![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the name of the liver capsule? |
Glisson's capsule |
|
|
What is the "bare" area of the liver? |
Posterior section of the liver against the diaphragm that is "bare" without peritoneal covering |
|
|
What is Cantle's line? |
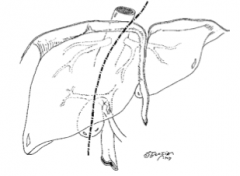
Line drawn from the gallbladder to a point just to the left of the IVC, which transects the liver into the right and left lobes
|
|
|
Which ligament goes from the anterior abdominal wall to the liver? |
Falciform ligament |
|
|
What does the falciform ligament contain? |
Ligamentum teres (obliterated umbilical vein) |
|
|
What is the coronary ligament? |
Peritoneal reflection on top of the liver that crowns (hence "coronary") the liver and attaches it to the diaphragm |
|
|
What are the triangular ligaments of the liver? |
Right and left lateral extents of the coronary ligament, which forms triangles |
|
|
What is the origin of the hepatic arterial supply? |
From the proper hepatic artery off of the celiac trunk (celiac trunk to common hepatic artery to proper hepatic artery) |
|
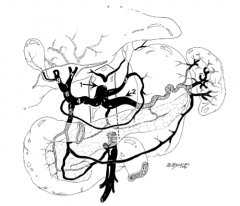
What is structure 1?
|
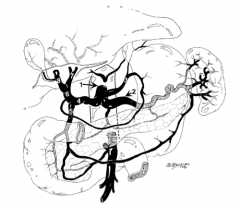
Celiac trunk |
|
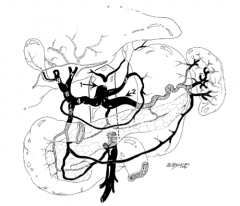
What is structure 2?
|
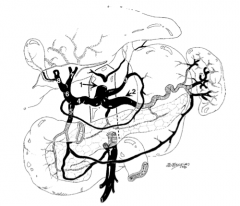
Splenic artery |
|
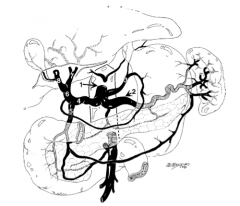
What is structure 3?
|
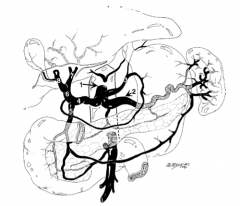
Left gastric artery |
|
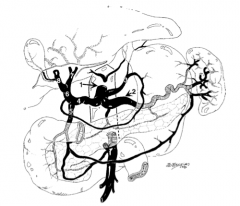
What is structure 4?
|
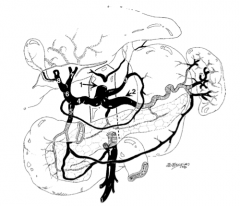
Common hepatic artery |
|
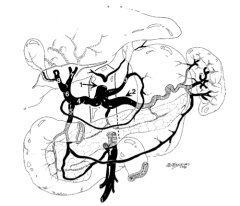
What is structure 5?
|
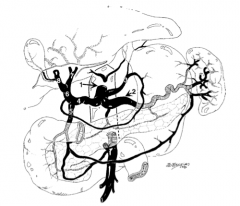
Gastroduodenal artery |
|
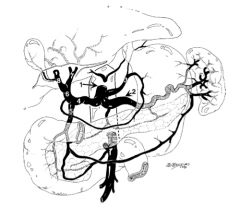
What is structure 6?
|
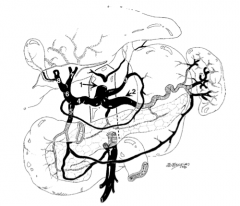
Proper hepatic artery |
|
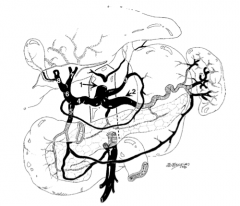
What is structure 7?
