![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Hepatobiliary
DDx for Circular Lesions in the Liver at USS |
- Primary tumour (HCC)
- Secondary tumour (mets) - Nodular regenerative hyperplasia - Cirrhosis - Lymphoma - Sarcoidosis - Hydatid cysts - Abscess - Fatty infiltration (NASH, Gaucher's) |
Conginetal:
- Riedel's Lobe - Polycystic liver disease Neoplastic: - Primary tumour (HCC) - Secondary deposits (mets) Cirrhosis: - Portal - Biliary - Hemochromatosis Inflammatory: - Hepatitis - Portal Pyaemia - Leptospirosis (Weil's disease) - Actinomycosis Parasytic: - Amoebic - Hydatid Metabolic: - Amyloid - Gaucher's disease |
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Describe bilirubin metabolism |
1) RBC degraded by reticuloendothelial cells (Mo) in spleen, liver, BM
2) Heme and globin separated 3) Heme ring >> biliverdin (via heme oxygenase) 4) Biliverdin >> UC bilirubin (biliverdin reductase) 5) UCB (insoluble) bound to albumin 6) UCB transported to liver.hepatocytes 7) UCB >> CB (via glucuronyl transferase) 8) CB excreted into biliary canaliculi to duodenum 9) CB > urobilinogen & stercobilinogen (via colonic bacteria) 10) Urobilinogen, stercobilinogen >> urobilin, stercobilin >> excreted in feces 11) Urobilinogen reabsorbed from intestine to portal blood 12) Urobilinogen >> urobilin (via kidney) |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
What imaging modality to confirm extrahepatic biliary obstruction? |
- USS (non-invasive, cheap, no radiation)
- ERCP - PTC |
- USS
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde CholangioPancreatography) - PTC (Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography) |
|
|
Hepatobiliary
List 3 Important causes of extrahepatic biliary obstruction |
- Choledocholithaisis
- Tumour: Pancreatic head, ampulla, bile duct (cholangiocarcinoma), duodenum - Strictures (post-surgical, post-inflammatory) - Pancreatitis / pancreatic pseudocyst - Lymphadenopathy - Ampulla of Vater dysfunction - Parasites |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Pre-hepatic jaundice causes |
- Hemolytic disorder
- spherocytosis - Incompatible blood transfusion |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Intra-hepatic jaundice - Causes |
- Hepatitis
- Cirrhosis - Cholestasis from drugs (chlorpromazine) - Liver poisons (paracetamol OD), halothane - Liver tumours |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Post-hepatic jaundice - causes |
Intraluminal:
- Gallstones Within the wall: - Atresia of CBD (congenital) - Traumatic stricture - Sclerosing cholangitis (1o, 2o) - Tumour of bile duct External Compression: - Pancreatitis, pancreatic pseudocyst - Head of pancreas tumour - Tumour of ampulla of Vater |
|
|

Indications?
Where to insert? Why? When to remove? |
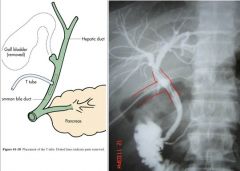
When?
- Following choledochotomy (incision into the CBD) Where? - CBD (distal to common cystic duct and common hepatic ducts) Why? - Prevent leakage from choledochotomy - To ensure no residual stones in CBD - Post-CBD trauma to prevent bile leakage When to remove? - 7-10d post-op - Pt in satisfactory state - Bile drainage clear and non-infected - No residual stones on T-tube cholangiogram |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Give 3 reasons for placing a T-tube in the CBD |
1) Post-choledochotomy
2) To allow for T-tube cholangiogram to ensure no residual stones in CBD or hepatic radicles 3) Post-CBD trauma to prevent bile leakage |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
When to removea T-Tube? Precautions before removing? |
- 7-10d post-op
- T-Tube cholangiogram for residual stones before removing - Patient in satisfactory state - Bile drainage must be clear and non-infected |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Charcot's Triad? |
1) RUQ
2) Jaundice 3) Fever/rigors |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Reynold's pentad |
Charcot 3 + ...
