![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
267 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where do you allow secondary intension wound healing?
|
good if dirty
perineum scalp |
|
|
What are the requirements for proceeding with tertiary wound intension healing?
|
< 10^5 bacteria
|
|
|
What are the three phases of healing? How long do they last?
|
Inflammatory 10 min to 4 days; lasts longer if secondary intension/wound closure
proliferative 2-3 days to 3-4 weeks remodeling ~ 9 months |
|
|
What does the inflammation phase of wound healing involve?
|
clot formation (platelets, fibrin)
vasoconstriction (PGF, Catecholamines, thromboxane) vasodilation after hemostasis (prostaglandins, histamine) brings in inflammatory cells to clear debris (platelet derived growth factor, complement C5a, leukotriene B4) |
|
|
What does the proliferation phase of wound healing involve?
|
Provisional matrix (mostly fibrin) becomes permanent matrix (collagen and ground substance, proteoglycans like hyaluronic acid)
Fibroblasts make collagen Macrophages attract endothelial cells Scar is red and raised |
|
|
What does the remodeling phase of wound healing consist of?
|
starts with 'collagen equilibration' - collagen breakdown = collagen building
old collagen replaced by new, better organized, longitudinally aligned, stronger collagen |
|
|
How fast do basal epithelial cells migrate?
|
1-2 mm day
|
|
|
What is epithelialization?
|
basal epithelial cells migrate along wound to create 1 cell layer, cell division and keratin formation creates stratum corneum
|
|
|
How long does epitheliazation take?
|
7-10 days
|
|
|
How does epithelialization occur in full thickness vs. partial thickness wounds?
|
full - damaged/no dermis - from wound edge
partial - dermis intact - epithelialize from dermal appendages (i.e. sweat glands and hair follicles) |
|
|
What is the progressive wound strength? What determines this strength?
|
50% by 6 weeks therefore no heavy lifting for 6 weeks
70% is maximum strength attained by scar determined by rate of collagen synthesis organization, and crosslinks |
|
|
What is the proper care of a closed wound/primary intension wound?
|
epithelialization takes 1-2 days
keep wound dry during this time after 2 days wash with water to clear debris may remove sutures 1-2 weeks - but only modest strength |
|
|
How is debris cleared from a wound?
|
PMN < 24 hrs
Mac 2-3 days Lymphocytes chronic infection |
|
|
What is considered in the proper care of a secondary intension or ulcer wound?
|
1. granulation tissue forms over subQ
2. epithelization marches over granulation tissue, front marching epthelium is inflammation, followed by proliferation, followed by reorganization of scar, faster w/moisture 3. wound contraction by fibroblasts accelerates closure but depends on availability of extra skin 4. bacterial colonization in all open wounds, bacterial infection deletrious to healing 5. role of O2 need 25-30 mmHg for PMN to kill bactera with superoxide radicals, edema reduces oxygenation 6. role of necrosis: dead tissue/protein exudates is good medium for bacteria, impairs healing |
|
|
What is granulation tissue?
|
immature collagen and ground substance, new leaky capillaries, inflammatory cells
|
|
|
What is the progressive wound strength? What determines this strength?
|
50% by 6 weeks therefore no heavy lifting for 6 weeks
70% is maximum strength attained by scar determined by rate of collagen synthesis organization, and crosslinks |
|
|
What is the proper care of a closed wound/primary intension wound?
|
epithelialization takes 1-2 days
keep wound dry during this time after 2 days wash with water to clear debris may remove sutures 1-2 weeks - but only modest strength |
|
|
How is debris cleared from a wound?
|
PMN < 24 hrs
Mac 2-3 days Lymphocytes chronic infection |
|
|
What is considered in the proper care of a secondary intension or ulcer wound?
|
1. granulation tissue forms over subQ
2. epithelization marches over granulation tissue, front marching epthelium is inflammation, followed by proliferation, followed by reorganization of scar, faster w/moisture 3. wound contraction by fibroblasts accelerates closure but depends on availability of extra skin 4. bacterial colonization in all open wounds, bacterial infection deletrious to healing 5. role of O2 need 25-30 mmHg for PMN to kill bactera with superoxide radicals, edema reduces oxygenation 6. role of necrosis: dead tissue/protein exudates is good medium for bacteria, impairs healing |
|
|
What is granulation tissue?
