![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is call establishment (call setup)?
|
Answer: to establish an end-to-end circuit.
|
|
|
What is a circuit in VoIP?
|
VoIP: socket ::= IP address + [UDP] Port Number
A.k.a media port, media channel, RTP channel |
|
|
What is call establishment or call setup intended to do?
|
It's about establsihing the voice connection, channel,or circuit. It really is a connection to an IP address a UDP por number
|
|
|
What is the primary purpose of SIP?
|
To determine the UDP port numbers?
|
|
|
How is the UDP port determined?
|
The INVITE and 200 ok
|
|
|
What protocol is encapsulated into SIP and is used to determine UDP ports?
|
Session Description Protocol
|
|
|
What are the SIP messages involved in Event Notification
|
SIP-specific event notification
be informed of some event(s) RFC 3265 SUBSCRIBE subscribe to certain event Event: header NOTIFY inform the user 200 (OK) response User uses the subsribe to subsribe to the service and the server uses the NOTIFY to provide events to the subscriber |
|
|
Show the call flow for Event Notifiacton
|
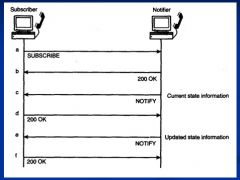
|
|
|
What are the SIP messages for SIP for Instant Messaging
|
SIP IM Standards:
RFC 3428: SIP Extension for Instant Messaging RFC 3856: A Presence Event Package for SIP RFC 3954: Indication of Message Composition for Instant Messaging The exchange of content between a set of participants in near real time IMs are usually grouped together into brief live conversations SIP Method: MESSAGE a message body in the form text/plain, or message/cpim (common presence and instant message) using XML |
|
|
What is the message for SIP for Instant Messaging
|

|
|
|
The SIP architecture uses Requests and Responses.What happens if a request fails to get a response?
|
If the caller does not provide an PRACK, the callee will resend the provisional response. Example if the caller does not receive an 180 ringing, it will not provide an PRACK to the callee. This will cause the callee to resent the 180 Ringing again
|
|
|
Show the call flow for Provisional Response assuming the 180 ringing message was not received
|

|
|
|
Exam: What is CLASS? What services are provided?
|
Supplementary Custom Local Area Signaling Service (CLASS) services
Call waiting, call forwarding, multi-party calling, call screening |
|
|
What is used to support legacy Intelligent Network services?
|
Proxy-controlled services: supporting legacy Intelligent Network (IN) services
|
|
|
Show call flow for Forwarding on-busy scenario
How do you know there is more than one call? What service is the Proxy performing? |

Call Sequence number
Switch. Since it is performing a cross connect function |
|
|
What is the difference between CAS and CCs?
|
Channel-Associated Signaling (CAS)
Signaling uses the same path as the speech R1 Multi-Frequency (MF) signaling Where is MF used? Could you give a few more examples of CAS? Common Channel Signaling (CCS) A separate transmission path for call signaling The signaling is handled in a different manner Some nodes may analyze the signals and take actions Signaling System 7 Enable a wide range of services Caller ID, toll-free calling, call screening, number portability, … |
|
|
What is the international standard similar to SS7?
|
C7
|
|
|
What are some features supported by SS7?
|
Caller ID, Toll-free, 411, Number portability
|
|
|
How is originatting number maintained with the call?
|
Origination and dstination number are data passed in the SS7 signaling
|
|
|
Is CAS inband or out of band singaling
|
in-band
|
|
|
Is CCS inband or out of band singaling
|
out-of-band
CCS has a separate network for signaling. SS7 is CCS |
|
|
What is SS7?
|
. A set of protocols that support the exchange of messages using a separate, dedicated common channel based packet switching network to convey signaling and database information
|
|
|
What is the purpose of SS7?
|
call establishment and call termination in the PSTN circuit switches
database query to support PSTN circuit switch number translation and account status |
|
|
What is the difference between UNI and NNI?
|
User to Network vs Network to Network
|
|
|
Give a few examples of UNI signaling?
|
SIP, ISDN, station signaling
|
|
|
The telephone network is circuit switched, but the signaling is ....
|
The telephone network is circuit switched, but the signaling is packet switched
|
|
|
Give another example of NNI signaling
|
Primarily SS7, but also X.25
|
|
|
What is the deployment status of SS7?
|
Today, most of the PSTN signaling exchange is via the SS7 network
|
|
|
What is an important service of SS7 regarding call setup?
|
SS7 will allow you establish a circuit from the originating party to the termination end
|
|
|
What important feature of SS7 opens the door to many new services?
|
SS7 supports database querys. Once you can map a telephone number to something else many new capabilites are possible
|
|
|
The central node of the SS7 network is called the
What are the links called? What is the database called? |

