![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

1. Action potential |
The last action potential (overshoot) generated on the axon sends electrical signal to the membrane of the axon terminal (terminal button) |
|
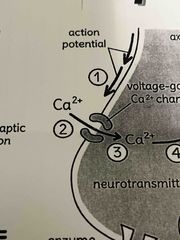
2. Voltage-gated ca^2+ |
The increase in energy along the membrane causes the voltage gated ca^2+ channels on the pre synaptic membrane of the axon terminal (terminal button) to reach threshold and open |
|
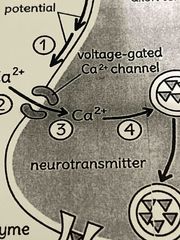
3. Ca^2t ions |
Ca^2+ ions enter the axon terminal (terminal button) through the open Ca^2+ channel |
|
4. Depolarization |
The depolarization caused by the entrance of the Ca^2+ ions activities the synaptic vesicles |
|

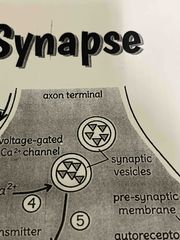
5. Synaptic vesicles |
Synaptic vesicles containing a specific type of neurotransmitters migrate to and fuse with pre synaptic membrane of the axon terminal (terminal button) |
|

6. Neurotransmitter |
The neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft |
|
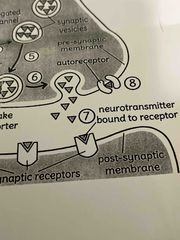
7. Neurotransmitter bound to receptor |
The Neurotransmitters diffuse the across the synaptic cleft and bind with receptor proteins on the post synaptic dendrite. If the neurotransmitter is excitatory, it will generate an excitatory post synaptic potential (EPSP). If the neurotransmitter is inhibitory, it will create an inhibitory post synaptic potential (IPSP) |
|

8. Auto receptor |
Some axon terminals (terminal button) have auto receptors help to regulate the ability of the pew synaptic neuron to release neurotransmitters. Some auto receptors can be activated by the same neurotransmitter being released, creating a feedback loop( an increase in binding of neurotransmitters to auto receptors results in a decrease In the release of neurotransmitters) |
|

9. Reputable transporter |
Transporter proteins on the axon terminal of the pre synaptic neuron help with the reuputake of Neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft back into the pre synaptic neuron |
|
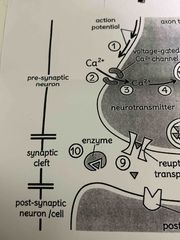
10. Enzyme |
Neurotransmitters, not taken back into the pre synaptic neuron by a transporter protein, are broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft |

