![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is telecommunications according to dictionary?
|
(used with a sing. verb) the science and technology of communications at a distance by electronic transmission of impulses, such as by telegraph, cable, telephone, radio, or television.
(used with a pl. verb) The electronic systems used in transmitting messages, as by telegraph, cable, telephone, radio, or television. |
|
|
When was last telegram sent?
|
early 2000's
|
|
|
What did acronym AT&T used to represent?
|
American Telegraph and Telephone
|
|
|
What is telephony?
|
The transmission of sound between distant stations, especially by radio or telephone.
|
|
|
What is IP Telephony
|
The transfer of sound over the IP network
|
|
|
In the US telecommunications is highly regulated by
|
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and by State Commission
|
|
|
What are the important events in the US regarding telecommunications?
|
1984 AT&T Divestiture & the 1996 Telecom Act
|
|
|
What was the primary objective of the 1984 Divesiture?
|
Open the market for long distance compeitiion
|
|
|
What was the primary objective of the 1996 Telecom Act
|
Opened the market for local market competition
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of International Telecom Industry
|
After 90's moving towards privitatization. However, privatization does not mean more competition. In many countries there are monoplies with one or two companies owning the entire industry.
True competition requies three or more companies for customers to choose in most markets |
|
|
Why are telecom standards important?
|
Standards are extremely important for interoperability between products from different vendors
|
|
|
Why are international telecom standards important?
|
International standards are important for phone calls between countries.
|
|
|
Who are the standard bodies?
|
Primary bodies are ANSI for US and ITU-T for International. Anything related to IP comes from IETF
|
|
|
What is the difference between telecom and datacom?
|
Signaling (telecom) vs. protocol (datacom)
The OSI 7-layer model is applicable to both telecom and data com. |
|
|
What happen on the following dates;
1847: 1876: 1878: 1881: 1885: 1893: . 1896: |
1847: Alexander Graham Bell was born in Ediburgh, Scotland.
1875: a gallows phone was developed 1876: 1st telephone call (03/10) “Mr. Watson, come here, I want you.” 1878: 1st telephone exchange office 1881: 1st long distance line, 45 miles (Boston and Providence) 1885: AT&T incorporated in New York 1893: Patent expired. Anyone can start a phone service company. 1896: Dial phone. The concept of switching was introduced, but there is no switching system. |
|
|
What happened on the following date;
1908: 1913: 1915: 1919: 1925: 1929: 1934: |
1908: Bell System: One Policy, One System, Universal Service.
1913: Kingsbury Commitment. AT&T committed to Attorney General that it would provide long distance connection for independent phone companies. 1915: 1st transcontinental line from NYC to SFO. “Mr. Watson, Come Here, I want you.” 1919: 1st telephone switching system in service. (Norfolk, VA) 1925: Bell Telephone Laboratories 1929: President Hoover got his phone on his desk. 1934: Communications Act – interstate phone business is regulated by FCC |
|
|
What is important about the following dates;
1938: 1949: **1956: 1965: 1971: 1974: 1976: |
1938: 1st crossbar central office switch
1949: Anti-trust suit against AT&T by Attorney General 1956: Judgment limiting AT&T business to common carrier communications and government projects. Phone services only, no computer business, no TV, nor anything else. 1965: eavesdropping is unconstitutional. 1971: Bell Systems served 100M lines. Independent telephone companies served 25M lines. Other countries had 160M lines in total. 1974: An anti-trust suit against AT&T by DoJ. Separation of inner city facilities from local facilities Separation from service providers from manufacturer 1976: 1st digital switching system |
|
|
What is important about the following dates;
1984: 1986: 1988: 1996: |
1984: AT&T Divestiture
AT&T Long Distance + Manufacture Seven Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOC) Who were these 7 Baby bells? Who are they now? Competition of Long Distance Market AT&T can enter into the computer market. IBM can enter into the telecommunications manufacturing market. (bought ROLM) 1986: 1st round “Equal Access” completed by RBOC 1988: Commercial offering of ISDN services 1996: Telecommunications Act |
|
|
What were the 7 RBOC's
|
Pacific Bell
Ameritech Southwestern Beel US South US West Bell Atlantic Nynex |
|
|
What companies now comprise AT&T (SBC)
|
Pacific Bell
Ameritech Southwestern Beel US South |
|
|
Which RBOC's became Verizon?