|
immature collagen and ground substance, new leaky capillaries, inflammatory cells
|
|
|
What does the post-op care for wounds involve?
|
clean
debride edema control ischemia control moist environment |
|
|
What and how do systemic factors influence wound healing?
|
nutrition - serum albumin < 3 g/dL bad
aging chemo and steroids - give Vit A to steroid users O2 - decreased with smoking/nicotine patches, radiation, edema, diabetes, atherosclerosis, vasculitis, pressure, venous insufficiency, fibrosis |
|
|
What topical antibiotics should be used when closing wounds? What about systemic antibiotics?
|
bacitracin/neosporin - moistens for epithelization
silvadene - penetrates eschar, good for burns Systemic anitbiotics - little use |
|
|
What is the proper care for a contusion?
|
evacuate hematoma
if early (12 - 24 hours) give ice to prevent pooling if late - keep warm to absorb blood |
|
|
What is the time limit on amputations?
|
replace if < 6hrs
|
|
|
How do you manage a dirty wound?
|
can be closed after debridement
may leave open if 1. heavy bacterial inoculum (think bites) 2. delayed closure 3. crushed/ischemic tissue 4. systemic steroids use follow up <48 hours to check for infection |
|
|
What constitutes a split thickness graft?
|
epidermis + part of dermis
|
|
|
What are the steps in graft healing?
|
serum/plasma inbibition (diffusion of nutrition) 48 hours
inosculation of capillary growth (vessels line up) 72 hours revascularization 5 days |
|
|
How do you evaluate a graft?
|
at 5 days
is it mobile? bad is it pink? good |
|
|
What are some reasons grafts fail?
|
hematoma
infection movement/shearing decreased vascularity traumatic handling |
|
|
How do you estimate the %TBSA?
|
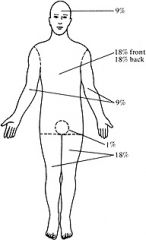
Hands are worth 2% each
|
|
|
Describe the four degrees of burn injury:
|
1st - erythema without break in skin
2nd - blister, can be superficial partial (upper dermis) or deep partial (lower dermis) 3rd - full thickness, painless 4th - into muscle, bone, etc. |
|
|
What are the main respiratory concerns for people with burns?
|
burn eschar may constrict chest - escharotomy
CO poisoning - displace CO with 100% O2 smoke inhalation, pulmonary injury - may need intubation |
|
|
What is the Parkland formula?
|
resuscitation for burns
4 cc LR/Kg/%TBSA 1/2 in first 8 hrs 1/2 in next 16 hours |
|
|
How do you monitor resuscitation efforts in burn patients?
|
UO 30-55 cc/hr in adults
UO 1.2 cc/kg/hr in children <12 y/o P<120, HCO3 > 18, CO > 3.1 L/m2 |
|
|
What is the standard treatment for burn wounds?
|
1. graft
2. topical antibiotics - silvadene, sulfamylon 3. debride - excise, layered, enzymatic, hydrotherapy |
|
|
What labs should be initially ordered on burn patients?
|
CBC
UA ABG electorlytes renal function tests type and cross carboxyhemoglobin! |
|
|
What are the major complications in burn victims?
|
renal failure
GI bleed - Rx antacids, H2 blockers burn wound sepsis - monitor with biopsies, mental status changes, CHF, ards pulmonary insufficiency - smoke, inhalation, CHF, sepsis |
|
|
How do identify pulmonary insufficiency in burn victims?
|
hypoxia
hypercarbia shunt acidosis |
|
|
What is the treatment strategy for chemical burns?
|
dilute for 12 hours
debride topical antibiotics close |
|
|
What are the complications of electrical burns?
|
cardiopulmonary - anoxia and fibrillation; early and late EKG rhythmn abnormalities
renal failure - myoglobin/hemoglobin: ATN, want 77 cc/hr UO spinal cord demyelination vascular thrombosis by current - continues - delayed rupture |
|
|
What is the treatment of myoglobin/hemoglobin induced acute tubular necrosis as a cause of renal failure in patients of electrical burns?
|
alkalinize urine with NaHCO3 (heme soluble) mannitol (to clear protein load)
|
|
|
How do you treat frostbite?
|
40 C waterbath
amputate after demarcation |
|
|
How do you treat hypothermia?
