![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How long is the duodenum? |
~12 inches |
|
|
What marks the end of the duodenum and the start of the jejunum? |
Ligament of Treitz |
|
|
What is the length of the entire small bowel? |
~6 meters (20 feet) |
|
|
What provides blood supply to the small bowel? |
Branches of the superior mesenteric artery |
|
|
What does the small bowel do? |
Major site of digestion and absorption |
|
|
What are the plicae circulares? |
Plicae means "folds", circulares means "circular"; therefore, circular folds of mucosa (aka valvulae conniventes) in small bowel lumen |
|
|
What are the major structural differences between the jejunum and ileum? |
- Jejunum: long vasa rectae, large plicae circulares, thicker wall - Ileum: shorter vasa rectae, smaller plicae circulares, thinner wall
(Ileum = Inferior) |
|
|
What does the terminal ileum absorb? |
- B12 - Fatty acids - Bile salts |
|
|
What is a small bowel obstruction? |
Mechanical obstruction to the passage of intraluminal contents |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of an SBO? |
- Abdominal discomfort - Cramping - Nausea - Abdominal distention - Emesis - High-pitched bowel sounds |
|
|
What lab tests are performed with SBO? |
- Electrolytes - CBC - Type and screen - Urinalysis |
|
|
What are classic electrolyte / acid-base findings with proximal obstruction? |
Hypovolemic hypochloremic hypokalemic alkalosis |
|
|
What must be ruled out on physical exam in patients with SBO? |
Incarcerated hernia (also look for surgical scars) |
|
|
What major AXR findings are associated with SBO? |
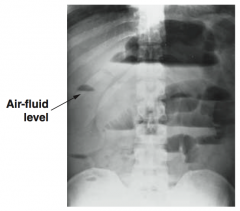
Distended loops of small bowel air-fluid levels on upright film |
|
|
Define complete SBO. |
Complete obstruction of the lumen; usually paucity or no colon gas |
|
|
What is the danger of complete SBO? |
Closed loop strangulation of the bowel leading to bowel necrosis |
|
|
What is partial SBO? |
Incomplete SBO; some colon gas |
|
|
What is initial management of all patients with SBO? |
NPO, NGT, IVF, Foley |
|
|
What tests can differentiate partial from complete bowel obstruction? |
CT with oral contrast, small bowel follow-through |
|
|
What are the ABCs of SBO? |
Causes of SBO: 1. Adhesions 2. Bulge (hernias) 3. Cancer and tumors |
|
|
What are the other causes of SBO? |
"GIVES BAD CRAMPS": - Gallstone ileus - Intussusception - Volvulus - External compression - SMA syndrome
- Bezoars, Bowel wall hematomas - Abscesses - Diverticulitis
- Crohn's disease - Radiation enteritis - Annular pancreas - Meckel's diverticulum - Peritoneal adhesions - Stricture |
|
|
What is Superior Mesenteric Artery (SMA) syndrome? |
Seen with weight loss - SMA compresses duodenum, causing obstruction |
|
|
What is the treatment of complete SBO? |
Laparotomy and lysis of adhesions |
|
|
What is LOA? |
Lysis of Adhesions |
|
|
What is the treatment of incomplete SBO? |
Initially, conservative treatment with close observation plus NGT decompression |
|
|
Intraoperatively, how can the level of obstruction be determined in patients with SBO? |
Transition from the dilated bowel proximal to the decompressed bowel distal to the obstruction |
|
|
What is the most common indication for abdominal surgery in patients with Crohn's disease? |
SBO |
|
|
Can a patient have complete SBO and BMs and flatus? |
Yes - the bowel distal to the obstruction can clear out gas and stool |
|
|
After a small bowel obstruction, why should the mesenteric defect always be closed? |
To prevent an internal hernia |
|
|
What may cause SBO if patient is on coumadin? |
Bowel wall hematoma |
|
|
What is the #1 cause of SBO in adults (industrialized countries)? |
Post-op adhesions |
|
|
What is the #1 cause of SBO around the world? |
Hernias |
|
|
What is the #1 cause of SBO in children? |
Hernias |
|
|
What are the signs of strangulated bowel with SBO? |
- Fever - Severe / continuous pain - Hematemesis - Shock - Gas in bowel wall or portal vein - Abdominal free air - Peritoneal signs - Acidosis (increased lactic acid) |
|
|
What are the clinical parameters that will lower the threshold to operate on a partial SBO? |
- Increasing WBC - Fever - Tachycardia / tachypnea - Abdominal pain |
|
|
What is an absolute indication for operation with partial SBO? |
Peritoneal signs, free air on AXR |
|
|
What classic saying is associated with complete SBO? |
"Never let the sun set or rise on complete SBO" |
|
|
What condition commonly mimics SBO? |
Paralytic ileus (AXR reveals gas distention throughout, including the colon) |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of paralytic (non-obstructive) ileus? |