|
Bell Atlantic
Nynex |
|
|
Which RBOC is now Quest
|
US West
|
|
|
Who are the incumbent Local Exchange Carriers (ILEC's) ?
|
AT&T, Verizon, and Quest
|
|
|
Show diagram local service before 1984
|
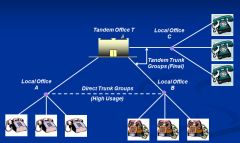
|
|
|
Show diagram of Toll Call before 1984.
|
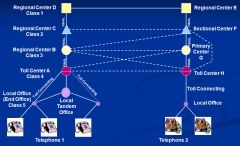
|
|
|
Show the architecture post 1984 for the PSTN. What is the primary difference pre & post
|
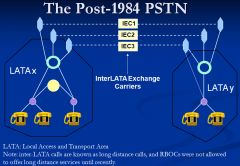
LEC and IXC are separate companies
|
|
|
What determines if a call is local or long distance?
|
LATA: Local Access and Transport Area
Note: inter-LATA calls are known as long distance calls, and RBOCs were not allowed to offer long distance services until recently. Long-distance calls has nothing to do with area codes Inter-lata calls must be serviced by a long distance carrier. |
|
|
What is meant by the term equal access?
|
The LEC must provide equal access for IXC's. In 1984 the large IXC's were AT&T, MCI and Sprint
|
|
|
Show a diagram of an Interlata call including the POP
|
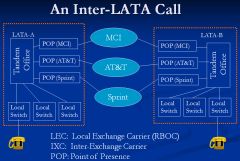
|
|
|
Telecommunication Act of 1996 Summary
|
“To provide a pro-competitive, de-regulatory national policy framework designed to accelerate private sector development of advanced telecommunications and information technologies and services to all Americans”
|
|
|
Telecommunication Act of 1996 included
|
remove entry barriers to allow local phone competition
CLECs (Competitive LEC) vs ILECs (Incumbent LEC) allow LEC’s to provide long distance service (in their region) after “opening up” their region to competition checklist defined as criteria for “opening up” region to competition allow LEC’s to manufacture telephone equipment deregulated Cable Television service (removed 1992 Cable Act regulations) |
|
|
Who are ILEC's
|
AT&T, Verizon, Quest, Embarq and Windstream
|
|
|
What is a CLEC? What are the two types of CLEC's?
|
Facility-based & Reseller
|
|
|
Do we have competition for local service?
|
Yes. VoIP Comcast is the largest VoIP provider in the US.
|
|
|
Show the diagram for the Central Office Environment
What is the Signaling System called? |
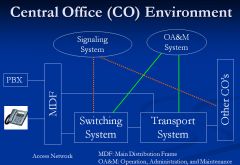
SS7
|
|
|
What is the connection between a phone and switch called?
What is the connection called between a PBX and a switch? What is the connection called between two switches associated with the same CO? What is the connection between two CO switches called? |
What is the connection between a phone and switch called? Line
What is the connection called between a PBX and a switch? Line or Trunk What is the connection called between two switches associated with the same CO? Intra-office trunk What is the connection between two CO switches called? Interoffice trunk |
|
|
Give some examples of Customer Premise Equipment (CPE)
|
Customer Premise Equipment (CPE) is any piece of equipment supplied by the customer to interface with the PSTN. Examples are:
Single Line Telephone Set Multi-Line Telephone Set Key Telephone System (KTS) Private Branch Exchange (PBX) Channel Bank (CB) |
|
|
Show a diagram of a voice network, Include the four types of networks
|
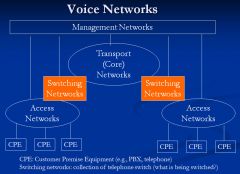
Switching Network -- Class 5 or 5ESS telephone switch in the CO
Access Network -- are the lines and/or trunks from the CPE to the CO switch Transport Network -- Are usually the optical network between the CO switches Managment Network -- Outside the scope |
|
|
Show a diagram of the Public Switched Telephone Network
|
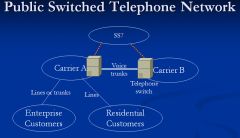
|
|
|
What is the common denominator between a called placed between Comcast and Vonage phones?
|
The PSTN.
