![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
172 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What widely accepted protocol does trauma care int he US follow? |
Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) precepts of the American College of Surgeons |
|
|
What are the three main elements of the ATLS protocol? |
1. Primary survey / resuscitation 2. Secondary survey 3. Definitive care |
|
|
How and when should the patient history be obtained? |
It should be obtained while completing the primary survey; often the rescue squad, witnesses, and family members must be relied upon |
|
|
What are the five steps of the primary survey? |
ABCDEs: - Airway (and C-spine stabilization) - Breathing - Circulation - Disability - Exposure and Environment |
|
|
What principles are followed in completing the primary survey? |
Life-threatening problems discovered during the primary survey are always addressed before preceeding to the next step |
|
|
What are the goals during assessment of the airway? |
Securing the airway and protecting the spinal cord |
|
|
In addition to the airway, what MUST be considered during the airway step? |
Spinal immobilization |
|
|
What comprises spinal immobilization? |
Use of a full backboard and rigid surgical collar |
|
|
In an alert patient, what is the quickest test for an adequate airway? |
Ask a question: if the pt can speak, the airway is intact |
|
|
What is the first maneuver used to establish an airway? |
Chin lift, jaw thrust, or both; if successful, often an oral or nasal airway airway can be used temporarily maintain the airway |
|
|
If these chin lift or jaw thrust is unsuccessful at establishing an airway, what is the next maneuver used to establish an airway? |
Endotracheal intubation |
|
|
If the chin left, jaw thrust, or endotracheal intubation is unsuccessful at establishing an airway, what is the definitive airway? |
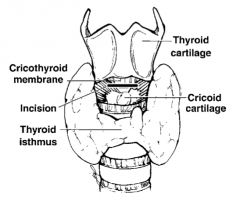
Cricothyroidotomy, aka "surgical airway":
Incise the cricothyroid membrane between the cricoid cartilage inferiorly and the thyroid cartilage superiorly and place an endotracheal or tracheostomy tube into the trachea |
|
|
What must always be kept in mind during difficult attempts to establish an airway? |
Spinal immobilization and adequate oxygenation; if at all possible, pts must be adequately ventilated with 100% oxygen using a bag and mask before any attempt to establish an airway |
|
|
What are the goals in assessing breathing? |
Securing oxygenation and ventilation; treat life-threatening thoracic injuries |
|
|
What comprises adequate assessment of breathing? |
1. Inspection: for air movement, respiratory rate, cyanosis, tracheal shift, JVD, asymmetric chest expansion, use of accessory muscles of respiration, open chest wounds 2. Auscultation: for breath sounds 3. Percussion: for hyperresonance or dullness over either lung field 4. Palpation: for presence of subcutaneous emphysema, flail segments |
|
|
What are the life-threatening conditions that MUST be diagnosed and treated during the breathing step? |
- Tension pneumothorax - Open pneumothorax - Massive hemothorax |
|
|
What is a pneumothorax? |
Injury to the lung resulting in release of air into the pleural space between the normally apposed parietal and visceral pleura |
|
|
How is a pneumothorax diagnosed? |
Tension pneumothorax is a clinical diagnosis: - Dyspnea - JVD - Tachypnea - Anxiety - Pleuritic chest pain - Unilateral decreased or absent breath sounds - Tracheal shift away from affected side - Hyperresonance on the affected side |
|
|
What is the treatment of a tension pneumothorax? |
- Rapid thoracostomy incision or immediate decompression by needle thoracostomy in the second intercostal space midclavicular line - Followed by tube thoracostomy placed in the anterior/midaxillary line in the fourth intercostal space (level of nipple in men) |
|
|
What is the medical term for a "sucking chest wound"? |
Open pneumothorax |
|
|
What is a tube thoracostomy? |
"Chest tube" |
|
|
