![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
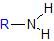
What functional group does this represent? |
Amino |
|

What functional group does this represent? |
Alcohol |
|
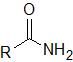
What functional group does this represent? |
Amido |
|
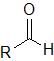
What is the name for the carbon and oxygen bonded together in this molecule? |
Carbonyl group |
|
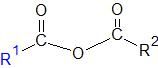
What functional group does this represent? |
Anhydride |
|
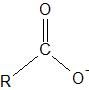
What functional group does this represent? |
Carboxylate |
|
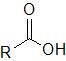
What functional group does this represent? |
Carboxylic acid |
|
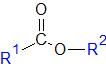
What functional group does this represent? |
Ester |
|
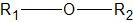
What functional group does this represent? |
Ether |
|
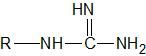
What functional group does this represent? |
Guanidino |
|
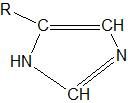
What functional group does this represent? |
Imidazole |
|
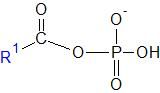
What functional group does this represent? |
Mixed Anhydride- Carboxylic acid and a phosphoric acid together. Also called acyl phosphate. |
|
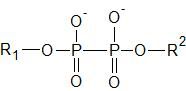
What functional group does this represent? |
Phosphoanhydride |
|
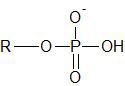
What functional group does this represent? |
Phosphoryl |
|

What functional group does this represent? |
Disulfide |
|

What functional group does this represent? |
Sulfhydryl |
|
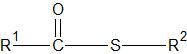
What functional group does this represent? |
Thioester |
|
|
How many bonds does carbon form? Which element(s) does it typically form bonds with? |
Carbon forms four bonds, typically with hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen. |
|
|
How many bonds does nitrogen form? Which element(s) does it typically form bonds with? |
Nitrogen forms 3 bonds, usually with carbon or hydrogen. |
|
|
How many bonds does sulfur form? Which element(s) does it typically form bonds with? |
Sulfur forms two bonds, typically with carbon or hydrogen. |
|
|
How many bonds does phosphorus form? Which element(s) does it typically form bonds with? |
Phosphorus forms five bonds with oxygen |
|
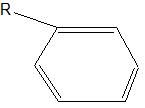
Which functional group is this? |
Phenyl |
|
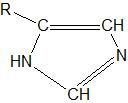
Name an example of this functional group. |
The side chain of histidine |
|
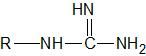
Name an example of this functional group. |
The side chain of arginine |
|

Name an example of this functional group. |
The side chain of cysteine. |
|

Name an example of this functional group |
The cystine bond formed by joining 2 cysteine residues together. |
|
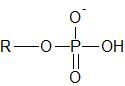
Name an example of where you might find this functional group. |
It can be added or removed from proteins to activate/deactivate them. (The group is a phosphoryl group). |
|
|
What are the four weak forces that are important in biomolecules? List them from the strongest to the weakest. |
Ionic interactions (attraction or repulsion), hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions, and Van der Waals forces. |
|
|
What does amphipathic mean? |
Molecules containing both polar and nonpolar parts are said to be amphipathic. |
|
|
Why are weak forces such a big deal in biochemistry? |
A lot of biochemistry requires that bonds are formed and broken transiently (such as the bonds between an enzyme and its substrate). Covalent bonds are too strong to do this. An enzyme is usually required to break a covalent bond and forming them requires too much energy input. |
|
|
What is the normal pH in the human body? |
7.2-7.4 |
|
|
What is a zwitterion? Why are these important? |
A zwitterion is a molecule that contains both acidic and basic functional groups. These functional groups on the zwitterion are charged at physiologic pH, but they contain equal numbers of positive and negative charges, so the net charge is 0. These are important because they form the basis for buffers that keep pH in the body within a very narrow range. |
|
|
What are the 7 nonpolar amino acids (excluding those with a phenyl group in their side chain)? |
Glycine (Gly or G), Alanine (Ala, A), Proline (pro, P), Valine (val, V), Leucine (leu, L), Isoleucine (ile, I), and methionine (met, M). |
|
|
Most of the amino acids (99%) in the human body are of which stereoisomeric form? |
The L form. |
|
|
Which amino acid does not have a D form and an L form? Why?
|
Glycine (gly, G) does not have stereoisomers because its side chain is only a hydrogen. Thus, the alpha carbon is bonded to two hydrogens, making stereochemistry impossible.
|
|
|
Which amino acids have an aromatic ring in their side chains? List in order from most to least polar. |
Tyrosine (tyr, Y), Tryptophan (trp, W), and Phenylalanine (phe, F). |
|
|
Which amino acid can form disulfide bonds in its side chain if you have two of them? |
Two cysteine (cys, C) residues can link side chains (covalently) via a disulfide bond. These strong bonds are very important for structural integrity of proteins. |
|
|
What are the polar, uncharged amino acids? |
Asparagine (asn, N), Glutamine (gln, Q), Serine (ser, S), and Threonine (thr, T) |
|
|
Which amino acids are negatively charged at physiologic pH? |
Glutamate (glu, E) and Aspartate (asp, D). At a lower pH, they will be neutral and will be called glutamic and aspartic acids, respectively. |
|
|
Which are the positively charged amino acids? |
Arginine (arg, R), Lysine (lys, K), and Histidine (his, H). |
|
|
If the Pka of an amino acid's side chain is less than 7.4 (physiologic pH), will it donate or accept a hydrogen? |
Donate, as in aspartate (asp, D) and glutamate (glu, E). |
|
|
Which functional group gets phosphorylated? What type of enzyme does that? |
Hydroxyl groups (-OH) get phosphorylated by enzymes called kinases. |
|
|
Which amino acids can be phosphorylated? |
Serine, Threonine, and Tyrosine. Serine and threonine are phosphorylated by the same kinase and tyrosine has its own. |
|
|
V
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Valine (val) |
|
|
L
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Leucine (leu) |
|
|
I
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Isoleucine (ile) |
|
|
F
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Phenylalanine (phe) |
|
|
Y
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Tyrosine (tyr) |
|
|
W
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Tryptophan (trp) |
|
|
N
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Asparagine (asn) |
|
|
Q
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Glutamine (gln) |
|
|
S
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Serine (ser) |
|
|
T
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Threonine (thr) |
|
|
M
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Methionine (met) |
|
|
C
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Cysteine (cys) |
|
|
D
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Aspartate (asp) |
|
|
E
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Glutamate (glu) |
|
|
R
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Arginine (arg) |
|
|
K
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Lysine (lys) |
|
|
H
(Which amino acid is this?) |
Histidine (his) |