Both Comcast and Vonage connect to the PSTN. |
|
|
Why do we need the PSTN in the middle? Why do we need convert IP to TDM and TDM-to-IP?
Why can't Comcast and Vonage customer connect to one anther directly without the PSTN? |
The PSTN provides the signaling that allows Comcvast and Vonage to communicate
|
|
|
What is IMS?
|
IMS – the IP Multimedia Subsystem – developed originally by the 3G mobile community, is now seen by many service providers (not just by vendors) as the key to migrating legacy wireline networks towards IP, next-generation networks, and voice over IP.
|
|
|
Is DSL covered in the Telecom ACt of 1996?
Is the LEC required to share DSL service |
FCC says yes. SBC says No.
FCC and SBC agrees that do not have to offer DSL |
|
|
What is the difference between the data network and voice network?
|
The architecure is the same. The CPE is different. For example, cable modem vs a telephone
|
|
|
In what circumstance will the technology for access network for data be the same technology as the access network for voice?
|
When the CPE is DSL. This is an example of multiplexing.
|
|
|
What is BGP?
|
Border Gateway Protocl (BGP) is routing protocol that allows service providers to send and receive data from one another
|
|
|
What is a peering agreement?
|
Large service providers agree to route each other data traffic
|
|
|
What is a converged or integrated network?
|
Answer: single facility for both voice and data traffic
Technical solution: TDM, ATM, and IP First Step: digitized the voice |
|
|
What is one of the first services to use the same physical facility for voice and data communication
|
ISDN
|
|
|
What types of converged services have been available for many years are used as part of the PSTN backbone?
|
SONET and ATM
|
|
|
Does Integrated Services require IP?
|
No. Integrated services does not require IP, which is one of protocols supporting integrated services.
|
|
|
Why - Integrated Service
|
Cost
The concept of integrated service is not new. Carrier prefer a single network supporting both voice and data traffic. Enterprise also prefer this way. Solution proposed: ISDN B-ISDN – what is B-ISDN? Why did they fail? Or, do they really fail? New service create new revenue opportunities |
|
|
Create a diagram that depicts Integrated Services on the Access Network
|
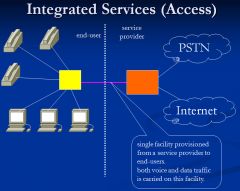
|
|
|
Show the first generation for Integrated Services using TDM
|
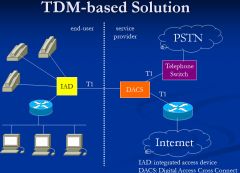
|
|
|
Show diagram of Integrated Services using ATM
|
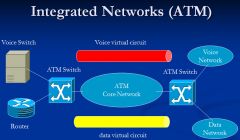
|
|
|
What is important to know about ATM based Integrated Services solution
|
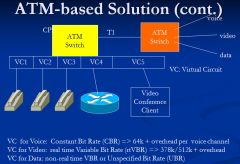
|
|
|
What is the main issue with TDM services?
|
Ineffeciency of the network bandwidth
|
|
|
What are the challenges of VoIP?
|
PSTN.
PSTN is good, reliable and cheap |
|
|
Does VoIP offer comparable services as PSTN?
|
No.
Over 1000 features on 5ESS. VoIP does not have same feature set as PSTN |
|
|
Does VOIP offer comparable quality as PSTN?
|
Yes and No.
|
|
|
Does VoIP offer comparable pricing as PSTN?
|
PSTN is really really cheap. Very difficult to compete with the low prices
|
|
|
Why VoIP?
|
IP is widely available.
IP is a connectionless service Voice must be carried in a circuit or a virtual circuit IP is engineered for data traffic Data integrity is important. Latency is not a major concern for data traffic. Traffic is asynchronous. |
|
|
Do we really need QoS?
|
Is needed if there is competition for bandwidth.
