![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the "risk factors" for Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy?
|
1) Age
2) Functional circulating androgens 3) Family history of BPH *(castration prevents BPH) |
|
|
List 3 complications with BPH
|
1) Urinary Retention from enlargement
2) Poor bladder control from changes in the bladder neck and tract 3) Infection, stones, hydronephrosis from urinary retention |
|
|
What are the surgical options for BPH treatment?
|
* Surgery attempts to reduce a mass effect
1) TURP 2) Subtotal/total prostatectomy 3) Laser/microwave ablation |
|
|
What are the two medical options for BPH management?
|
1) Androgen receptor blockade with 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor
2) Alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade (modulate smooth muscle tone) |
|
|
What are three risk factors for prostatic carcinoma?
|
1) Functional androgen endocrinology
2) African American race 3) Family History * Diet not yet established |
|
|
What's wrong with the PSA test?
|
1) Low predictive value
2) Many false positives and unnecessary workups 3) No change in outcome for those with prostate CA 4) High rate of complications |
|
|
What's the difference between a prognostic and a predictive factor?
|
Prognostic factors relate to SURVIVAL.
Predictive factors indicate a chance a tumor will respond to THERAPY |
|
|
What are three PROGNOSTIC factors for prostate cancer?
|
1) Tumor Stage (clinical and pathologic)
2) Tumor Grade 3) Serum PSA at time of Dx |
|
|
Explain the reasoning and indications behind a surgical tx of prostate cancer.
|
Radical prostatectomy removes all cancer cells and will prevent recurrence.
|
|
|
Explain the reasoning and indications behind radiation therapy of prostate cancer.
|
External beam or seed implants will destroy rapidly-dividing tumor cells.
|
|
|
Explain the reasoning and indications behind hormonal therapy of prostate cancer?
|
Prostate cancers are androgen-dependent and respond to androgen blockade, orchiectomy, estrogenic agents.
|
|
|
Explain the reasoning and indications behind watchful waiting with prostate cancer.
|
Prostate cancer does not grow as rapidly as other cancers, and typically presents later in life. Many cancer patients die of unrelated causes first.
|
|
|
What are the most frequent sites of metastasis for prostate cancer?
|
1) Lymph nodes
2) BONE (vertebral column) - 65% 3) Lung 4) Liver |
|
|
Anatomically, where do most prostate cancers grow? BPH?
|
BPH - anteromedially, in the "Transition Zone"
Prostate CA - Posteriorly in the "Peripheral Zone" |
|
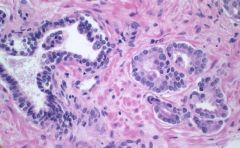
What's the pathology?
|
Prostate Cancer. Normal glands on Left, cancer glands on Right.
|