How is an open pneumothorax diagnosed and treated? |
- Diagnosis: usually obvious with air movement through chest wall defect and pneumothorax on CXR - Treatment in ER: tube thoracostomy (chest tube), occlusive dressing over chest wall defect |
|
|
What does a pneumothorax look like on chest x-ray? |
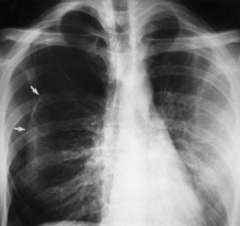
Loss of lung markings
(Figure shows a right-sided pneumothorax; arrows point out edge of lung-air interface) |
|
|
What is flail chest? |
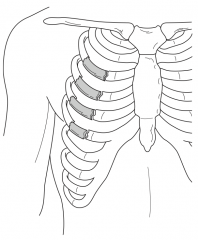
Two separate fractures in three or more consecutive ribs |
|
|
How is flail chest diagnosed? |
Flail segment of chest wall that moves paradoxically (sucks in with inspiration and pushes out with expiration opposite the rest of the chest wall) |
|
|
What is the major cause of respiratory compromise with flail chest? |
Underlying pulmonary contusion |
|
|
What is the treatment of flail chest? |
Intubation with positive pressure ventilation and PEEP PRN (let ribs heal on their own) |
|
|
What is cardiac tamponade? |
Bleeding into pericardial sac, resulting in constriction of heart, decreasing inflow and resulting in decreased cardiac output (pericardium does not stretch) |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of cardiac tamponade? |
Tachycardia / shock with Beck's triad, pulsus paradoxus, Kussmaul's sign |
|
|
What is Beck's triad? Sign of? |
1. Hypotension 2. Muffled heart sounds 3. JVD
--> Cardiac Tamponade |
|
|
What is Kussmaul's sign? Sign of? |
JVD with inspiration
--> Cardiac Tamponade |
|
|
How is cardiac tamponade diagnosed? |
Ultrasound (echocardiogram) |
|
|
What is the treatment of cardiac tamponade? |
Pericardial window - if blood returns then median sternotomy to rule out and treat cardiac injury |
|
|
How is a massive hemothorax diagnosed? |
- Unilaterally decreased or absent breath sounds - Dullness to percussion - CXR, CT scan, chest tube output |
|
|
What is the treatment of massive hemothorax? |
- Volume replacement - Tube thoracostomy (chest tube) - Removal of blood (which will allow apposition of parietal and visceral pleura, sealing the defect and slowing the bleeding) |
|
|
What are indications for emergent thoracotomy for hemothorax? |
Massive hemothorax = 1. >1500 cc of blood on initial placement of chest tube 2. Persistent >200 cc of bleeding via chest tube per hour x4 hours |
|
|
What are the goals in assessing circulation? |
Securing adequate tissue perfusion; treatment of external bleeding |
|
|
What is the initial test for adequate circulation? |
Palpation of pulses: - If a radial pulse is palpable, then systolic pressure is at least 80 mm Hg - If a femoral or carotid pulse is palpable, then systolic pressure is at least 60 mm Hg |
|
|
What comprises adequate assessment of circulation? |
- HR, BP - Peripheral perfusion - Urinary output - Mental status - Capillary refill (normal <2 seconds) - Exam of skin: cold, clammy = hypovolemia |
|
|
Who can be hypovolemic with normal BP? |
Young pts: autonomic tone can maintain BP until CV collapse is imminent |
|
|
Which patients may not mount a tachycardic response to hypovolemic shock? |
- Those with concomitant spinal cord injuries - Those on beta-blockers - Well-conditioned athletes |
|
|
How are sites of external bleeding treated? |
By direct pressure; +/- tourniquets |
|
|
What is the best and preferred IV access in trauma patients? |
Two large-bore IVs (14-16 gauge), IV catheters in upper extremities (peripheral IV access) |
|
|
What are the alternate sites of IV access (upper extremities) in trauma patients? |
Percutaneous and cutdown catheters in the lower leg saphenous; central access into femoral, jugular, subclavian veins |
|
|
For a femoral vein catheter, how can the anatomy of the right groin be remembered? |
Lateral to medial "NAVEL": - Nerve - Artery - Vein - Empty space - Lymphatics
Thus the vein is medial to the femoral artery pulse (or think: venous close to penis) |
|
|
What is the trauma resuscitation fluid of choice? |
Lactated Ringer's (LR) solution (isotonic, and the lactate helps buffer the hypovolemia-induced metabolic acidosis) |