|
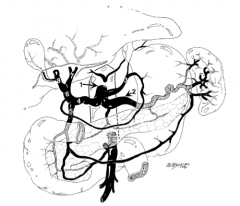
Left hepatic artery |
|
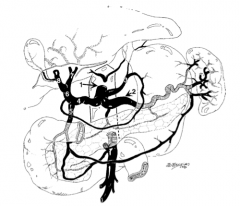
What is structure 8?
|
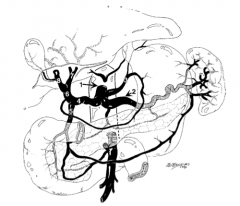
Right hepatic artery |
|
|
What is the venous supply to the liver? |
Portal vein (formed from splenic vein and superior mesenteric vein) |
|
|
What is the hepatic venous drainage? |
Via the hepatic veins, which drain into the IVC (three veins: left, middle, and right) |
|
|
What sources provide O2 to the liver? |
- Portal vein blood (50%) - Hepatic artery blood (50%) |
|
|
From what sources does the liver receive blood? |
- Portal system (75%) - Hepatic artery system (50%) |
|
|
What is the overall arrangement of the sgements in the liver? |
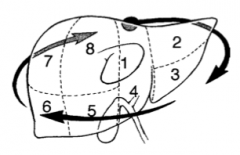
Clockwise, starting at segment 1
|
|
|
What is the maximum amount of liver that can be resected while retaining adequate liver function? |
>80%; if given adequate recovery time, the original mass can be regenerated! |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of liver disease? |
- Hepatomegaly - Splenomegaly - Icterus - Pruritus (from bile salts in skin) - Blanching - Spider telangiectasia - Gynecomastia - Testicular atrophy - Caput medusae - Dark urine - Clay-colored stools - Bradycardia - Edema - Ascites - Fever - Fetor hepaticus (sweet musty smell) - Hemorrhoids - Variceal bleeding - Anemia - Body hair loss - Liver tenderness - Palmar erythema |
|
|
Which liver enzymes are made by hepatocytes? |
AST and ALT |
|
|
What is the source of alk phos? |
Ductal epithelium (thus, elevated with ductal obstruction) |
|
|
What is Child's class? |
Classification that estimates hepatic reserve in patients with hepatic failure and mortality |
|
|
What comprises the Child's classification? |
- Lab: bilirubin, albumin - Clinical: encephalopathy, ascites, prothrombin time (PT) |
|
|
How can the criteria comprising the modified Child's classification be remembered? |
"A BEAP": - Ascites
- Bilirubin - Encephalopathy - Albumin - PT |
|
|
What are the criteria for Child's class A? |

- Ascites: none - Bilirubin: <2 - Encephalopathy: none - Albumin: >3.5 - PT: <1.7 |
|
|
What are the criteria for Child's class B? |

- Ascites: controlled - Bilirubin: 2-3 - Encephalopathy: minimal - Albumin: 2.8-3.5 - PT: 1.7-2.2 |
|
|
What are the criteria for Child's class C? |

- Ascites: uncontrolled - Bilirubin: >3 - Encephalopathy: severe - Albumin: <2.8 - PT: >2.2 |
|
|
What is the operative mortality for a portocaval shunt vs overall intra-abdominal operations with cirrhosis in Child class A? |
<5% vs overall = 10% |
|
|
What is the operative mortality for a portocaval shunt vs overall intra-abdominal operations with cirrhosis in Child class B? |
<15% vs overall = 30% |
|
|
What is the operative mortality for a portocaval shunt vs overall intra-abdominal operations with cirrhosis in Child class C? |
~33% vs overall = 75% |
|
|
What does the MELD score stand for? |
Model for End-stage Liver Disease |
|
|
What is measured in the MELD score? |
- INR - T. bili - Serum creatinine
|
|
|
What is the mortality in cirrhotic patients for non-emergent non-transplant surgery? |
Increased in mortality by 1% per 1 point in the MELD score until 20, then 2% for each MELD point |
|
|
What is the mortality in cirrhotic patients for emergent non-transplant surgery? |
14% increase in mortality per 1 point of the MELD score |
|
|
What is the most common liver cancer? |
Metastatic disease outnumbers primary tumors 20:1, primary site is usually the GI tract |
|
|
What is the most common primary malignant liver tumor? |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (hepatoma) |
|
|
What is the most common primary benign liver tumor? |
Hemangioma |
|
|
What lab tests comprise the workup for the liver metastasis? |
- LFTs (AST and alk phos are most useful) - CEA for suspected primary colon cancer |
|
|
What are the associated imaging studies to workup a liver metastasis? |
- CT scan - U/S - A-gram |
|
|
What is a right hepatic lobectomy? |
Removal of the R lobe of the liver (ie, removal of all the liver tissue to the left of Cantle's line) |
