![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is cleaner production (CP) |
CP is a method and tool to identify where and why a company are losing resources in the form of waste and pollution, and how these losses can be minimised |
|
|
List some of the key points of CP |
1. Adds value to the EMS 2. Does not deny or impede growth but insists growth can be ecologically sustainable 3. It can be applied to manufacturing industries as well as the provision of services 4. Includes safety and protection of health 5. Emphasises risk reduction 6. Improves immediate efficiency as well as long term efficiency 7. Benefits the environment, communities and business |
|
|
CP industrial benefits |
- Improves products and services - Lowers risks (liability) - Improves company image - Improves working conditions - Reduces waste treatment and disposal costs - Improved production and resource use efficiency - Saves costs on raw material, energy and water |
|
|
CP Internal barriers |
- Lack of environmental awareness - Limited information, data and expertise on waste and emissions - Focus on end of pipe solutions and short term profits |
|
|
CP External Barriers |
- Difficulty in accessing cleaner technology - Difficulty in accessing external finance |
|
|
Explain a passive environmental strategy |
This is when the companies dilute and disperse the wastes instead of finding its root causes and treating them Ignores pollution Regulatory non-compliance |
|
|
Explain a reactive environmental strategy |
This is an end of pipe approach where the pollution or wastes are treated as a knee jerk reaction. This involves onsite recycling Costly and inefficient |
|
|
Explain a proactive environmental strategy of CP |
This is when the wastes are properly managed and the root cause of the problems are determined and tackled accordingly Cost effective Regulatory compliance More efficient use of raw materials and energy |
|
|
Key points to define ‘good housekeeping’ in relation to CP |
- Reusing or recycling ‘wastes’ rather than sending them to landfill - Reducing or reusing packaging - Turning off equipment when not in use - Installing water saving devices and checking for leaks |
|
|
8 CP practises that prevent waste generation |
1. Good housekeeping 2. Input substitution 3. Better process control 4. Equipment modification 5. Technology change 6. On-site recovery/reuse 7. Production of a useful by-product 8. Product modification |
|
|
Ways in which SME’s can achieve clean production |
1. Knowing the chemicals used and their quantities 2. Assessing the hazard of each chemical and material 3. Ensuring that information of all hazardous substances are publicly available for free 4. Establishing reduction targets and timelines for complete elimination of current hazardous chemicals 5. Making the plan publicly available to chart progress against goals |
|
|
What is FMEA |
Stands for Failure Modes and Effects Analysis It is a methodology to identify potential failures of a system and its effects |
|
|
Benefits of FMEA |
- Improvements in safety, quality and reliability - Improved company image - Improved satisfaction - Lower development costs |
|
|
Applications of FMEA |
- Concept - Design - Process - Service - Equipment |
|
|
Summarise the FMEA procedure |
1. Determine the likelihood of detecting the failure 2. Determine which risks take priority 3. Address the highest risks and assign a Risk Priority Number (RPN) 4. Update the FMEA as action is taken |
|
|
Causes for early failure of FMEA |
- Poor quality control - Substandard materials - Contamination - Human error |
|
|
Causes of normal life failure of FMEA |
- Design errors - Insufficient safety margins - Abuse of equipment |
|
|
Causes of wear out failure of FMEA |
- Corrosion - Fatigue - Poor maintenance |
|
|
How to calculate RPN |
Severity x occurrence x detection = RPN |
|
|
Define sustainable development |
It is the economical development that is conducted without the depletion of natural resources |
|
|
What is the triple bottom line approach |
Environmental Integrity (Protection) - protecting the air, water and land. Enhance the environment through development decisions Economic Prosperity (Growth) - Enhancing the community by attracting residential, commercial and industrial development and encouraging sustained practices Social Benefit (Equity) - Plan, build and rebuild communities so they are desirable places that enhance quality of life |
|
|
What is EIA |
An Environmental Impact Assessment is a decision support tool to help decide whether a project should be authorised or not |
|
|
8 guiding principles of of EIA |
1. Participation 2. Transparency 3. Certainty 4. Accountability 5. Credibility 6. Cost effectiveness 7. Flexibility 8. Practicality |
|
|
Steps of EIA |
1. Screening 2. Scoping 3. Impact analysis 4. Reporting 5. Review 6. Decision making 7. Monitoring |
|
|
Steps of EIA |
1. Screening 2. Scoping 3. Impact analysis 4. Reporting 5. Review 6. Decision making 7. Monitoring |
|
|
Steps of EIA |
1. Screening 2. Scoping 3. Impact analysis 4. Reporting 5. Review 6. Decision making 7. Monitoring |
|
|
Benefits of EIA |
- environmentally friendly and sustainable design - Reduced time and costs for approvals - Better compliance with standards Better protection of human health |
|
|
What is ERA |
An Environmental Risk Assessment is a process of predicting whether there may be a risk or adverse effects on the environment caused by a chemical substance |