The central node of the SS7 network is called the Signal Transfer Point (STP).
Each switching office is connected to both mated STPs with high speed data links called A-links, or access links. The mated STPs are interconnected with C-links, or cross links. B-links, bridge links, and D-links, diagonal links, are used when different mated pairs of STPs interconnect. Two additional links are also defined but are seldom used. E-links are extended access links used to connect a switching office to non-home STPs. F-links are used to directly connect two switching offices. In addition to the STP and the switching offices a third node in the SS7 network is the Service Control Point (SCP). An SCP is a database containing detailed logic and data used to provide diversified calling services and features. Routing and service related queries from switching offices are received at the SCP where replies are formulated and returned to the originating switching office. Examples of an SCP database include 800 Number Services, Local Number Portability, and Advanced Intelligent Network Services. |
|
|
In the SS7 architecture the what do the follwoing represent
SSP= STP= SCP= |
In the SS7 architecture the what do the follwoing represent
SSP=Signaling Service Point=Telephone Switch STP= Singaling Transfer Point= Router of telephone network and will route the SS7 message over the SS7 network SCP= Sigaling Control Point= Database |
|
|
A central office has connections to at least ______
STP's |

|
|
|
Show the SS7 protocol stack
|

|
|
|
What is the physical layer for SS7?
What is the bandwidth required |
DS0 or DS1 over T1.
The bandwidth is 56K or 64K. SS7 over IP would save money MTP level 1 defines physical and electrical signaling link characteristics usually DS0A (56K) or V.35 (64K) or DS1 (1.544M) |
|
|
What is the data link layer (Layer 2) for SS7
|
MTP2
MTP level 2 ensures two end-points of signaling link can reliably exchange messages performs error detection and correction, retransmissions |
|
|
What is used to ensure messages are delivered if a SS7 link is down?
How is this accomplished? |
MTP level 3
ensures messages can be delivered in SS7 network performs node addressing, routing, alternate routing, congestion control, and management messages Redundancy |
|
|
What are the three types of MTP2 messages?
|
MTP2
The transfer of messages on a given link from one node to another MTP2 messages Message Signal Unit (MSU) Link Status Signal Unit (LSSU) Ensure alignment and correct link functioning Fill-In Signal Unit (FISU) Sent when there is nothing else to send (the link is idle) Why? |
|
|
Why do we need FISU?
|
It like a heartbeat or keep alive message, This is how we know the link is not down when there are no messages
|
|
|
What are the Layer 3 messages called?
What is the addressing called? |
MTP3
Every switching office assigned a Point Code (PC) Addresses assigned using three-level hierarchy Origination and Destination point codes 4-bit Signaling Link Selector (SLS) code identifies one of 16 fixed paths between CO’s All messages pertaining to a particular call follow the same path (same SLS). In case of link outage, traffic can be transferred to another link (signaling route management). Point Code |
|
|
What is the purpose of ISUP?
|
Were focused on cal establishment, which are
ISUP supports the following message types (a sub-list) IAM: call connection request (sent from originating office) Caller ID Called Number Circuit Identification Code (CIC) ACM: end office is ringing subscriber (sent from terminating office) ANM: subscriber answered at end office (sent from terminating office) REL: release request (sent from office that subscriber hangs-up) RLC: indication that office release a trunk others many, used for exception handling, management The most important is IAM |
|
|
Exam: How many CICs are in a DS3 link?
|
28 * 24 = 672 DS0 = 672 CIC
|
|
|
What is the circuits in the following protocols
POTS ISDN VoIP SS7 |
POTS=Line
ISDN=B-Channel VoIP=RTP SS7=CIC |
|
|
What is a switch?
|
Used to cross connect circuits.
|
|
|
SS7 Call Setup
|
IAM message establishes a circuit.
The first switch will reserve the trunk via the CIC, It will put the origination and destination code in the message. The intermediate switch will do the same. |
|
|
A given circuit (i.e., a TDM trunk) between two switches is identified by OPC, DPC and Circuit Identification Code (CIC)
What are the boxes in the diagram? IAM: Initial Address Message ACM: Address Complete Message ANM: Answer Message CPG: Call Progress Message (optional) |