|
|
What is a left hepatic lobectomy? |
Removal of the left lobe of the liver (ie, removal of all the liver tissue to the right of Cantle's line) |
|
|
What is a right trisegmentectomy? |
Removal of all the liver tissue to the right of the falciform ligament |
|
|
What are the three common types of primary benign liver tumors? |
1. Hemangioma 2. Hepatocellular adenoma 3. Focal nodular hyperplasia |
|
|
What are the four common types of primary malignant liver tumors? |
1. Hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatoma) 2. Cholangiocarcinoma (when intrahepatic) 4. Hepatoblastoma (most common in infants and children) |
|
|
What chemical exposures are risk factors for angiosarcoma? |
- Vinyl chloride - Arsenic - Thorotrast contrast |
|
|
What is a hepatoma? |
Hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
What are the other benign liver masses? |
- Benign liver cyst - Bile duct hamartoma - Bile duct adenoma |
|
|
What is a liver "hamartoma"? |
White hard nodule made up of normal liver cells |
|
|
What is a hepatocellular adenoma? |
Benign liver tumor |
|
|
What are the histologic findings of a hepatocellular adenoma? |
Normal hepatocytes without bile ducts |
|
|
What are the associated risk factors for hepatocellular adenoma? |
- Women - Birth control pills (think: ABC = adenoma birth control) - Anabolic steroids - Glycogen storage disease |
|
|
What is the female:male ratio with hepatocellular adenoma? |
9:1 |
|
|
What is the average age of occurrence for hepatocellular adenoma? |
30-35 years of age |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hepatocellular adenoma? |
RUQ pain / mass, RUQ fullness, bleeding (rare) |
|
|
What are the possible complications of hepatocellular adenoma? |
- Rupture with bleeding (33%) - Necrosis - Pain - Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
How do you diagnose hepatocellular adenoma? |
- CT scan - U/S - +/- biopsy (rule out hemangioma with RBC-tagged scan!) |
|
|
What is the treatment for a small hepatocellular adenoma (<5cm)? |
Stop birth control pills - it may regress; if not, surgical resection is necessary |
|
|
What is the treatment for a large (>5cm), bleeding, painful, or ruptured hepatocellular adenoma? |
Surgical resection |
|
|
What is focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
Benign liver tumor |
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
Normal hepatocytes and bile ducts (adenoma has no bile ducts) |
|
|
What is the average age of occurrence for focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
~40 years |
|
|
What are the associated risk factors for focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
Female gender |
|
|
Is focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) associated with birth control pills? |
Yes, but not as clearly associated as with adenoma |
|
|
How do you diagnose focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
- Nuclear technetium-99 study - U/S - CT scan - A-gram - Biopsy |
|
|
What is the classic CT scan finding associated with focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
Liver mass with "central scar" (think focal = central) |
|
|
What are the possible complications of focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
Pain (no risk of cancer, very rarely hemorrhage) |
|
|
Is there a cancer risk with focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
No (there is a cancer risk with adenoma) |
|
|
What is the treatment of focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
Resection or embolization if patient is symptomatic, otherwise follow if diagnosis is confirmed; stop birth control pills |
|
|
Why does embolization work for focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? |
FNH tumors are usually fed by one major artery |
|
|
What is hepatic hemangioma? |
Benign vascular tumor of the liver |
|
|
What is a hepatic hemangiomas claim to fame? |
Most common primary benign liver tumor (up to 7% of population) |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hepatic hemangioma? |
RUQ pain/mass, bruits |