|
|
How does ERA benefit EIA |
- Offers a more holistic assessment - systematically identifies potential hazards of a proposal - It sets EIA priorities and manages uncertainty |
|
|
What is FTA |
Failure Tree Analysis is a top down approach to failure analysis Starts with identifying an undesirable event (TOP event) then determining all the ways it can happen |
|
|
Benefits of using FTA |
- Helps in visualising the analysis - Determines the probability of occurrence of each of the root causes - Provides evidence of compliance with safety requirements |
|
|
What is lean |
Lean is an operations system that aims to maximise values by cutting out unnecessary resources and delays |
|
|
The 5 principles of lean |
1. Identify your customers and what they value 2. Map the value stream 3. Create flow to the customer 4. Establish pull based on customer demand 5. Seek continuous improvement |
|
|
Potential barriers to implementing lean |
- Insufficient workforce skill - Insufficient management time to make changes - Dealing with employee resistance to change |
|
|
What is DfE |
Design for Environment is a method to minimise or eliminate environmental impacts of a product over its life cycle |
|
|
7 Key elements of DfE |
1. Embed life-cyclethinking into the product development process. 2. Evaluate the resourceefficiency and effectiveness of the overall system. 3. Select appropriatemetrics to represent product life-cycle performance. 4. Maintain and apply aportfolio of systematic design strategies. 5. Use analysis methodsto evaluate design performance and trade-offs.6. Provide softwarecapabilities to facilitate the application of DFE practices. 7. Seek inspiration fromnature for the design of products and systems. |
|
|
What are greenhouse gases and 4 examples |
Greenhouse gases are gases that absorb and emit radiant energy within the thermal infrared range - water vapour (H2O) - Carbon dioxide (CO2) - Methane (CH4) - Nitrous Oxide (N2O) |
|
|
What is the greenhouse effect |
It is a process that occurs when gases in the Earths atmosphere trap the suns heat causing the planet to warm |
|
|
Four rules of DfE |
1. Design products and processes with industrial materials that can be recycled continually with no loss in performance, thereby creating new industrial materials 2. Design products and processes with natural materials that can be fully returned to the Earths natural cycles, thereby creating new natural resources 3. Design products and processes that do not produce unnatural, toxic materials that cannot be safely processed by either natural or industrial cycles 4. Design product and processes with clean, renewable sources of energy, rather than fossil fuels |
|
|
3 priorities of DfE |
1. Energy efficiency 2. Materials Innovation 3. Design for recyclability |
|
|
7 Key elements of DfE |
1. Embed life cycle thinking into product development process 2. Evaluate the resource efficiency and effectiveness of the overall system 3. Select appropriate metrics to represent product life-cycle performance 4. Maintain and apply a portfolio of systematic design strategies 5. Use analysis methods to evaluate design performance and trade-offs 6. Provide software capabilities to facilitate the application of DfE practices 7. Seek inspiration from nature for the design of products and systems |
|
|
What are the goals of Cleaner Production |
- Continuous strategy for products, processes and services which reduces risk to humans and the environment - Preventive strategy for products, processes and services which reduces risk to humans and the environment - Integrated strategy for products, processes and services which reduces risk to humans and the environment |
|
|
What are sustainable development indicators |
They are a synthetic variable, giving indications, describing or measuring the state of a phenomenon or a situation |
|
|
Typical properties of good SD indicators |
- Clearly defined goals and objectives - Developed and selected in a logical, structured selection process that is scientifically rigorous and transparent - Broad regional agreement on the criteria/framework |
|
|
Benefits of good SD indicators |
- Better decision making - Lower risks and costs - Greater public accountability and better communication - Identification of impacts - Continuous improvement |
|
|
List 3 main purposes of environmental indicators in relation to policy making |
1. Supply information on environmental problems, in order to allow policy makers to enable their seriousness 2. Support policy development and priority setting by identifying key factors that cause pressure on the environment 3. To assess the effects of policy responses |
|
|
Benefits of implementing lean |
- Lower manpower requirements - Higher product quality and reliability - Reduction in waste and costs |
|
|
How does ERA differ from EIA |
Firstly it focuses on environmental conditions then moves on to factors causing these conditions EIA generally focuses on a specific project and the nature of its impacts on the environment |
|
|
List the 4 main phases of a PLCA |
1. Goal and scope definition 2. Inventory analysis 3. Impact assessment 4. Interpretation |
|
|
List the 4 main phases of a PLCA |
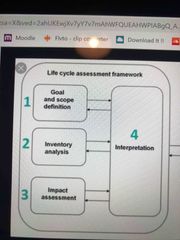
1. Goal and scope definition 2. Inventory analysis 3. Impact assessment 4. Interpretation |