|
|
What types of decompression do trauma patients receive? |
Gastric decompression with an NG tube and Foley catheter bladder decompression after normal rectal exam |
|
|
What are the contraindications to placement of a Foley? |
Signs of urethral injury: - Severe pelvic fracture in men - Blood at the urethral meatus (penile opening) - "High-riding" "ballotable" prostate (loss of urethral tethering) - Scrotal/perineal injury/ecchymosis |
|
|
What test should be obtained prior to placing a Foley catheter if urethral injury is suspected? |
Retrograde UrethroGram (RUG): - Dye in penis retrograde to bladder and x-ray looking for extravasation of dye |
|
|
How is gastric decompression achieved with a maxillofacial fracture? |
NOT with an NG tube because the tube may perforate through the cribriform plate into the brain; place an oral-gastric tube (OGT), not an NG tube |
|
|
What are the goals in assessing disability? |
Determination of neurologic injury (think: neurologic disability) |
|
|
What comprises adequate assessment of disability? |
1. Mental status: Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) 2. Pupils: a blown pupil sugests ipsilateral brain mass (blood) as herniation of the brain compresses CN III 3. Motor/sensory: screening exam for lateralizing extremity movement, sensory deficits |
|
|
What are the categories for the GCS scoring system? |
- Eye opening (4) - "four eyes" - Motor response (6) - "6-cylinder motor" - Verbal response (5) - "Jackson 5 = verbal" |
|
|
What is the GCS scoring system that is out of 4 points? |
Eye Opening: 4 - opens spontaneously 3 - opens to voice (command) 2 - opens to painful stimulus 1 - does not open eyes |
|
|
What is the GCS scoring system that is out of 6 points? |
Motor Response: 6 - obeys commands 5 - localizes painful stimulus 4 - withdraws from pain 3 - decorticate posture 2 - decerebrate posture 1 - no movement |
|
|
What is the GCS scoring system that is out of 5 points? |
Verbal Response: 5 - appropriate and oriented 4 - confused 3 - inappropriate words 2 - incomprehensible sounds 1 - no sounds |
|
|
What is a normal human GCS? |
GCS 15 |
|
|
What is the GCS score for a dead man? |
GCS 3 |
|
|
What is the GCS score for a patient in a "coma"? |
GCS ≤ 8 |
|
|
How does scoring differ if the pt is intubated? |
Verbal evaluation is omitted and replaced with a "T"; thus, the highest score for an intubated pt is 11 T |
|
|
What are the goals in obtaining adequate exposure? |
Complete disrobing to allow a thorough visual inspection and digital palpation of the pt during the secondary survey |
|
|
What is the "environment" of the E in ABCDEs? |
Keep a warm environment (ie, keep the pt warm, a hypothermic pt can become coagulopathic) |
|
|
What principle is followed in completing the secondary survey? |
Complete physical exam, including all orifices: ears, nose, mouth, vagina, rectum |
|
|
Why look in the ears during the secondary survey? |
Hemotympanum is a sign of basilar skull fracture; otorrhea is a sign of basilar skull fracture |
|
|
Examination of what part of the trauma pt's body is often forgotten? |
Patient's back (logroll the pt and examine!) |
|
|
What are typical signs of basilar skull fracture? |
- Racoon eyes - Battle's sign - Clear otorrhea or rhinorrhea - Hemotympanum |
|
|
What diagnosis in the anterior chamber must not be missed on the eye exam? |
Traumatic hyphema = blood in the anterior chamber of the eye |
|
|
What potentially destructive lesion must not be missed on the nasal exam? |
Nasal septum hematoma: must be evacuated, if not, it can result in pressure necrosis of the septum! |
|
|
What is the best indication of a mandibular fracture? |
Dental malocclusion: Tell the pt to "bite down" and ask, "does that feel normal to you?" |
|
|
What signs of thoracic trauma are often found on neck exam? |
- Crepitus or subcutaneous emphysema from tracheobronchial disruption/PTX - Tracheal deviation from tension pneumothorax - JVD from cardiac tamponade - Carotid bruit heard with seatbelt injury resulting in carotid artery injury |
