![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
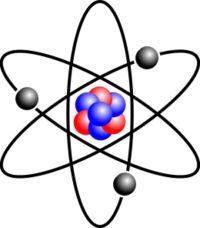
ATOM
|
The smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still have the properties of that element.
|
Still the same.
If an atom is divided by a chemical reaction two new substances will be created. |
|

ATOMIC MASS
|
Superscript number that gives total of number of protons and neutrons in an atom
|
Left superscript
In a neutral atom the atomic mass will be 2 times the number of protons in the atom |
|

ATOMIC MASS UNIT
|
(amu) is defined to be 1/12 the mass of the carbon 12 nuclide.
|
carbon 12
Carbon 12 is the standard for the atomic mass scale. |
|

ATOMIC NUMBER
|
Number of protons in an atom. Is shown as a subscript.
|
Left subscript
In a neutral atom the atomic number will be 1/2 of the mass number |
|

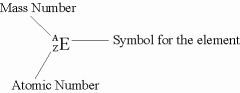
ATOMIC SYMBOL
|
Atomic symbol has 3 parts. Body is the element. Left subscript is the number of protons. Left superscript is the mass number, equal to protons and neutrons in isotope
|
Has 3 parts.
The atomic symbol tells what type of element and quantity of protons+neutrons |
|
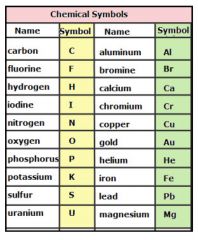
CHEMICAL SYMBOL
|
Symbol that denotes the name of an element. Pb is the symbol for lead from the Latin word plumbum
|
Pb
Lead is an element shown on the periodic table as Pb |
|
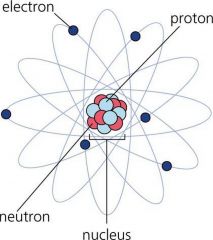
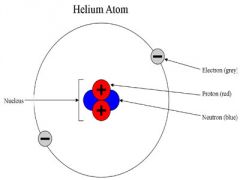
ELECTRON
|
A negatively charged atom that is located outside the nucleus of the atom.
|
Negative
Electrons were discovered by J.J. Thomson in 1897. |
|
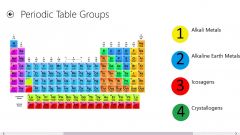
GROUP
|
Vertical column of elements on the periodic table.
|
Up and down.
Elements in the same group have similar properties. |
|
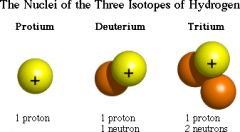
ISOTOPE
|
Atoms of the same type, they have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
|
Same # P, different # N
Carbon-12 and carbon-13 both have 6 protons. C-12 has 6 neutrons and C-13 has 7 neutrons |
|
MASS NUMBER
|
The total number of protons plus neutrons in an atom.
The total number of protons plus neutrons in an atom. |
Total number.
The mass number is the left superscript. |
|

METAL
|
An element that is shiny, ductile, malleable and a good conductor.
|
good conductor.
Metals are elements found on the left side of the periodic table. |
|
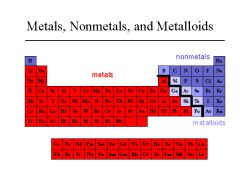
METALLOID
|
An element that has properties of both metals and nonmetals.
|
Is and Is not.
Metalloids are found along the zigzag on the periodic table. |
|
NEUTRON
|
A neutral particle located in the nucleus of an atom
|
Inside center
If you subtract the atomic number from the mass number you will find the number of neutrons in and atom. |
|

NONMETAL
|
An element that is not shiny, ductile or malleable and is not a good conductor.
|
Right had side of the periodic table.
Nonmetals accept electrons when reacting with metals. |
|

NUCLEUS
|
The center of an atom. Contains the protons and neutrons.
|
Center
Electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. |
|
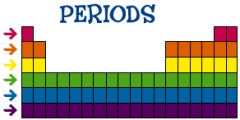
PERIOD
|
Horizontal row on the periodic table.
|
Across
Elements in the same period have the same number of energy levels. |
|
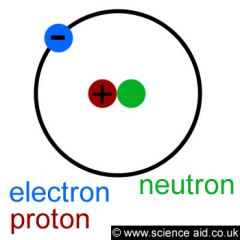
PROTON
|
Positively charged particle that is located in the nucleus of the atom.
|
Positive
Carbon 12 has six protons |
|
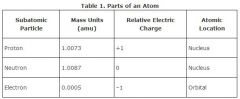
SUBATOMIC PARTICLE
|
Particles that are smaller then atoms.
|
Not on Earth
Subatomic particles have been studied in particle accelerators. |