|
LRS with 1 amp NaHCO3
EKG monitoring - lidocaine for arrhythmia |
|
|
Breast cancer has an increased chance (i.e. marker not precursor) in both breasts with?
a. LCIS b. DCIS |
a. LCIS
|
|
|
Breast cancer tends to reoccur in the same area (i.e. precursor not maker) with?
a. LCIS b. DCIS |
b. DCIS
|
|
|
What is the most common form of invasive breast cancer?
|
ductal carcinoma 80%
lobular 10% |
|
|
What are the characteristics of medullary carcinoma of the breast?
|
large cancer cells
immune cells |
|
|
What are the characteristics of colloid carcinoma of the breast?
|
mucinous
makes mucinous better prognosis |
|
|
What are the characteristics of inflammatory breast cancer?
|
spread through lymphatics
indicates stage IIIb |
|
|
What are various biopsy techniques for breast cancer?
|
core needle
fine needle aspiration sterotactic needle biopsy |
|
|
What additional tests should be considered in breast cancer?
|
Everyone: CXR
If Symptoms: Bone scan, CT (organs), MRI (brain) PET if looking for entire body mets CBC, liver fx PR +ER, HER-2/neu (if invasive) |
|
|
What are the various T levels in the TNM staging of breast cancer?
|
Tis - DCIS/LCIS
T1 < 2 cm T2 2-5 cm T3 > 5 cm T4 skin or cest wall |
|
|
What are the various N levels in the TNM staging of breast cancer?
|
N0 no nodes
N1 1-3 ipsilateral nodes N2 3-10 nodes N3 > 10 nodes |
|
|
What stage is a T4 NM breast cancer?
|
IIIb (inflammatory)
|
|
|
What stage is a T N1 M breast cancer?
|
IIIa
|
|
|
What stage is a TN M1 breast cancer?
|
IV
|
|
|
What are the indications for mastectomy in the local treatment of breast cancer?
|
Hx of radiation
multifocal Dx Pregnant > 5cm tumor |
|
|
What are the treatments for systemic disease?
|
chemo: trastuzumab (herceptin) only with mets
hormone therapy: tamoxifen for mets and to prevent reoccurance, toremifene, fulvestrant, aromatase ihibitors, GRNH agonists, megase |
|
|
What is the treatment algorithm for LCIS?
|
LCIS is a RF for Cx therefore
close observation w/H&P mammograms +/- 5 yrs Tamoxifen or double mastectomy |
|
|
What is the treatment algorithm for DCIS?
|
excision bx then...
widespread dz/+ margins - masectomy 2 w/o node resection negative margins - lumpectomy + radiation or masectomy negative margins/low grade/<0.5 cm - lympectomy w/o radiaiton ok 5 yrs tamoxifen, H&Ps Q 6 months, mammogram and pelvic q year |
|
|
What is the work up for invasive carcinomas?
|
CBC, LFTS, CXR, bilateral dx mammograms, ER/PR/HER, bone scan if symptomatic, CT or MRI for Stage II
|
|
|
What is the treatment for invasive carcinomas?
|
Tumor < 2cm lumpectomy + radiation + node resection
if no nodes - radiate breast Tumor > 2cm mastectomy or neoadjubant if + nodes/>5 cm radiate post mastectomy |
|
|
What are the indications for adjuvant therapy wrt breast cancer?
|
<0.5 cm, < 1cm tubular, colloid, or low grade ductal w/o nodes - no chemo
> 1 cm always get chemo + nodes and HR positive - 5 yrs tamoxifen and chemo |
|
|
What are the characteristics of cardiogenic shock?
|
decreased CO
increased PCWP, SVR white skin |
|
|
What are the characteristics of hypovolemic shock?
|
decreased CO, PCWP
increased SVR white skin |
|
|
What are the characteristics of vasogenic (spetic/anaphylactic) shock?
|
decreased CO, PCWP, and SVR
pink skin |
|
|
What are the characteristics of neurogenic shock?
|
decreased CO< PCWP, and SVR
pink skin |
|
|
What is the path of a swan-ganz catheter?
|
jugular
SVC RA RV Pulmonary artery |
|
|
What is the normal PCWP? What is this indicative of?
|
6-12 mm Hg
LAP/end-systolic LVP (preload) |
|
|
Cardiac Output = ?