|
|
|
The IAM message will not perform the cross cross connect function, but will perform the
|
reserve function
|
|
|
What is IN?
|
The Intelligent Network, typically stated as its acronym IN, is the standard network architecture specified in the ITU-T Q.1200 series recommendations. It is intended both for fixed as well as mobile telecom networks. It allows operators to differentiate themselves by providing value-added services in addition to the standard telecom services such as PSTN, ISDN and GSM services on mobile phones.
The intelligence is provided by network nodes on the service layer, distinct from the switching layer of the core network, as opposed to solutions based on intelligence in the core switches or telephone equipments. The IN nodes are typically owned by telecommunications operators (Telecommunications Service Providers). IN is supported by the Signaling System #7 (SS7) protocol between telephone network switching centers and other network nodes owned by network operators. |
|
|
What are the SIP stack components?
|
USER AGENT CLIENT (UAC)
Supports the caller application that initiates and sends the SIP requests USER AGENT SERVER (UAS) Receives and responds to SIP the requests on behalf of the clients Accepts, redirects, or refuses the calls PROXY SERVER Receives requests from clients and forwards them to next-hop servers Contains the UAC and UAS REDIRECT SERVER Accepts the SIP requests, maps the address into zero or more new addresses, and returns those addresses to the client Does not initiate SIP requests or accept calls REGISTRAR/LOCATION SERVER Provides information about a caller’s possible locations to redirect and proxy servers Capable of being co-located with a SIP server |
|
|
What is the protocol stack for SIP?
|

|
|
|
Q1: What is the purpose of ISUP call setup?
|
Answer 11: to setup an end-to-end circuit from the origination switch to the termination switch.
Answer 12: to determine the Circuit Identification Code (CIC) from the origination switch to the termination switch. |
|
|
Q2: What is a circuit?
|
ISDN: B channel
SS7: CIC VoIP: IP address + UDP Port |
|
|
What is call establishment in SS7?
|
Reservation of trunk or selection of CIC
|
|
|
What is IAM?
|
Initial Address Message
An Initial Address Message (IAM) is sent in the "forward" direction by each switch needed to complete the circuit between the calling party and called party until the circuit connects to the destination switch. An IAM contains the called party number in the mandatory variable part and may contain the calling party name and number in the optional part. |
|
|
What is a CIC?
|
Circuit Ientification Code
The ISDN Services User Part (ISUP) Circuit Identification Code (CIC) is part of the Signaling System #7 which is used to set up telephone calls in Public Switched Telephone Networks.[1][2] as part of the Initial Address Message (IAM). When a telephone call is set up from one subscriber to another, many telephone exchanges will be involved, possibly across international boundaries. To allow a call to be set up correctly, where ISUP is supported, a switch will signal call-related information like called or calling party number to the next switch in the network using ISUP messages. The CIC provides information about where the voice part of the call is carried - on which trunk and in which timeslot. |
|
|
What component provides the dial tone for the following;
analog phone VoIP phone ISDN phone |
analog phone=Origination switch
VoIP phone=phone ISDN phone=phone |
|
|
What component provides the audible ringing for the following;
analog phone VoIP phone ISDN phone |
Termination switch provides the ringing
In an SS7 network the audible ringing is provided by the origination switch. |
|
|
What is the difference between a TFN and a regular 10-digit phone number
|
The routing for a TFN is based on the originating number and the routing for a regular 10-digit phone number is based on the dialed number
|
|
|
What is a TCAP message?
|
TCAP Messages
TCAP provides transaction capabilities carried out by non-circuit based messages used to access remote databases and invoke remote feature capabilities |
|
|
Local Number Portability (LNP)
|
Phone numbers are tied to Central Office (CO)
LNP allows phone numbers to be ported to other COs Each Phone has two numbers (internal and public) Translation is support by SS7 |
|
|
Voice VPN (legacy)
|
Private dialing within an enterprise network over a public network (PSTN or Internet)
Translation is supported by SS7 |
|
|
Why Local Number Portability (LNP)
|
Result of 1996 Telecom Act which opened local competition.
|
|
|
What are advantages of Voice VPN?
|
What are the advantages of data VPN
4-, 5-, 7-digits dialing plan between offices Cost savings (no or reduced toll charge) Ease of network management (by carriers) Virtual offices, even virtual companies How does it work? [Legacy] Number translation (via SS7) at the Central Office (CO) switches [VoIP] Number translation by the SIP proxy server |
|
|
Q: Can you move outside your LATA and keep the same phone number?
|
No
|
|
|
What types of signaling are supported at the local switch?
|
On the UNI side station signaling and ISDN Q.931. On the NNI side station signaling, ISDN Q.931, and SS7 are supported
|
|
|
If you have H.323 and SIP does the bearer traffic go through the voice gateway?
|
??
|