|
|
What are the possible complications of hepatic hemangioma? |
- Pain - CHF - Coagulopathy - Obstructive jaundice - Gastric outlet obstruction - Kasabach-Merritt syndrome - Hemorrhage (rare) |
|
|
What is Kasabach-Merritt syndrome? |
Hemangioma and thrombocytopenia and fibrinogenopenia |
|
|
How do you diagnose hepatic hemangioma? |
CT scan with IV contrast, tagged red blood scan, MRI, U/S |
|
|
Should biopsy be performed on hepatic hemangioma? |
No (risk of hemorrhage with biopsy) |
|
|
What is the treatment of hepatic hemangioma? |
Observation (>90%) |
|
|
What are the indications for resection of hepatic hemangioma? |
Symptoms, hemorrhage, cannot make a diagnosis |
|
|
What is hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Most common primary malignancy of the liver |
|
|
What is a hepatocellular carcinoma also known as? |
Hepatoma |
|
|
What is the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Accounts for 80% of all primary malignant liver tumors |
|
|
What are the geographic high-risk areas of hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Africa and Asia |
|
|
What are the associated risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma? |
- Hep B - Cirrhosis - Aflatoxin (fungi toxin of Aspergillus flavus) - alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency - Hemochromatosis - Liver fluke (Clonorchis sinensis) - Anabolic steroids - Polyvinyl chloride - Glycogen storage disease (type I) |
|
|
What percentage of patients with cirrhosis will develop hepatocellular carcinoma? |
~5% |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hepatocellular carcinoma? |
- Dull RUQ pain - Hepatomegaly (classic presentation is painful) - Abdominal mass - Weight loss - Paraneoplastic syndromes - Signs of portal HTN - Ascites - Jaundice - Fever - Anemia - Splenomegaly |
|
|
What tests should be ordered to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma? |
- U/S - CT scan - Angiography - Tumor marker elevation |
|
|
What is the tumor marker associated with hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein |
|
|
What is the most common way to get a tissue diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Needle biopsy with CT scan, U/S, or laparoscopic guidance |
|
|
What is the most common site of metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Lungs |
|
|
What is the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma? |
- Surgical resection, if possible (eg, lobectomy) - Liver transplant |
|
|
What are the treatment options if the patient with hepatocellular carcinoma is not a surgical candidate? |
Percutaneous ethanol tumor injection, cryotherapy, and intra-arterial chemotherapy |
|
|
What are the indications for liver transplant in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Cirrhosis and NO resection candidacy as well as no distant or lymph node metastases and no vascular invasion
The tumor must be single, <5 cm tumor or have three nodules, with none >3 cm |
|
|
What is the prognosis for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Almost none survive a year |
|
|
What is the prognosis for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma? |
~35% are alive at 5 years |
|
|
Which subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma has the best prognosis? |
Fibrolamellar hepatoma (young adults) |
|
|
What is a liver abscess? |
Abscess (collection of pus) in the liver parenchyma |
|
|
What are the types of liver abscess? |
- Pyogenic (bacterial) - Parasitic (amebic) - Fungal |
|
|
What is the most common location of liver abscess? |
Right lobe > Left lobe |
|
|
What are the sources of liver abscess? |
- Direct spread from biliary tract infection - Portal spread from GI infection (eg, appendicitis, diverticulitis) - Systemic source (bacteremia) - Liver trauma (eg, liver gunshot wound) - Cryptogenic (unknown source) |
|
|
What are the two most common types of liver abscess? |
- Bacterial (most common in US) - Amebic (most common worldwide) |
|
|
What are the three most common bacterial organisms affecting the liver? |