|
BP/SVR
HR*SV O2 consump/(O2 Pul Vein - O2 Pul Artery) |
|
|
What are the classes of shock? What is the blood loss? What are the characteristics?
|
I - 0-15% VS nml
II - 15-30% HR+, postural hypotension III - 30-40% HR++, BP- IV - > 40% HR+++, BP<60 |
|
|
What is the treatment of hypovolemic shock?
|
ABCs
resuscitation with isotonic solution to maintain pressures O- blood if not responsive |
|
|
What is the treatment of cardiogenic shock?
|
O2
treat arrhythmia mechanical ventilation to remove the work of breathing |
|
|
In cardiogenic shock, DDx includes? How to work up?
|
MI - angiogram, thrombolytics or cath/stent/balloon
MONAB - morphine, oxygen, nitro, aspirin, beta blockers |
|
|
What is the marker of sufficiently treated cardiogenic shock?
|
target PCWP - 15-20 mmHg
|
|
|
What are the common causes of SBO?
|
adhesions, neoplasms, hernias, Crohn's
|
|
|
What are the common causes of LBO?
|
colon cancer, diverticulitis, volvulus (cecum, sigmoid), hernia
|
|
|
What are the common causes of adynamic ileus?
|
celiotomy
inflammatory retroperitoneal (ureter, blood) thoracic (pneumonia) systemic (hypokalemia, hyponatremia, sepsis) drugs (anticholenergics, opiates, Ca++ blockers) |
|
|
How do you tell if it is a partial or complete bowel obstruction? What are the differences in treatment?
|
partial - flatus, colonic gass on AXR, adhesions ~ 70% nonoperative
complete - no gas, no colonic gas - operate |
|
|
What are the signs of strangulation?
|
tachycardia, fever, increased WbC, focal pain
|
|
|
Hypokalemic, hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis means:
|
vomiting
|
|
|
What are the indications for operation of bowel obstruction?
|
strangulated
peritonitis >48 hours pneumoperitoneum (perforation) closed loop complete no hx of surgery large bowel |
|
P11
|
elimina viento, elimina calor y beneficia graganta (exceso), abre los orificios, recobra conciencia ( anapilectico), descenso y dispersion de pulmon, exceso corazon
Expel Wind, release exterior, clear Heat, cool Blood, resolve Dampness, benefits sinews & joints, regulate Ying & Blood |
|
|
What is thoracic outlet syndrome?
|
compression of subclavian artery, vein, or brachial plexus
|
|
|
What causes thoracic outlet syndrome?
|
congenital (cervical rib)
trauma (crush injuries) repetitive motion |
|
|
What are the symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome?
|
paresthesias, weakness (arterial or nerve), cold arm (arterial), edema (veinous)
|
|
|
What is the most common depressed nerve in thoracic outlet syndrome?
|
ulnar
|
|
|
Most common chest wall benign tumors? treatment?
|
fibrous rib dysplasia
chondroma osteochondroma wide excision + graft |
|
|
Most common malignant chest wall tumors? treatment?
|
fibrosarcoma, chondroxarcoma, osteosarcoma, rhabdymyosarcoma, myeloma, Ewing's tumor
wide excision, possible radiation |
|
|
What are the causes of pleural effusion?
|
transudates: systemic
CHF, constrictive pericarditis, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome exudates: local lung parenchymal infection, malignancy, PE, CVD, GI: pancreatitis, hemothorax, post-CABG |
|
|
How do you diagnose pleural effusion?
|
thoracentesis - transudate or exudate? check LDH, protein, cytology
Lights criteria protein in fluid/serum > 0.5 and LDH in fuid/serum > 0.6 - exudate |
|
|
What is the diagnosis of recurrent pneumothorax? treatment?
|
pleurodesis
scar lung with talc or abrasion |
|
|
What are the 4 most common causes of anterior mediastinum masses?
|
teratoma 14% malignant
T-cell lymphoma - nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's Lymphoma Thymoma - 75% with myasthenia gravis thyroid malignancy |
|
|
What are the risk factors for SCC of the esophagus?
|
smoking
alcohol achalasia radiation nitrosamines |
|
|
What are the risk factors for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus?
|
obesity
Barrett's radiaiton smoking anticholinergics |
|
|
What is the conversion rate for Barrett's to adenocarcinoma? What is the treatment for Barrett's?