|
|
What is the best physical exam for broken ribs or sternum? |
Lateral and anterior-posterior compression of the thorax to elicit pain/instability |
|
|
What physical signs are diagnostic for thoracic great vessel injury? |
None: diagnosis of great vessel injury requires a high index of suspicion based on the mechanism of injury, associated injuries, and CXR/radiographic findings (eg, widened mediastinum) |
|
|
What is the best way to diagnose or rule out aortic injury? |
CT angiogram |
|
|
What must be considered in every penetrating injury of the thorax at or below the level of the nipple? |
Concomitant injury to abdomen: remember, the diaphragm extends to the level of the nipples in the mall on full expiration |
|
|
What is the significance of subcutaneous air? |
Indicates PTX until proven otherwise |
|
|
What is the physical exam technique for examining the thoracic and lumbar spine? |
Logrolling the pt to allow complete visualization of the back and palpation of the spine to elicit pain over fractures, step off (spine deformity) |
|
|
What conditions must exist to pronounce an abdominal physical exam negative? |
Alert pt without any evidence of head/spinal cord injury or drug/EtOH intoxication (even then, the abdominal exam is not 100% accurate) |
|
|
What physical signs may indicate intra-abdominal injury? |
- Tenderness - Guarding - Peritoneal signs - Progressive distention (always use a gastric tube for decompression of air) - Seatbelt sign |
|
|
What is the seatbelt sign? |
Ecchymosis on lower abdomen from wearing a seatbelt (~10% of pts with this sign have a small bowel perforation) |
|
|
What must be documented from the rectal exam on secondary survey? |
- Sphincter tone (as an indication of spinal cord function) - Presence of blood (as an indication of colon or rectal injury) - Prostate position (as an indication of urethral injury) |
|
|
What is the best physical exam technique to test for pelvic fractures? |
Lateral compression of the iliac crests and greater trochanters and anterior-posterior compression of the symphisis pubis to elicit pain/instability |
|
|
What is the halo sign? |
Cerebrospinal fluid from nose/ear will form a clear "halo" around the blood on a cloth |
|
|
What must be documented from the extremity exam on the secondary survey? |
- Any fractures or joint injuries - Any open wounds - Motor and sensory exam, particularly distal to any fractures - Distal pulses - Peripheral perfusion |
|
|
What complication after prolonged ischemia to the lower extremity must be treated immediately? |
Compartment syndrome |
|
|
What is the treatment for compartment syndrome? |
Fasciotomy (four compartments below the knee) |
|
|
What injuries must be suspected in a trauma patient with progressive decline in mental status? |
- Epidural hematoma - Subdural hematoma - Brain swelling with rising intracranial pressure - But hypoxia / hypotension must be ruled out! |
|
|
What are the classic blunt trauma ER x-rays? |
1. AP (anterior-to-posterior) chest film 2. AP pelvis film |
|
|
What are the common trauma labs? |
- CBC - Chemistries - Amylase - LFTs - Lactic acid - Coagulation studies - Type and crossmatch - Urinalysis |
|
|
Will the hematocrit be low after an acute massive hemorrhage? |
No (no time to equilibrate) |
|
|
How can a C-spine be evaluated? |
1. Clinically by physical exam 2. Radiographically |
|
|
What patients can have their C-spines cleared by a physical exam? |
No neck pain on palpation with full range of motion (FROM) with no neurologic injury (GCS 15), no EtOH/drugs, no distracting injury, no pain meds |
|
|
How do you rule out C-spine bony fracture? |
With a CT scan of C-spine |
|
|
What do you do if no bony C-spine fracture is apparent on CT scan and you cannot obtain an MRI in a COMATOSE patient? |
This is controversial; the easiest answer is to leave the pt in a cervical collar |
|
|
Which x-rays are used for evaluation of cervical spine LIGAMENTOUS injury? |
