![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ideal suture material |
✔ maintains adequate tensile strength ✔ nonelectrolytic, noncapillary, nonallergenic, noncarcinogenic ✔ comfortable to use ✔good knot security ✔ stimulate little tissue reaction ✔ non corrosive/ toxic ✔ doesn't create situation favorable for bacterial growth |
|
|
General classification of suture materials |
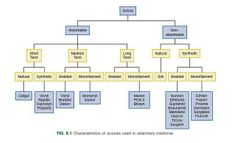
✔ absorbable ✔ non absorbable |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Absorbable sutures are those that undergo degeneration and rapid loss of tensile strength is 60 days |
True |
|
|
Further classification of absorbable sutures |
✔synthetic ✔ natural |
|
|
Examples of natural fiber absorbable suture materials |
◾surgical gut (catgut) ◾collagen |
|
|
Examples of synthetic absorbable suture materials |
◾ polyglycolic acid ◾ polyglactin 910 ◾ polydioxanone ◾ polyglyconate ◾ poliglecaprone 25 |
|
|
Examples of natural fiber nonabsorbable suture materials |
◾ silk ◾ cotton ◾ stainless steel ◾ tantalum |
|
|
Examples of synthetic nonabsorbable suture materials |
◾ polyamides (nylon, polymerized caprolactum) ◾ polyester (including polybutester) ◾ polyolefin plastics (polypropylene, polyethylene) |
|
|
Surgical gut (catgut) is made from _____. |
✔ submucosa of sheep ✔ serosal layer of cattle SI |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Catgut is essentially composed formaldehyde-treated collagen |
True |
|
|
This suture material is a capillary multifilament suture that is machine ground and polished to yield a relatively smooth surface resembling a monofilament material |
Surgical gut (catgut) |
|
|
Absorption of catgut through ___. |
Phagocytosis |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Medium chromic gut loses 33% of its original strength after 7 days of implantation and 67% after 28 days |
True |
|
|
Forms of surgical gut |
✔ plain ✔ chromic |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Plain catgut produces severe tissue reaction and loses tensile strength rapidly |
True |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Chromic catgut has increased tensile strength, resistant to digestion and decreased tissue reaction |
True |
|
|
Disadvantages of surgical gut suture |
✔ swells, weakens and exhibits poor knot security when wet ✔ intense inflammatory reaction ✔ capillarity ✔ sensitivity reaction (primarily seen in cats) |
|
|
This is a multifilament suture material that is processed from bovine flexor tendon and treated with formaldehyde and/or chromium salts |
Collagen |
|
|
Collagen sutures are only used in ____. |
Opthalmic surgery |
|
|
This is a braided multifilament polymer of glycolic (hydroxyacetic) acid |
Polyglycolic acid |
|
|
Absorption of polyglycolic acid through _____. |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Hydrolysis of polyglycolic acid proceeds more rapidly in alkalinic environment |
True |
|
|
Absorption of polyglycolic acid (days) |
✔ 14 days after implantation ✔ 120 days (complete) |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. PGA suture is recommended to be used in urinary bladder |
False |
|
|
This suture material is similar to pilyglactin 910 & monofilament nylon, and is relatively strong and ductile. |
Polyglycolic acid |
|
|
Loss of tensile strength of PGA |
✔ 33% by 7 days of implantation ✔ 80% within 14 days |
|
|
Disadvantages of PGA |
✔ tends to drag through tissues ✔ tends to cut friable tissues ✔ relatively poor knot security |
|
|
This suture material is braided synthetic fiber composed of glycolic and lactic acid (9:1) |
Polyglactin 910 |
|
|
This suture material is more hydrophobic, and more resistant to hydrolysis than PGA |
Polyglactin 910 |
|
|
Absorption of polyglactin through ____. |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
Polyglactin 910 stronger than PGA ___ |
21 days after implantation |
|
|
Suture material that is made from a polymer of paradioxanone available as a monofilament |
Polydioxanone |
|
|
Absorption of polydioxanone through ___. |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
Advantages of polydioxanone |
✔ exhibits less tissue drag ✔ has acceptable handling characteristics |
|
|
Polydioxanone loses tensile strength in (days) |
◾ 26% after 14 days ◾ 42% after 28 days ◾ 84% after 56 days ◾ completed 182 days after implantation |
|
|
A monofilament suture that is a copolymer of glycolic acid and trimethylene carbonate |
Polyglyconate |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Absorption of polyglyconate through the action of macrophages between 6-7mo after implantation |
True |
|
|
It is a monofilament synthetic suture that has high initial tensile strength, excellent pliability, and relative rapid loss of tensile strength. |
Poliglecaprone 25 |
|
|
Poliglecaprone 25 loses its its tensile strength (days) |
◾75% at 14 days ◾ 100% after 21 days |
|
|
This nonabsorbable suture material is made from the cocoon of silkworm, and is available as braided or twisted multifilament |
Silk |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Silk is absorbed within 2 years after implantation |
True |
|
|
This suture material is introduced as a replacement for silk during WWII |
Cotton |
|
|
Disadvantages of cotton |
✔ capillarity ✔ tissue reactivity ✔ inferior handling activity due to electrostatic properties ✔ ability to potentiate infection |
|
|
This suture material is biologically inert, noncapillary as monofilament, and easily sterilized by autoclaving. |
Stainless steel |
|
|
This suture material has highest tensioe strength and great knot security of all suture materials, and maintains its strength on implantation on tissues |
Stainless steel |
|
|
Disadvantages of stainless steel suture |
✔ tendency to cut tissues ✔ poor handling characteristics ✔ diminished ability to withstand repeated bending without breaking |
|
|
Metallic suture used for hernia repair, and for ligating clips |
Tantalum |
|
|
It is an amine-containing thermoplastic, and is available as monofilament or multifilament suture |
Nylon |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Nylon has minimal tissue reaction even in canine tendon |
True |
|
|
Disadvantages of nylon |
✔ poor handling characteristic ✔ poor knot security |
|
|
This suture is one of the strongest nonmetallic suture material |
Polyester fibers |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Suture should be as strong as the normal tissue to which they are placed |
True |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Visceral tissue heal rapidly, attaining strength in 14-21 days |
True |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Monofilament sutures can withstand infection than multifilament |
True |
|
|
Principles of selecting suture materials |

|
|
|
Suture characteristics |
1. Easy to handle 2. Reacts minimally on the tissue 3. Inhibit bacterial growth 4. Holds securely when knotted 5. Resist shrinking in tissue 6. Non-allergenic and non-carcinogenic 7. Absorb with minimak reaction after the tissue has healed |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Stainless steel suture incites little to no inflammatory reaction |
True |
|
|
Uses of stainless steel suture |
✔ for suturing tissues that heal slowly ✔ for contaminated and infected wounds |