|
0.5% conversion to cancer/year
surveillance with endoscopy, ablation + PPIs |
|
|
What are the symptoms of esophageal cancer?
|
dysphagia
weight loss hx of reflux |
|
|
What are the signs of esophageal cancer?
|
lymphadenopathy (Virchow's node)
pleural effusion |
|
|
What studies to do conduct if you are suspicious of esophageal cancer?
|
esophogogram - structure or ulcer
endoscopy, CT for mets, PET |
|
|
What % of esophageal cancers are found to be unresectable or have distant mets upon Dx?
|
50%
|
|
|
How do you Rx esophageal cancer?
|
local - surgery or radiotherapy
advanced - chemo but palliative, last a few months |
|
|
What cancers are associated with MEN1?
|
parathyroid
pituitary pancreatic islet tumor |
|
|
What cancers are associated with MEN2A?
|
parathyroid
medullary pheo |
|
|
What cancers are associated with MEN2B?
|
Medullary
Pheo Mucosal and GI neuromas |
|
|
What is the DDx for a thyroid nodule?
|
CA (thyroid, PT, lymphoma)
thyroditis multinodular goiter cyst adenoma |
|
|
What is the best test for determining what a thyroid nodule is?
|
FNA (5% FN)
can use US, I 123 scan, TSH, Ca++ |
|
|
What is the histological hallmark for papillary thyroid cancer? What are the metastatic spread patterns?
|
psammoma bodies
node spread - no effect on prog |
|
|
What are the characteristics of follicular CA of the thyroid?
|
heme spread to bone
slightly worse prog Hurthe variant |
|
|
What is the treatment for medullary CA of the thyroid?
|
total thyroidectomy
median node resection |
|
|
What are the most common causes of primary hyperparathyroidism?
|
90% adenomas (high Ca++)
10% hyperplasia (MEN) 1% CA |
|
|
How do you diagnose primary hyperparathyroidism?
|
sestamibi scan Tc99 to dx and localize
|
|
|
How do you treat primary hyperparathyroidism?
|
fluids + lasix
explore 4 glands, remove adenoma, biopsy 3 nml glands |
|
|
What are the causes of secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism?
|
secondary - from low Ca++ renal failure
tertiary - after renal transplant PT glands remain hypertrophic (high Ca++) |
|
|
How do you treat tertiary hyperparathyroidism?
|
remove 3 1/2 glands or 4+ forearm transplant (leave at least 30 mg)
|
|
|
How do you Dx a pheo?
|
urine VMA, metanephrine
|
|
|
What are the patterns of melanoma?
|
superficial spreading
nodular (deep - worst) lentigo maligna (best) acral lentiginous |
|
|
What is the clarks classification of melanomas?
|
I in situ (epidermis)
II papillary dermis III papillary/reticular dermis jnctn IV reticular dermis V subQ fat |
|
|
What is the breslow classification of melanomas?
|
<0.76 mm 90% cure
>4 mm 80% reoccurance/met |
|
|
What are the common sites of melanoma mets?
|
brain
bone liver lungs heart bowel Anus |
|
|
What is the most common met to the bowel?
|
melanoma
|
|
|
What are the rules for rx of melanoma?
|
basted on depth
in situ (0.5 mm) - 0.5 margin < 1 mm - 1 cm margin +/- SLND 1-4 mm - 2 cm margin + SLND > 4 mm - 2 cm margin +/- SLND (often already distant mets) node + - INF-a (chemo and radiation do not work, regional node resection) |
|
|
How do you handle brain metastatic melanoma?
|
radiation
|
|
|
What are some extrapulmonary signs of lung cancer?
|
Horner's syndrome
Hoarse voice SVC syndrome Dysphagia |
|
|
What is SVC syndrome? Treatment?
|
central tumor
SVC compression face or arm swelling, venous distension of neck and chest wall, dyspnea, cough, headach initial treatment steroids, diuretics until dx |
|
|
What are the characteristics of SCLC?
|
neuroendocrine - ACTH, PTH-rp
fast doubling time early metastasis |
|
|
What is the Rx for SCLC?
|
chemo +/- radiation
platinum agents like cisplatin (crosslinks DNA) most effective |
|
|
What is the staging for SCLC?
|
limited - encompassed by single tolerable radiaiton port (hemithorax)
extensive - get CT, bone scan, MRI of brain |
|
|
What are the types of NSCLC?