4) Hypotension / shock (due to vomiting & dehydration) 5) Altered metal status |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Charcot's triad / Reynold's pentad ... What is the Dx? |
Cholangitis
|
|
|
|
Cholangitis
Aetiology |
1) Choledocholithasis - most common cause
2) Stricture 3) Extrinsic compression - tumours, pancreatic pseudocyst, pancreatitis 4) Instrumentation of bile ducts (PTC, ERCP) 5) Biliary Stent |
|
|
|
Cholangitis
Pathophysiology of Charcot/Reynold's sign |
1) Blockage of CBD
2) Pressurized biliary tree <RUQ pain> 3) Obstructive jaundice <Jaundice> 4) Overflow of gut flora (retrograde via sphincter of Oddi) 5) Septicaemia <Fever> 6) Septic shock <Hypotension, ALOC> |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy - Informed consent. |
Procedure:
- Key hole surgery - 4 small incisions made in the abdomen, filled with CO2 Benefits: - Relieve pain and prevent further complications of gallstones Risks of not having surgery: - Symptoms continue - Complication and sequelae: - Inflammation of pancreas, gall bladder - Jaundice Specfic risks: - Air embolus - Bleeding - Conversion to open surgery - Escape of stones into abdomen - Bile leak |
General risks:
- Atelectasis, adhesions, anaphylaxis - Bleeding - Constipation (ileus), cardiac arrest (MI) - DVT/PE, damage to surrounding structures, death - Incisional hernia - Infection - Ileus |
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Cholecystectomy - specific risks? |
- Mortality 1 in 1000
- Gas embolus - Collection - bile (biloma), blood, pus - Bile leaks - Bile duct striricture - Damage to vasculature - Damage to nearby structures - Adhesions - Missed stones - Post-cholecystectomy syndrome |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
What is post-cholecystectomy syndrome? |
Upper GI symptoms
- Due to bile flow upwards - Oesophagitis - Gastritis Lower GI symptoms: - Diarrhoea - Colicky, lower abdominal pain |
|
|
|
Hepatobiliary
Length of hospital stay for cholecystectomy |
- May require T-tube (7-10d)
- ambulation @ 24h - Discahrged 1-2d - NBM <24h - Recovery 2/52 - Analgesia 4-5d |
|
|
|
What are these signs?
|
Left: Cullen's sign
Right: Grey-Turner's sign |
|
|
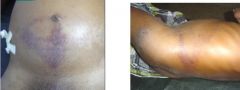
What are these signs?
Pathogenesis? |
Left: Cullen's Sign
Right: Grey-Turner's sign |
Pathogenesis:
1) Haemorrhagic acute pancreatitis >> necrosis 2) Bleeding into parenchyma and reptroperitoneal structures 3) Retroperitoneal hemorrhage @ ant abdo wall through fascial plains <Cullen's sign> (Bluish disculoration of periumbilical area) 4) Retroperitoneal hemorrhage >> ecchymoses of the flank <Grey-Turner> |
|
|
Pancreatitis
Fox's sign. Describe. |
- Ecchymoses of the inguinal ligament
- Due to retroperitoneal bleeding |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
Aetiology |
"GET SMASHED"
- Gall stones - EtOH - Trauma - Steroids - Mumps, mycoplasma - Autoimmne: PAN, SLE - Scorpion bite - Hyperlipidemia / hypercalcemia - ERCP - Drugs (azathioprine) |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
Other causes of Cullen's/Grey-Turner's signs |
Retroperitoneal bleeding:
- Ruptured AAA - Malignancy - Coagulopathy |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
Symptoms |
- Pain: Epigastric
- Pain: Severe, constant - Pain: radiates to back - Acute onset - 15-60min - Nausea and vomiting - Fever - Jaundice |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
Signs |
- Sepsis: tachycardia, hypotension, pyrexia
- Jaundice - Epigastric tenderness - Reduced bowel sounds - Large pseudocyst >> palpable mass - Hypoxaemia, hypovolemic shock |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
Ix - What is the biochemical investigation of choice? |
- *Serum amylase (>1000U/L)
Also: - FBC - Serum lipase - E/LFT - Glucose - Calcium - ABG Radiological: - USS - AXR, CXR |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
What criteria used to assess severity of pancreatitis? |
- Ranson's Criteria
- IMRIE score - APACHE II |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
Ranson's Criteria |
GALAW CHOBBS
On admission: - ++ Glucose - Age > 55y - ++ LDH - ++ AST - ++WBC At 48h: - --Calcium - --HCT - --O2 (<60mmHg) - ++ BUN - Base deficit - Sequestration of fluids > 6L |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
APACHE II |
- Oliguria
- O2 -- - BUN ++ - Obesity - Age ++ - Calcium -- - Peritoneal bleeding signs - Hypotension |
|
|
|
Pancreatitis
Mx |
Medical:
- NBM (TPN) - Oxygen (correct hypoxia) - Fluid resuscitation (IV) - H2-blocker - Analgesia - opioid - Antibiotic prophylaxis - Monitoring - Supportive therapy Surgical: - Drain pseudocyist - ERCP (clear CBD of gallstones) - Laproscopic cholecystectomy (if cased by stones) |
|