MRI, lateral flexion and extension C-spine films |
|
|
What findings on chest film are suggestive of thoracic aortic injury? |
- Widened mediastinum (most common finding) - Apical pleural capping - Loss of aortic contour / KNOB / AP window - Depression of L main stem bronchus - Nasogastric tube / tracheal deviation - Pleural fluid - Elevation of R main stem bronchus - Clinical suspicion - High-speed mechanism |
|
|
What study is used to rule out thoracic aortic injury? |
- Spiral CT of mediastinum looking for mediastinal hematoma with CTA - Thoracic arch aortogram (gold standard) |
|
|
What is the most common site of thoracic aortic traumatic tear? |
Just distal to the take-off of the L subclavian artery |
|
|
What studies are available to evaluate for intra-abdominal injury? |
- FAST exam - CT scan - DPL |
|
|
What is a FAST exam? |
Ultrasound: Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) |
|
|
What does the FAST exam look for? |
Blood in the peritoneal cavity looking at Morison's pouch, bladder, spleen, and pericardial sac |
|
|
What does DPL stand for? |
Diagnostic Peritoneal Lavage |
|
|
What diagnostic test is the test of choice for evaluation of the unstable patient with blunt abdominal trauma? |
FAST (ultrasound) |
|
|
What is the indication for abdominal CT scan in blunt trauma? |
Normal vital signs with abdominal pain / tenderness / mechanism |
|
|
What is the indication for DPL or FAST in blunt trauma? |
Unstable vital signs (hypotension) |
|
|
How is a DPL (diagnostic peritoneal lavage) performed? |
- Place a catheter below the umbilicus (in pts without a pelvic fracture) into the peritoneal cavity - Aspirate for fluid and if <10 cc are aspirated, infuse 1L of saline or LR - Drain the fluid (by gravity) and analyze |
|
|
What is a "grossly positive" DPL? |
≥10 cc of blood aspirated |
|
|
Where should the DPL catheter be placed in a pt with a pelvic fracture? |
Above the umbilicus
Common error: if you go below the umbilicus, you may get into a pelvic hematoma tracking between the fascia layers and thus obtain a false-positive DPL |
|
|
What constitutes a positive peritoneal tap? |
Prior to starting a peritoneal lavage, the DPL catheter should be aspirated; if >10 mL of blood or any enteric contents are aspirated, then this constitutes a positive tap that requires laparotomy |
|
|
What are the indicators of a positive peritoneal lavage in blunt trauma? |
Classic: - Inability to read newsprint through lavaged fluid - RBC ≥100,000/mm3 - WBC ≥500/mm3 - Lavage fluid (LR/NS) drained from chest tube, Foley, NG tube
Less common: - Bile present - Bacteria present - Feces present - Vegetable matter present - Elevated amylase level |
|
|
What must be in place before a DPL is performed? |
NG tube and Foley catheter (to remove the stomach and bladder from the line of fire) |
|
|
What injuries does CT scan miss? |
Small bowel injuries and diaphragm injuries |
|
|
What injuries does DPL miss? |
Retroperitoneal injuries |
|
|
What study is used to evaluate the urethra in cases of possible disruption d/t blunt trauma? |
Retrograde Urethrogram (RUG) |
|
|
What are the most emergent orthopaedic injuries? |
1. Hip dislocation - must be reduced immediately 2. Exsanguinating pelvic fracture (binder or external fixator) |
|
|
What findings would require a celiotomy in a blunt trauma victim? |
- Peritoneal signs - Free air on CXR/CT scan - Unstable pt with positive FAST exam or positive DPL results |
|
|
What is the treatment of a gunshot wound to the belly? |
Exploratory laparotomy |
|
|
What is the evaluation of a stab wound to the belly? |
- If there are peritoneal signs, heavy bleeding, shock, perform exploratory laparotomy - Otherwise, many surgeons either observe the asymptomatic stab wound pt closely, use local wound exploration to rule out fascial penetration, or use DPL |
|
|
What depth of neck injury must be further evaluted? |
Penetrating injuries through the platysma |
|
|
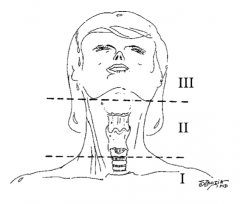
What is trauma zone I of the neck? |
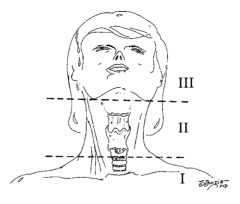
