brightness |
Is the proper term for the Luminous intensity (measured in candela) of the display monitors light emission |
|