|
adenocarcinoma
SCC large cell carincoma |
|
|
Where to NSCLC drain to?
|
drains to hilum and mediastinal nodes
|
|
|
What is the appropriate workup of NSCLC?
|
CXR: 96% abnormal
CT: detects local invasion, node status PET: improves sens/spec of node status with CT Bronchoscopy: standard node biospy Mediastinoscopy: standard for node biopsy Brain MRI and Bone scan: if N2 (mediastinal, subcarinal nodes) |
|
|
When is surgery appropriate in the treatment of NSCLC? What is the surgery? What is the most important post op consideration?
|
if IIIa or less (no nodes or isplat hilar nodes, not extensively invasive)
pneumonectomy or lobecotmy + lymph node dissection need post-op FEV1 of 1 L |
|
|
What is the work-up of a solitary incidental nodule on CXR in someone without CA RFs?
|
follow growth over time
doubling - 28% increase in Diameter cancer doubling is about 25-250 days if less than 500 days is benign Ca++ benign |
|
|
Where is foregut pain referred?
|
phayrynx - D3
epigastric |
|
|
Where is midgut pain referred?
|
periumbilical
|
|
|
Where is hindgut pain referred?
|
rectum
suprapubic |
|
|
I say 'board-like' abdomen, you say?
|
perforated ulcer
|
|
|
What can abdominal films show you in the eval of acute abdomen?
|
calcification
gas pattern fluid levels fecolith |
|
|
What can a CXR show you in the eval of acute abdomen?
|
pneumoperitoneum
|
|
|
What can US show you in the eval of acute abdomen?
|
liver
spleen gallbladder pancreas appendix kidneys gyn |
|
|
What can a CT show you in the eval of acute abdomen pain?
|
diverticulosis
abcess pancreatitis |
|
|
Indications for operation of acute abdominal pain?
|
peritonitis
pain + sepsis perforation ischemic |
|
|
What is the root cause of aneurysms?
|
collagen/elastin defect
|
|
|
What is the typical aneurysm patient?
|
male
70 smoker HTN + FHx |
|
|
What is the normal size of the abdominal aorta? At what size do we consider it an AAA?
|
1.2 - 2cm
> 3cm |
|
|
What is the management of AAA?
|
> 3.8 cm yearly U/S mointoring
> 5 cm U/S every month > 5.5 cm repair (women 5 cm) consider growth average 1/2 cm/year |
|
|
What is the mortality of a ruptured AAA?
|
70%
|
|
|
What are popliteal aneurysms assocaited with?
|
limb loss
aneurysms elsewhere |
|
|
What is aorto-illiac disease? AKA? Typical patient? Rx?
|
Lariche syndrome: butt/thigh claudication, impotence, proximal atrophy
Typical patient: 50, smoker, often effects life style Surgery usually successful |
|
|
What is the typical femoral-politeal patient?
|
70
DM patients often adapt to Dx |
|
|
What is the thearpy for fem-pop disease?
|
medical therapy often effective - stop smoking, exercise, cilostazol, pentoxiphylline
|
|
|
What is the indications for surgery of fem-pop disease?
|
limb threat - rest pain, ischemic ulcer, gangrene
refractory to medical treatment |
|
|
What is the difference between stroke and a TIA?
|
stroke > 24 hours CNS deficit
TIA < 24 hours CNS deficit |
|
|
What is the treatment of stroke?
|
CEA prevent future strokes
|
|
|
What is the treatment of TIA?
|
Sx + 50% stenosis = CEA
No Sx + 80% stenosis = CEA, NNT = 7 |
|
|
How much time do I have to restore arterial blood supply to an area undergoing acute arterial insufficiency?
|
6 hours
|
|
|
What are the causes of acute arterial insufficiency?
|
trauma
emboli thrombosis (rare) |
|
|
What are the 6 (P) symptoms of acute arterial insufficiency?
|
pain
paralysis parasthesis (1st) pallor pulselessness poikilothermia |
|
|
What is one complication of re-perfusion after acute arterial insufficiency?
|
compartment syndrome
|
|
|
What is the indication for surgery with hemothorax?
|
chest tube gives off >1500 cc or > 200 cc/hr
|
|
|
How is the GCS determined?
