![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Categories of surgical needles |
✔ swaged/ eyeless ✔ eyed |
|
|
This type of surgical needle is readily available, less traumatic on the tissue, always sharp and sterility is always guaranteed. |
Swaged needles |
|
|
This type of surgical needle is reusable, less expensive but less efficient and more traumatic than swaged needles. |
Eyed needles |
|
|
Parts of a surgical needle |
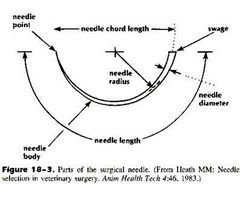
|
|
|
Double-armed suture needle is used in ___. |
Cardiovascular surgery |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Too large a needle diameter results in increased tissue trauma |
True |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. The needles that exceed a length-to-diameter ratio of 8:1 may tend to buckle or bend easily |
True |
|
|
Common needle shapes |
◾ straight ◾ half curved ◾ parts of circle |
|
|
Where do you use straight needles? |
Best used near body surfaces |
|
|
Where do you use half-curved needles? |
Small wounds and wounds deep within the cavity |
|
|
Types of needle point |
✔ noncutting (taper) ✔ cutting |
|
|
These are round needles with no edges |
Noncutting (taper) needles |
|
|
Where do you use noncutting needles? |
✔ viscera ✔ fat ✔ muscles |
|
|
These needles are ground and honed to produce an edge that penetrates dense tissues |
Cutting needles |
|
|
Types of cutting needles |
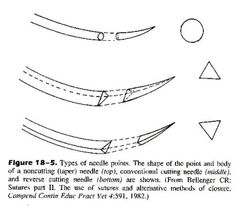
◾ conventional ◾ reverse ◾ tapered |
|
|
The cutting edge of this needle is along the concave surface |
Conventional curved cutting needles |
|
|
The cutting edge of this needle is along the convex surface |
Reverse curved cutting |
|
|
Advantages of reverse cutting needle |
✔ minimize risk of cutting out the tissue ✔ increased needle strength |
|
|
Type of cutting needle that combine a round shaft with a cutting point |
Tapered cutting needles |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE. Tapered cutting needles are used when both delicate and dense tissue are to be penetrated |
True |
|
|
Requirements to be met when choosing suture needles |
✔ needle makes a hole large enough to introduce the suture material ✔ architecture of sutured tissue is not weak ✔ foreign bodies are not introduced into the wound ✔ material and design minimizes trauma/damage and breakage ✔ large enough and appropriate shape to permit precise, accurate and smootn suturing |
|
|
Group of material that is used most extensively as tissue adhesives |
Cyanoacrylates |
|
|
Uses of tissue adhesives |
✔ oral surgery ✔ intestinal anastomosis ✔ control of hemorrhage ✔ microvascular anastomosis ✔ cutaneous incision (MOST COMMON) ✔ skin grafts |
|
|
Uses of surgical staplers |
✔ GI anastomosis ✔ skin apposition ✔ pulmonary resection ✔ cardiovascular resection ✔ hepatic resection |
|
|
1st use of surgical stapling |
Gastric and duodenal transection |
|
|
These are single, rectangular staplers that are placed while the slightly everted skin edges are he,d together by thumb forceps |
Skin staples |
|
|
Advatages of surgical staplers |
✔Consistency of application ✔Security of hemostasis ✔Improved efficiency ✔Utility in areas of difficult accessibility |
|
|
Primary precaution when using stapling instruments |
Amount of tissue to be stapled is not excessive |
|
|
Advatages of ligating clips |
✔ ease of application ✔ high strength ✔ structural stability ✔ improved security |
|
|
1st use of ligating clips |
Small silver clips used to control bleeding during brain tumor excision |
|
|
Metallic clips are ade from: |
◾tantalum ◾stainless steel ◾titanium |
|
|
Absorbable clips are made from: |
◾polyglactin 910 ◾ polydioxanone |
|
|
Uses of ligating clips |
✔ neutering ✔ splenectomy ✔ mastectomy ✔ amputation ✔ tumor excision ✔ nephrectomy ✔ intestinal resectiom ✔ liver biopsy |
|
|
Disadvantages of ligating clips |
✔ relative instability of clip applicator ✔ insecurity of clip ✔ permanence of metallic clips to tissue ✔ limited to vessels less than 11mm in diameter |
|
|
Other needle point types |
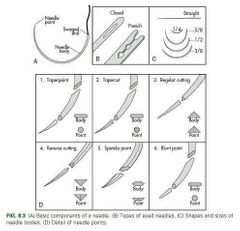
✔ Blunt point needles ◾ can dissect through friable tissue without cutting ◾used for soft, parenchymal organs (eg. Spleen, liver) ✔ Tapercut needles ◾ combination of reverse cutting edge tip and taperpoint body ◾ used for suturing dense, tough fibrous tisse (eg. Tendon), and cardiovascular procedures (eg. Vascular grafts) |
|
|
Characteristics of surgical needles |
◾Surgical yield- angular deformation a needle can withstand before becoming permanently deformed ◾Ductility- needle's resistance to breaking after a specified amount of bending ◾Sharpness- related to the angle of the point and the taper ratio of the needle |

