![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sudeck's Atrophy
|
Context: Post trauma/#
Reflex Sympathetic Atrophy (SNS dysfunction) A type of chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS). RSD/Sudeck's (type 1) is characterized by severe, burning pain at the site of the injury. Muscle spasm, joint stiffness, restricted mobility, rapid hair and nail growth, and vasospasm (a constriction of the blood vessels) that affects color and temperature of the skin can also occur. |
|
|
Tinel's Sign
|
Context: Neuropraxia, carpal tunnel
Tinel sign: a sensation of tingling felt at the lesion site or more distally along the course of a nerve when the latter is percussed; indicates a partial lesion or early regeneration in the nerve. |
|
|
Sural Nerve
|
Context: Nerve grafting
Short saphenous nerve |
|
|
Fromet's sign
|
Context: Ulnar nerve palsy
Tests adductor pollicis; place paper between index and thumb. Unable to grasp = (+) |
|
|
Cobb's Angle
|
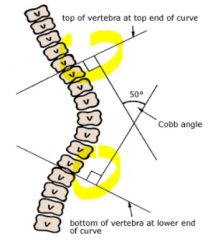
Context: Scoliosis
Tangent line above and below. Acute angle at intersection = Cobb's angle. |
|
|
Risser Sign
|
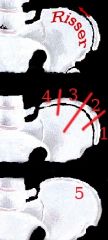
Context: Scoliosis
Measures iliac apophysis fusion in 25% increments (1-4). Helps to determine potential for progression in scoliosis. Bone age determination. |
|
|
Milwaukee Brace
|
Context: Scoliosis
|
|
|
Harrington Rod
|
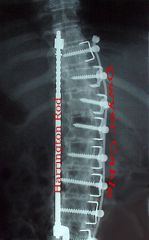
Context: Scoliosis
Internal fixation device Indications: 1) Rapid progression 2) Cobb angle >40deg 3) Respiratory compromise 4) Failure of brace correction |
|
|
Trethowan's Sign
|
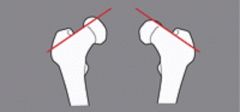
Context: SUFE
Line drawn along superior border of femoral neck remains superior to femoral head = (+) Threthowan's sign. (Normal = pass through head) |
|
|
Ortolani's test
Bartlow's test |
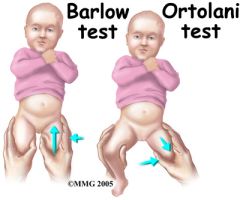
Context: CDH (Congenital Dislocation of Hip)
Ortolani's (OUT) Test: - Hips flexed to 90deg - Abduct hips - "Click" into acetabulum on full abduction - Standard infant exam until 8-12/52 - Tests for DDH, CDH Bartlow's (BACK) test: - On abduction / adduction - Backwards force agaisnt hip - Dislocation |
|
|
Shenton's Line
Perkin's Line Hilgrenreiner's line |
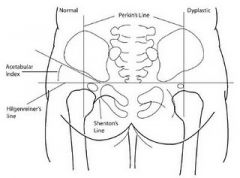
Context: CDH
X-ray features for CDH: - Loss of Shenton's Line - Lateral movement to Perkin's line - Movement superior to Hilgrenreiner's line |
|
|
Von Rosen's Splint
Pavlik Harness Cambridge Splint |
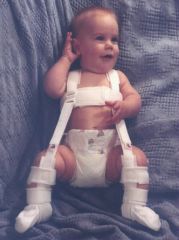
Context: CDH Mx
0-6 wk: Abduction pillow 6wk: Abduction splinting: Von rosen's splint, Pavlik harness, Cambrdige splint 6mo-6y: Spica cast >6y: Surgical correction |
|
|
Adam's Forward Bending Test
|
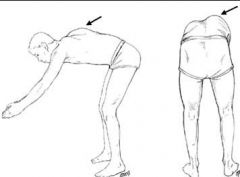
Tests for: Scoliosis
- 90deg at waste - arms extended - look for asymmetry thoracic prominence (shoulder blade, lumbar prominence) |
|
|
Special Test:
Anterior Drawer (Ankle) |
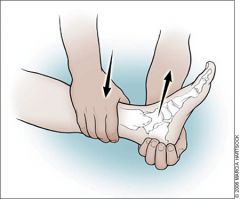
Tests for: instability of the ankle
