![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Approx. what percentage of HBV infections progress to chronic?
|
5-10%
|
|
|
Approx. what percentage of HCV infections progress to chronic? How many of these will develop cirrhosis?
|
>50% progress to a chronic state, and of these 20% will eventually develop cirrhosis.
|
|
|
What histologic feature is specific for HBV?
|
"Ground Glass" hepatocytes.
|
|
|
What histologic feature is specific for HCV?
|
HCV-specific Changes:
* Portal lymphoid aggregates * Fatty changes |
|
|
What are the major pathologic features of Alcoholic Liver Disease?
|
* Steatosis
* Centrilobular (zone 3) injury pattern * Inflammatory infiltrate * Mallory bodies * Centrilobular perivenular/pericellular fibrosis |
|
|
What epidemiological factors correlate with Primary sclerosing Cholangitis?
|
1) Common in young men
2) 70% co-morbidity with IBD 3) Risk of cholangiocarcinoma |
|
|
What laboratory values are elevated in primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
* Alkaline Phosphatase
* Conjugated Bilirubin |
|
|
What are the histopathologic features of primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
* Fibroinflammatory destruction of the bile ducts
* Concentric periductal (onion-skin) fibrosis * Eventual cirrhosis |
|
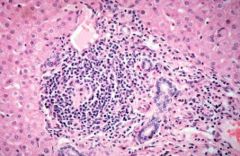
What's the pathology? (liver slide)
|
Interface hepatitis with a lymphoid aggregate. Note the lymphocytes trying to invade a new area.
|
|
|
What is the major developing feature in the staging of chronic hepatitis?
|
The development of Bridging Fibrosis, altering the flow of blood and bile, i.e. the development of cirrhosis.
|
|
|
What fibrotic pattern is seen in alcoholic liver disease?
|
Chicken Wire Fibrosis.
|
|
|
What is the most common presenting symptom of primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Puritus. Jaundice comes later.
|
|
|
What are the two major chronic biliary tract disorders?
|
1) Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
2) Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis |
|
|
With what two autoimmune disorders is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis associated?
|
1) Sjögren syndrome
2) Scleroderma |
|
|
What two laboratory values are indicative of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
|
* Positive AMA
* Elevated alkaline phosphatase |
|
|
What's the pathology behind Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
|
PBC is an auto-immune disorder targeting the bile duct canaliculi cells.
|
|
|
What metabolic disease of iron metabolism affects the liver?
|
Hereditary hemochromatosis, an autosomal recessive disorder resulting in excessive accumulation of iron. Results from an HFE gene mutation. Associated with cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, increased skin pigmentation. High risk for developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
|
|
|
Kayser-Fleischer rings in the eyes indicate which metabolic disease?
|
Wilson Disease, an autosomal recessive disorder resulting in the accumulation of copper.
|
|
|
What serum protein is decreased in Wilson's Disease?
|
The copper binding protein ceruloplasmin.
|
|
|
What is the gold-standard for the diagnosis of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
|
An ERCP Study
|
|
|
What are the 5 major complications of hepatic cirrhosis?
|
1) Portal Hypertension
2) Portal-Caval Shunts (varices) 3) Liver Failure (both productive and detoxifying) 4) Ascites 5) Hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
What are the risk factors for Cholangiocarcinoma?
|
* Thorotrast (contrast) administration
* Liver Fluke Infection * Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis * Cirrhosis * EtOH, HBV, HCV |
|
|
What are the risk factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
|
1) Chronic HBV infection
2) Cirrhosis 3) Aflatoxin exposure |