Gram negatives: - E. coli - Klebsiella - Proteus |
|
|
What are the most common sources / causes of bacterial liver abscesses? |
- Cholangitis - Diverticulitis - Liver cancer - Liver metastasis |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of liver abscesses? |
- Fever/chills - RUQ pain - Leukocytosis - Increased LFTs - Jaundice - Sepsis - Weight loss |
|
|
What is the treatment of liver abscesses? |
IV antibiotics (triple antibiotics with metronidazole), percutaneous drainage with CT scan or U/S guidance |
|
|
What are the indications for operative drainage of a liver abscess? |
Multiple / loculated abscesses or if multiple percutaneous attempts have failed |
|
|
What is the etiology of amebic liver abscess? |
Entamoeba histolytica (typically reaches liver via portal vein from intestinal amebiasis) |
|
|
How does an amebic liver abscess spread? |
Fecal-oral transmission |
|
|
What are the risk factors for amebic liver abscesses? |
- Patients from countries south of the US-Mexican border - Institutionalized patients - Homosexual men - Alcoholic patients |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of amebic liver abscesses? |
- RUQ pain - Fever - Hepatomegaly - Diarrhea
- Note: chills are much less common with amebic abscesses than with pyogenic abscesses |
|
|
Which lobe is most commonly involved by amebic liver abscess? |
Right lobe of liver |
|
|
What is the classic description of amebic liver abscess contents? |
"Anchovy paste" pus |
|
|
How do you diagnose amebic liver abscess? |
Lab tests, U/S, CT scan |
|
|
What lab tests should be performed in a patient with amebic liver abscess? |
Indirect hemagglutination titers for Entamoeba antibodies elevated in >95% of cases, elevated LFTs |
|
|
What is the treatment of amebic liver abscesses? |
Metronidazole IV |
|
|
What are the indications for percutaneous surgical drainage of an amebic liver abscess? |
Refractory to metronidazole, bacterial co-infection, or peritoneal rupture |
|
|
What are the possible complications of large left lobe liver amebic absess? |
Erosion into the pericardial sac (potentially fatal!) |
|
|
What is a hydatid liver cyst? |
Usually a right lobe cyst filled with Echinococcus granulosus |
|
|
What are the risk factors for hydatid liver cyst? |
Travel; exposure to dogs, sheep, and cattle (carriers) |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of hydatid liver cyst? |
- RUQ abdominal pain - Jaundice - RUQ mass |
|
|
How do you diagnose a hydatid liver cyst? |
Indirect hemagglutination antibody test (serologic testing), Casoni skin test, U/S, CT, radiographic imaging |
|
|
What are the findings of hydatid liver cyst on AXR? |
Possible calcified outline of cyst |
|
|
What are the major risks for hydatid liver cyst? |
- Erosion into the pleural cavity, pericardial sac, or biliary tree - Rupture into the peritoneal cavity causing fatal anaphylaxis |
|
|
What is the risk of surgical removal of echinococcal (hydatid) cysts? |
Rupture or leakage of cyst contents into the abdomen may cause a fatal anaphylatic reaction |
|
|
When should percutaneous drainage of a hydatid liver cyst be performed? |
Never - may cause leaking into the peritoneal cavity and anaphylaxis |
|
|
What is the treatment of hydatid liver cysts? |
- Mebendazole, followed by surgical resection - Large cysts can be drained and then injected with toxic irrigant (scoliocide) into the cyst unless aspirate is bilious (which means there is a biliary connection) followed by cyst removal |
|
|
Which toxic irrigations are used with hydatid liver cysts? |
- Hypertonic saline - Ethanol - Cetrimide |
|
|
What is hemobilia? |
Blood draining via the common bile duct into the duodenum |
|
|
What is the diagnostic triad of hemobilia? |
1. RUQ pain 2. Guaiac positive / upper GI bleeding 3. Jaundice |
|
|
What are the causes of hemobilia? |
- Trauma with liver laceration - Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) - Tumors |
|
|
How do you diagnose hemobilia? |
EGD (blood out of ampulla of Vater), A-gram |
|
|
What is the treatment of hemobilia? |
A-gram with embolization of the bleeding vessel |