1) Leg stabilized 2) Hand cups heel 3) Anterior force applied to ankle 4) Compare with other foot 5) Laxity due to sprain of anterior talofibular ligament |
|
|
Special Test:
Anterior Drawer Test (Knee) |
Tests for: Anterior cruciate liagment tear
1) Knee flexed 90deg 2) Anterior force on proximal tibia 3) Laxity = Ant. cruciate tear |
|
|
Special Test
Anterior Drawer Test (Knee) |
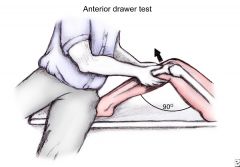
Tests for: Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
1) Knee 90deg 2) Anterior force on proximal tibia |
|
|
Special Test:
Apparent (functional) leg length |
1) Patient supine
2) Both legs parallel 3) Measure umbilicus to tip of medial malleolus 4) Diff. in length = deformity causing functional shortening |
|
|
Special Test:
Shoulder Apprehension Test |
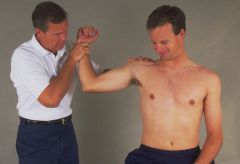
Tests for: Anterior glenohumeral instability
1) Patient erect 2) Shoulder abducted 90deg 3) Apply anterior pressure to humerus + external rotation 4) Feeling of impending subluxation or dislocation indicates ant glenohumeral instability |
|
|
Special Test:
Carpal tunnel compression test / Durkin's test |

Tests for: Carpal tunnel syndrome
1) Pressure applied over ventral wrist 2) Pain, parasthesia, numbness within a minute = carpal tunnel syndrome |
|
|
Special Test:
Chest expansion test |
Tests for: Ankylosing spondylitis
1) Chest expansion measured from maximal exhalation to max inspiration 2) Expansion < 1" = arthritis affecting spine and rib cage (ankylosing spondylitis) |
|
|
Special Test:
Clonus |
Tests for: Pressure on spinal cord
1) Foot dorsiflexed 2) Repetitive, uncontrolled, up and down motion of ankle |
|
|
Special Test:
Arm Drop Test |
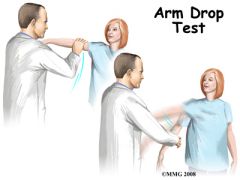
Tests for: Rotator cuff tear or supraspinatus dysfunction
1) Shoulder abducted passively 2) Allow arm to drop 3) Uncontrolled drop = (+) |
|
|
Special Test:
Ely's Test Femoral Nerve Stretch Test |

Tests for: Nerve lesion @ L3 L4 (compression, inflammatory, traumatic)
1) Patient supine 2) Flex knee; heel to buttocks 3) If pelvis raises from table with pain radiating down FRONT of thigh = (+) |
|
|
Special Test:
Galleazzi Test |
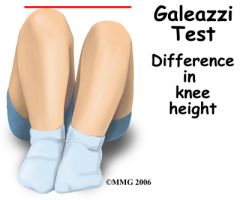
Tests for: Pediatric dislocation of the hip
1) Patient supine 2) Knee flexed 90deg 3) Look for length differences in tibia and femur 4) Short side = dislocation of hip |
|
|
Special Test:
Hawkin's Test |
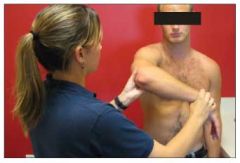
Tests for: Rotator cuff tendonitis; Subacromial impingement
1) Arm elevated to 90deg 2) Elbow flexeed 90deg 3) Hand pointing down 4) Internal rotate shoulder 5) Pain = impingement/tendonitis |
|
|
Special Test:
Lachman test |
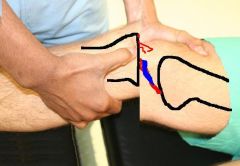
Tests for: Anterior cruciate ligament tear
1) Flex knee 20deg 2) Proximal tibia pulled forward 3) Laxity = (+) |
|
|
Special Tests:
Patellar Apprehension Test |
Tests for: Patellar dislocation
1) Knee slightly flexed 2) Push patella laterally 3) Pain and apprehension = subluxation or dislocation |
|
|
Special Test:
Patrick's Test |
