![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
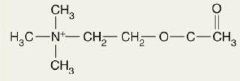
ACh
|
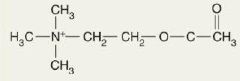
It has a chemical structure significantly different from other neurotransmitters and for this reason is placed in its own structural category; active in both the CNS and PNS; in the PNS it is released into the neuromuscular junction to stimulate skeletal muscle contraction, inhibits cardiac muscle, either inhibits or excites smooth muscle and glands.
|
|
|
Amino Acids
|
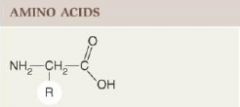
Molecules with both carboxyl (-COOH) and amine (-NH2) groups and various R groups; building blocks of proteins; act as signaling molecules in the nervous system.
Glutamate, apartate; serine; gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine |
|
|
Structural category: monoamines
|
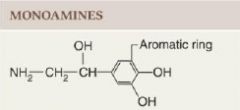
Molecules synthesized from an amino acid by removal of the carboxyl group and retaining the single amine group; also called biogenic amines.
histamine, serotonin, catecholamines, dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline). |
|
|
Structural category: neuropeptides
|

Small moleuels made of chains of amino acids; act as signals to assist in and modulate communication between neurons and other cells.
Enkephalin, neuropeptide Y, somatostatin, substance P, cholecystokinin, Beta-endorphin, neurotensin |
|
|
Structural category: It has a chemical structure significantly different from other neurotransmitters and for this reason is placed in its own structural category; active in both the CNS and PNS; in the PNS it is released into the neuromuscular junction to stimulate skeletal muscle contraction, inhibits cardiac muscle, either inhibits or excites smooth muscle and glands.
|
ACh
Acetylcholine |
|
|
Structural category: Molecules with both carboxyl (-COOH) and amine (-NH2) groups and various R groups; building blocks of proteins; act as signaling molecules in the nervous system.
Glutamate, apartate; serine; gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine |
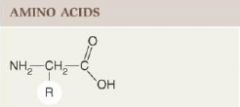
Amino Acids
|
|
|
Structural category: Molecules synthesized from an amino acid by removal of the carboxyl group and retaining the single amine group; also called biogenic amines.
histamine, serotonin, catecholamines, dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline). |
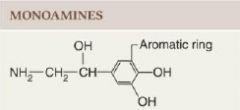
Monamines
|
|
|
Structural category: Small moleuels made of chains of amino acids; act as signals to assist in and modulate communication between neurons and other cells.
Enkephalin, neuropeptide Y, somatostatin, substance P, cholecystokinin, Beta-endorphin, neurotensin |

Neuropeptides
|
|
|
List the amino acids in this structural category: (5)
|
Glutamate
Aspartate serine gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) Glycine |
|
|
List the monoamines in this structural catetory: (6)
|
histamine
serotonin catecholamines - dopamine, norepinepherine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline) |
|
|
List the neuropeptides in this structural category: (7)
|
enkephalin
neuropeptide Y somatostatin substance P cholecystokinin beta-endorphin neurotensin |
|
|
List the "other" neurotransmitters in this structural category: (2)
|
adenosine
nitric oxide |
|
|
Excites activity in nervous system to promote cognitive function in the brain (learning and memory); most common neurotransmitter in the brain.
|
glutamate
(amino acid) |
|
|
glutamate
(amino acid) |
Excites activity in nervous system to promote cognitive function in the brain (learning and memory); most common neurotransmitter in the brain.
|
|
|
Most common neurotransmitter in the brain
|
glutamate
(amino acid) |
|
|
Excites activity primarily in descending motor pathways through the spinal cord to skeletal muscle
|
aspartate
(amino acid) |
|
|
aspartate
(amino acid) |
Excites activity primarily in descending motor pathways through the spinal cord to skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Activates specific receptors in diverse areas of the brain.
|
serine
(amino acid) |
|
|
serine
(amino acid) |
Activates specific receptors in diverse areas of the brain.
|