- Post-op ileus after abdominal surgery (normally resolves in 3-5 days) - Electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia is most common) - Meds (anticholinergics, narcotics) - Inflammatory intra-abdominal process - Sepsis / shock - Spine injury / spinal cord injury - Retroperitoneal hemorrhage |
|
|
What tumor classically causes SBO d/t "mesenteric fibrosis"? |
Carcinoid tumor |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of benign tumors of the small intestine? |
- Leiomyoma - Lipoma - Lymphangioma - Fibroma - Adenoma - Hemangioma |
|
|
What are the signs / symptoms of small bowel tumors? |
- Abdominal pain - Weight loss - Obstruction (SBO) - Perforation |
|
|
What is the most common benign small bowel tumor? |
Leiomyoma |
|
|
What is the most common malignant small bowel tumor? |
Adenocarcinoma |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of malignant tumors of the small intestine? |
1. Adenocarcinoma (50%) 2. Carcinoid (25%) 3. Lymphoma (20%) 4. Sarcoma (<5%) |
|
|
What is the workup of a small bowel tumor? |
UGI with small bowel follow-through, enteroclysis, CT scan, enteroscopy |
|
|
What is the treatment for malignant small bowel tumor? |
Resection and removal of mesenteric draining lymph nodes |
|
|
What malignancy is classically associated with metastasis to small bowel? |
Melanoma |
|
|
What is a Meckel's diverticulum? |
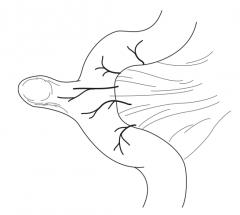
Remnant of the omphalomesenteric duct / vitelline duct, which connects the yolk sac with the primitive midgut in the embryo
|
|
|
What is a Meckel's diverticulum claim to fame? |
Most common small bowel congenital abnormality |
|
|
What is the usual location of a Meckel's diverticulum? |
Within 2 feet of the ileocecal valve on the anti-mesenteric border of the bowel |
|
|
What is the major differential diagnosis of a Meckel's diverticulum? |
Appendicitis |
|
|
Is a Meckel's diverticulum a true diverticulum? |
Yes - all layers of the intestine are found in the wall |
|
|
What is the incidence of Meckel's diverticulum? |
2% of the of the population at autopsy |
|
|
What is the gender ratio for Meckel's diverticulum? |
Twice as common in men |
|
|
What is the average age at onset of symptoms for Meckel's diverticulum? |
Most frequently in the first 2 years of life, but can occur at any age |
|
|
What are the possible complications of Meckel's diverticulum? |
- Intestinal hemorrhage (painless): 50%; accounts for half of all lower GI bleeding in patients <2 years - Bleeding results from ectopic gastric mucosa secreting acid --> ulcer --> bleeding - Intestinal obstruction: 25%; most common complication in adults; includes volvulus and intussusception - Inflammation (+/- perforations): 20% |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of Meckel's diverticulum? |
- Lower GI bleeding - Abdominal pain - SBO |
|
|
What is the most common complication of Meckel's diverticulum in adults? |
Intestinal obstruction |
|
|
In what percentage of cases of Meckel's diverticulum is heterotopic tissue found in the diverticulum? |
>50% |
|
|
What heterotopic tissue type is most often found in Meckel's diverticulum? |
Gastric mucosa (60%), but duodenal, pancreatic, and colonic mucosa are also found |
|
|
What is the "rule of 2's" for Meckel's diverticulum? |
- 2% of patients are symptomatic - Found 2 feet from ileocecal valve - Found in 2% of population - Most sx occur before 2 years of age - Ectopic tissue found in 1 of 2 patients - Most diverticula are 2 inches long - 2 to 1 male to female ratio |
|
|
What is the role of incidental Meckel's diverticulotomy (surgical removal upon finding asymptomatic diverticulum)? |
Most experts would remove in children (very controversial in adults) |
|
|
What is a Meckel's scan? |
Scan for ectopic gastric mucosa in Meckel's diverticulum; uses technetium pertechnetate IV, which is preferentially taken up by gastric mucosa |
|
|
What is the treatment of a Meckel's diverticulum that is causing bleeding and obstruction? |
Surgical resection, with small bowel resection as the actual ulcer is usually on the mesenteric wall opposite the diverticulum |
|
|
What is the name of the hernia associated with incarcerated Meckel's diverticulum? |
Littre's hernia (LM) |
|
|
In patients with guaiac positive stools and a negative upper and lower GI workup, what must be ruled out? |
- Small bowel tumor - Evaluate with enteroclysis (small bowel contrast study) |
|
|
What is the most common cause of small bowel bleeding? |
Small bowel angiodysplasia |

