![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
greasy pig dz (exudative dermatitis)
a. etiology b. pathogenesis c. epidemiology |
a. Staph hyicus
b. part of normal skin flora: ubiquitous virulent strains produce exfoliative toxin (ET) multiple management & environmental factors likely involved c. frequently observed in modern production systems during 1st year of production (start-up herd) offspring from gilts or parity 1 sows at highest risk most positive herds don’t have dz |
|
|
greasy pig dz (exudative dermatitis)
a. signs b. dx c. tx d. prevention |
a. lesions start on nose & face before weaning & quickly spread caudally after weaning
typically a nursery dz black greasy exudates death d/t starvation & dehydration: proteins & electrolytes lost thru skin b. hx, **signs**, could do culture (not done) c. early tx w/ penicillin or ceftiofur tx entire pen or move affected pigs to sick pen d. clip needle teeth: fighting --> open wounds --> bacteria colonize sanitation & disinfection keep litters together at weaning if possible to ↓ fighting |
|
|
sarcoptic mange
a. etiology b. pathogenesis c. epidemiology |
a. Sarcoptes scabei var. suis
b. mites complete life cycle on pig all stages develop in epidermis can survive in environment for hours to 15 d. c. uncommon in commercial setting, but still found in small operations, hobby farms, pasture farms, & pot belly pig farms high morbidity, low mortality sows can be asymptomatic carriers spread by direct contact, commercial pig haul trailers considered a “purchased dz”: buy mange free replacements |
|
|
sarcoptic mange
a. signs b. dx c. eradication |
a. external ear canal often 1st colonized
nursery & finisher pigs: acute - intense pruritis (hallmark: constant rubbing) -allergic hypersensitivity & papules -↓ feed efficiency, ↓ rate of gain, penalty at packing plant for skin lesions adults: chronic, hyperkeratosis b. hx & signs, scraping of external ear canal hard to find in growing pigs insect bites can produce similar lesions to acute form: mange active in winter vs. insect bites in spring & fall c. avermectins (Ivomec) -injectable: inject every pig twice 14 d. apart to eradicate -feed grade: feed for 7 d., wait 30 d. feed for 7 more days depop w/ 30 d. down time & mange free replacements: difficult |
|
|
diamond skin dz
a. etiology b. signs c. dx d. tx e. prevention |
a. Erysipelas rhusiopathiae, Actinobacillus suis
b. +/- skin lesions: necrosis & sloughing if severe lethargy, off feed, elevated temperature possible sequelae: vegetative endocarditis --> sudden death, arthritis c. blood culture is gold standard (rarely done) d. penicillin or ceftiofur e. Erysipelas: all sows vaccinated 2x yr. to prevent abortion backyard pigs should be vaccinated: can get from soil |
|
|
pityriasis rosea: "pseudo ringworm"
a. etiology b. signs c. possible sequelae |
common but economically unimportant
a. unknown b. lesions w/ erythematous borders & central scabbing start in inguinal area & ventral abdomen gradually spread & coalesce resolve spontaneously c. may get 2º Staph infection: tx w/ penicillin or ceftiofur |
|
|
What are some other skin diseases of swine?
|
sunburn --> abortion
swine pox melanoma epitheliogenesis imperfecta foreign animal diseases: African swine fever, foot & mouth dz (vesicles!) |
|
|
pityriasis rosea
|
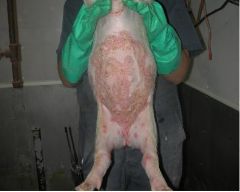
What skin dz is this?
|
|
|
greasy pig dz
|
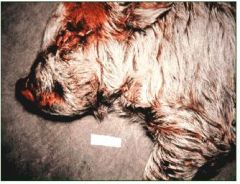
What skin dz is this?
|
|
|
diamond skin dz
|
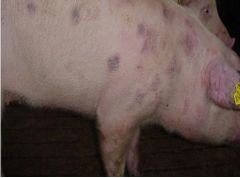
What skin dz is this?
|