One solution is priority, which is QoS. Another solution is increase the bandwidth |
|
|
Why VoIP?
|
“If it is not broken, don’t fix it”
some truth to this statement telephony is not “broken” so what is “broken”? Why carry voice over IP? Internet has provided NEW SERVICES There are potential $$$ in carrying voice over IP Integration: one network for both voice and data traffic Price (does it save money?) and performance (does it offer better services – quality and features?) New features lead to new revenue opportunity |
|
|
Are Equipment Cost higher or lower with VoIP?
|
CO telephone switches are proprietary.
PBX are generally proprietary. Difficult to deploy 3rd party software Not many choices of telephone until 1984. IP networks Open standards Competition Moore’s Law tends to motivate data networking |
|
|
What are the Advanced Services capability with VoIP?
|
Some inherent characteristics of IP
Voice Virtual Private Network (VPN) What is voice VPN? Number Portability Advanced user interface with HTML (point-and-click) are much easier to deal Unified messaging service Can you get your voice mail from your e-mail? |
|
|
Describe the lower bandwidth requirements with VoIP
|
DS0: 64 kbps – legacy networks (PCM)
Could be reduced to 32 kbps (ADPCM) G.711: 64 kbps G.729A: 8 kbps G.723.1: 5.3-6.3 kbps take advantage of low-rate vocoders What is the significance of bandwidth reduction? |
|
|
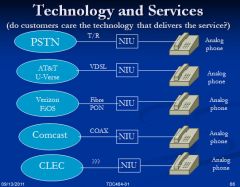
AT&T U-Verse – is it VoIP?
|
U-Verse based on VDSL. Supports up 20Mb. The U-Verse box has a POTS and Ethernet. Since the U-Verse supports SIP its likely that the voice is carried VoIP
|
|
|
Verizon FiOS – is it VoIP?
|
FIOS is fiber to the home. FIOS uses GPON. GPON uses multiplexing to carry voice and data. Separate channels carry data and voice. So this solution does carry voice traffic as VoIP
|
|
|
3G – is it VoIP?
Dual mode - what does it mean? |
No.3G is dual mode. Voice and data are carried over different channels
|
|
|
4G
WiMAX (802.16) – is it VoIP? Long Term Evolution (LTE) |
4G does not support voice. So it must be VoIP
|
|
|
No
|
|
|
What are the VoIP Challenges
|
Speech Quality
Traffic Prioritization (Quality of Service) Network Reliability and Scalability Location Based Services (e.g., E911) Security |
|
|
What is the perception of the telephone network?
|
It is always available
|
|
|
5 9’s availability. What does it mean?
|
No more than five minutes of downtime per year
|
|
|
What is the perception of the data network?
|
??
|
|
|
What is the typical service level agreement (SLA) for data services?
|
No more than four hours of downtime per month.
|
|
|
What are the reliability requirements for router/switch?
|
??
|
|
|
Scalable vs. non-scalable
Give an example of each for router |
Scalability growing the network without major infrastructure changes
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of voice and data traffic?
|
Voice: sensitive to delay
Data: sensitive to bit error |
|
|
If voice and data are carried on the same physical link, how do we prevent the data traffic from congesting the network which will cause long delay and packet loss on the voice traffic.
|
??
|
|
|
What is QoS? Does IP support QoS?
|
Prioritaztion of voice traffice over non voice traffic. Yes
|
|
|
Data traffic is usually best-effort service
|
??
|
|
|
VoIP Regulation
|
Regulation
Location Based Routing (1-800) N11 services E911 CALEA – wiretapping Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act |
|
|
Numbering Plan
|
What is the numbering plan for VoIP
|
|
|
Network convergence: from two separated voice and data networks into a single network
|
Carrier Core Network
Carrier Access Network Enterprise Network Residential Network |
|
|
IP – the common denominator
|
The industry is moving in this direction but very slowly.
|
|
|
Note that there are still over 100 million traditional telephone lines in U.S.
What does it mean to the VoIP equipment vendors and service providers? |
??
|
|
|
What do customers want?
|
Dial Tone
Public Phone Number - why is this important? E911 Voice Mails Call Features (Call waiting, call forwarding, etc.) N11 ??? do you need 211/311/411? Detailed billing? Detailed call records? |
|
|
Which of the N11 services are required by the FCC
|
No. Only E911 is required by FCC
|