Below the cricoid cartilage |
|
|
What is trauma zone II of the neck? |
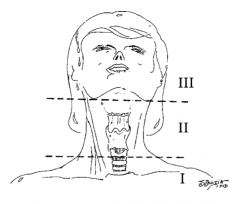
Angle of the mandible to the cricoid cartilage |
|
|
What is trauma zone III of the neck? |
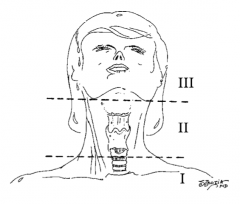
Angle of the mandible and up |
|
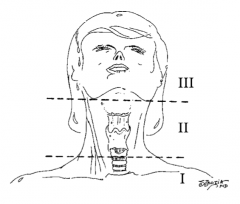
How do most surgeons treat penetrating neck injuries (those that penetrate the platysma) to zone I? |
Selective exploration |
|
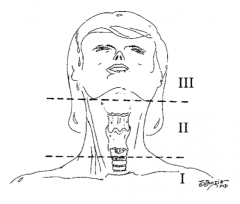
How do most surgeons treat penetrating neck injuries (those that penetrate the platysma) to zone II? |
Surgical exploration vs selective exploration |
|
How do most surgeons treat penetrating neck injuries (those that penetrate the platysma) to zone III? |
Selective exploration |
|
|
What is selective exploration? |
Based on diagnostic studies that include A-gram or CT A-gram, bronchoscopy, esophagoscopy |
|
|
What are the indications for surgical exploration in all penetrating neck wounds (zones I, II, III)? |
"Hard signs" of significant neck damage: - Shock - Exsanguinating hemorrhage - Expanding hematoma - Pulsatile hematoma - Neurologic injury - SubQ emphysema |
|
|
How can you remember the order of the neck trauma zones and Le Forte fractures? |
In the direction of carotid blood flow |
|
|
What is the "3-for-1" rule? |
Trauma patients in hypovolemic shock acutely require 3L of crystalloid (LR) for every 1L of blood loss |
|
|
What is the minimal urine output for an adult trauma patient? |
50 mL/hr |
|
|
How much blood can be lost into the thigh with a closed femur fracture? |
Up to 1.5L of blood |
|
|
Can an adult lose enough blood in the "closed" skull from a brain injury to cause hypovolemic shock? |
Absolutely not! But infants can lose enough blood from a brain injury to cause shock |
|
|
Can a patient be hypotensive after an isolated head injury? |
Yes, but rule out hemorrhagic shock |
|
|
What is the brief ATLS surgery? |
AMPLE history: - Allergies - Medications - PMH - Last meal (when) - Events (of injury, etc) |
|
|
In what population is a surgical cricothyroidotomy not recommended? |
Any pt younger than 12 years; instead perform needle cricothyroidotomy |
|
|
What are the signs of a laryngeal fracture? |
- Subcutaneous emphysema in neck - Altered voice - Palpable laryngeal fracture |
|
|
What is the treatment of rectal penetrating injury? |
- Diverting proximal colostomy - Closure of perforation (if easy, and definitely if peritoneal) - Pre-sacral drainage |
|
|
What is the treatment of EXTRAperitoneal minor bladder rupture? |
"Bladder catheter" (Foley) drainage and observation; intraperitoneal or large bladder rupture requires operative closure |
|
|
What intra-abdominal injury is associated with seatbelt use? |
Small bowel injuries (L2 fracture, pancreatic injury) |
|
|
What is the treatment of a pelvic fracture? |
- +/- pelvic binder until external fixator is placed - IVF/blood - +/- A-gram to embolize bleeding pelvic vessels |
|
|
Bleeding from pelvic fractures is most commonly caused by arterial or venous bleeding? |
Venous (~85%) |
|
|
If a pt has a laceration through an eyebrow, should you shave the eyebrow prior to suturing it closed? |
No - 20% of the time, the eyebrow will not grow back if shaved |
|
|
What is the treatment of extensive irreparable biliary, duodenal, and pancreatic head injury? |
Trauma Whipple |
|
|
What is the most common intra-abdominal organ injured with penetrating trauma? |
Small bowel |
|
|
How high up do the diaphragms go? |
To the nipples (intercostal space #4); thus, intra-abdominal injury with penetrating injury below the nipples must be ruled out |
|
|
"If you have only one vial of blood from a trauma victim to send to the lab, what test should be ordered?" |
Type and cross (for blood transfusion) |
|
|
What is the treatment of penetrating injury to the colon? |
- If the pt is in shock, resection and colostomy - If the pt is stable, the trend is primary anastomosis / repair |
|
|
What is the treatment of small bowel injury? |