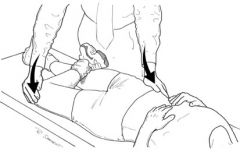
Tests for: Hip or sacro-iliac joint disease
1) Supine 2) Make a figure 4 (lat malleolus on knee) 3) Pressure on flexed knee 4) Anterior groin pain = hip disorder 5) Sacro-iliac pain = sacro-iliac joint |
|
|
Special Test:
Phalen's Sign |
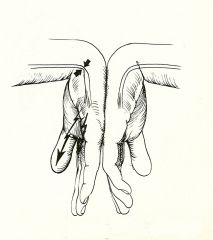
Tests for: Median nerve compression
1) Flexion of wrist produces parasthesia and pain (carpal tunnel syndrome) 2) Hyperextension of wrist (reverse Phalen) |
|
|
Special Test:
Posterior Drawer Test |
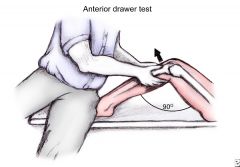
Tests for: Posterior cruciate ligament tear
1) Supine 2) Knee @ 90deg 3) Posterior force on distal tibia 4) Laxity = post. cruciate tear |
|
|
Special Test:
Posterior Sag Sign |
Tests for: Posterior cruciate ligament tear
1) Supine 2) Hip flexed 45 3) Knee 90deg relaxed 4) Tibial sag backward = (+) |
|
|
Special Test:
Quadriceps Contraction Test |
Tests for: Posterolateral instability
1) supine 2) Knee flexed 90, externally rotated 3) lateral condyle of tibia is subluxed posteriorly relative to femoral condyle = posterolateral instability 4) Quad contraction will reduce |
|
|
Special Test:
Quadriceps contraction test |
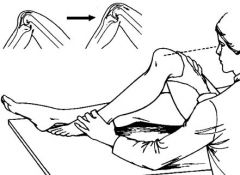
Tests for: Posterolateral instability
1) supine 2) Knee flexed 90, externally rotated 3) lateral condyle of tibia is subluxed posteriorly relative to femoral condyle = posterolateral instability 4) Quad contraction will reduce |
|
|
Special Test:
Quadriceps inhibition test |
Tests for: Chondromalacia of the patella
1) Supine 2) pressure on superior aspect of patella 3) Active straight leg (contract quads) 4) Pain and grinding = (+) |
|
|
Special Test:
True (real) leg length |
Tests for: Bony shortening of limb, without deformity compensation
1) Measure from ASIS to tip of medial malleolus |
|
|
Special Test:
Resisted middle finger extension test |
Tests for: Epicondylitis of elbow
1) Arm forward 2) Elbow straight 3) Wrist neutral 4) Pt asked to resist ditial force applied over dorsum of middle finger 5) Pain = lateral epicondylitis |
|
|
Special Test:
Schober Test |
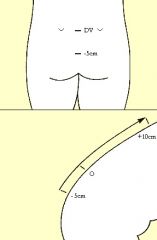
Tests for: Spinal range of motion
1) Erect 2) Mark 5cm above and 10 cm below PSIS 3) Pt bend maximally forward 4) <20cm = decreased ROM |
|
|
Special Test: Straight Leg Raise
|
Tests for: Sciatic nerve lesion
1) Supine 2) Hip flexed 3) Leg straight 3) <70 deg pain = disc herniation (L5-S1) |
|
|
Special Test
Thessaly test |

Tests for: Meniscal tear
1) Standing on 1 foot 2) 20deg knee flexion 3) Rotate internally and externally 4) Medial or lateral joint-line discomfort = (+) |
|
|
Special Test
Thomas Test |

Tests for: Fixed flexion deformity
1) Supine 2) Back flat on table (lumbar lordosis elimiated) 3) Hip raised 4) Flex hip 5) Opposite hip raises = fixed flexion deformity |
|
|
Special Test
Thompson Test |
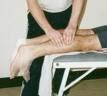
Tests for: Achilles tendon rupture
1) Prone 2) Ankle over side of bed 3) Squeeze middle of calf 4) Passive plantar flexion = normal (absent = rupture) |