Primary closure or resection and primary anastomosis |
|
|
What is the treatment of minor pancreatic injury? |
Drainage (eg, JP drains) |
|
|
What is the most commonly injured abdominal organ with blunt trauma? |
Liver (in recent studies) |
|
|
What is the treatment for significant duodenal injury? |
Pyloric exclusion: 1. Close duodenal injury 2. Staple off pylorus 3. Gastrojejunostomy |
|
|
What is the treatment for massive tail of pancreas injury? |
Distal pancreatectomy (usually perform splenectomy also) |
|
|
What is "damage control" surgery? |
- Stop major hemorrhage and GI soilage - Pack and get out of OR asap to bring pt to the ICU to warm, correct coags, and resuscitate - Return pt to OR when stable, warm, and not acidotic |
|
|
What is the lethal triad? |
ACHe: 1. Acidosis 2. Coagulopathy 3. Hypothermia |
|
|
What comprises the workup/treatment of a stable parasternal chest gunshot / stab wound? |
1. CXR 2. FAST, chest tube +/- OR for sub-xiphoid window; if blood returns, then sternotomy to assess for cardiac injury |
|
|
What is the diagnosis with NGT in chest on CXR? |
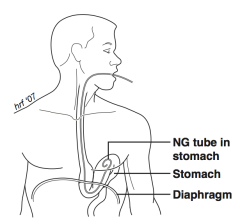
Ruptured diaphragm with stomach in pleural cavity (go to ex lap) |
|
|
What films are typically obtained to evaluate extremity fractures? |
Complete views of the involved extremity, including the joints above and below the fracture |
|
|
What should be done for a pt in the ER with severe blunt trauma? |
- Airway - Physical exam - IV x3 - Labs - Type and cross - OGT/NGT - Foley - Chest tube PRN |
|
|
What imaging should be done for pt with severe blunt trauma in ER? |
- CXR - Pelvic x-ray - Femur x-ray (if femur fracture suspected) |
|
|
What additional workup should be done for pt with severe blunt trauma with normal vital signs? |
- Chest CT, C-spine/head CT, Abd/pelvic CT --> - Extremity films PRN --> - ICU PRN --> - Flex/ext lat C-spine films or MRI C-spine or physical exam C-spine |
|
|
What additional workup should be done for pt with severe blunt trauma with hypotension? |
Check for pelvic fracture and get FAST exam |
|
|
What should be done for a pt with severe blunt trauma, hypotension, pelvic fracture, and +FAST exam? |
- OR ex lap --> - External pelvic fixator --> - Pelvic A-gram PRN --> - Chest CT, C-spine/head CT --> - Ext films PRN --> - ICU |
|
|
What should be done for a pt with severe blunt trauma, hypotension, pelvic fracture, and -FAST exam? |
- DPL exam --> if (+) treat like +FAST
- Neg DPL exam --> - Ext fixator PRN --> - Pelvic A-gram PRN --> - Chest CT, Abd/pelvic CT --> - C-spine / head CT --> - Ext films PRN --> - ICU |
|
|
What should be done for a pt with severe blunt trauma, hypotension, NO pelvic fracture, and +FAST exam? |
- OR ex lap --> - Chest CT --> - C-spine / head CT --> - Ext films PRN --> - ICU |
|
|
What should be done for a pt with severe blunt trauma, hypotension, NO pelvic fracture, and -FAST exam? |
- Chest CT, abd/pelvic CT, C-spine/head CT --> - Ext films PRN --> - ICU |
|
|
What finding on abd/pelvic CT scan requires ex lap in the blunt trauma pt with normal vital signs? |
Free air, also strongly consider in the pt with no solid organ injury but lots of free fluid --> both to rule out hollow viscus injury |
|
|
Can you rely on a negative FAST in an unstable pt with a pelvic fracture? |
No --> perform DPL (above umbilicus) |
|
|
What lab tests are used to look for intra-abdominal injury in children? |
Liver function tests (LFTs) = increased AST and/or ALT |
|
|
What is the only real indication for MAST trousers? |
- Pre-hospitalization - Pelvic fracture |
|
|
What is the treatment for human and dog bites? |
- Leave wound open - Irrigation - Antibiotics |
|
|
What percentage of pelvic fracture bleeding is exclusively venous? |
85% |
|
|
What is sympathetic ophthalmia? |
Blindness in one eye that results in subsequent blindness in the contralateral eye (auto-immune) |
|
|
What can present after blunt trauma with neurological deficits and a normal brain CT scan? |
- Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI) - Carotid artery injury |