|
motor 1-6
voice 1-5 eye 1-4 |
|
|
Trauma patient arrives with blown pupils, what are you suspicious of?
|
ipsilateral mass (hematoma, etc.)
|
|
|
Trauma patient with hemotympanum, raccoon eyes, ororrhea, rhinorrhea. Dx?
|
Basilar Fracture
|
|
|
What are the indications for exploratory laporatomy of a trauma patient?
|
+ 10 cc blood from syringe or > 10,000 RBC/mm3 or > 500 WBC/mm3
|
|
|
Patient with abdominal bullet wound, what do you do?
|
ex lap
|
|
|
Patient with abdominal knife wound, what do you do?
|
local exploration
DPL ex lap |
|
|
What do you do if you have an increased intracranial pressure?
|
head up
mannitol craniectomy + hyperventalate anticonvulsant prophylaxis |
|
|
What are the zones of penetrating neck trauma?
|
zone I to cricoid
zone II to mandible zone III above mandible explore with zone II |
|
|
What is the initial s/s of spinal cord injury? Rx?
|
spinal shock causes decreased BP
fluids, steroids < 48 hours |
|
|
What are 4 things that can kill a trauma patient in 15 min?
|
tension PTX
sucking PTX massive hemoTX tamponade |
|
|
What genes are associated with colorectal cancer?
|
FAP
Gardner's HNPCC |
|
|
What are the risk factors for colorectal cancer?
|
genetic
UC>Chronh's Diet |
|
|
What is the usual presentation of L sided colorectal cancer?
|
anemia
|
|
|
What is the usual presentation of R sided colorectal cancer?
|
obstructive symptoms
|
|
|
What is the usual presentation of rectal cancer?
|
hematochezia
|
|
|
What is the Dukes' stages for colorectal cancer?
|
A - submucosa
B - serosa C - nodes |
|
|
What are the prognostic factors for colorectal cancer?
|
sx
obstruction perf rectosigmoid ulcerative invasion CEA age |
|
|
What is the appropriate surgery for cecal, ascending colon colorectal cancer?
|
R hemicolectomy (ileocecal, R colic arteries cut)
|
|
|
What is the appropriate surgery for hepatic flexure colorectal cancer?
|
R hemicolectomy including middle colic artery
|
|
|
What is the appropriate surgery for transverse colorectal cancer?
|
transverse colectomy
|
|
|
What is the appropriate surgery for descending colon colorectal cancer?
|
L hemicolectomy IMA cut
|
|
|
What is the appropriate surgery for upper 1/3 rectum colorectal cancer?
|
anterior resection
|
|
|
What is the appropriate surgery for middle 1/3 rectum (8-12 cm from the anal verge) colorectal cancer?
|
low anterior resection
|
|
|
What is the appropriate surgery for distal 1/3 rectum (<8 cm from the verge) rectal cancer?
|
abdominoperineal resection
|
|
|
What is the appropriate surgical treatment of colorectal cancer associated with FAP, UC or Gardners'?
|
total proctocolectomy + ileostomy OR
total colectomy + mucosal proctectomy + ileoanal anastomosis |
|
|
What do you do if your colorectal cancer has nodes or mets?
|
chemotherapy 5FU
|
|
|
What do you do if your RECTAL cancer has positive nodes?
|
radiation
|
|
|
What is the follow-up after surgery for colorectal cancer?
|
CEA
Hx PE + hemocult q 6 M for 3 years then q 12 months LFTs, CT, CSR, colonoscopy q 12 months |
|
|
What are the s/s of Gardner's syndome?
|
neoplastic polyps
sebaceous cysts osteomas desmoid tumors |
|
|
How do you Dx diverticulosis? What is the treatment?
|
barium enema
not surgical unless complications increase fiber in diet |
|
|
How do you Dx diverticulitis? What is the Rx?
|
Dx: CT, not BE or colonoscopy in acute setting
Rx: IV antibiotics, fluids, bowel rest, +/- NG |
|
|
What are the indications for surgery in diverticulosis/itis? What is that surgery?
|
for recurrence, complications
elective primary or emergent Hartmann's |
|
|
Causes of acute pancreatitis?
|
I - idiopathic. Thought to be hypertensive sphincter or microlithiasis.
G - gallstone. E - ethanol (alcohol) T - trauma S - steroids M - mumps (paramyxovirus) and other viruses (Epstein-Barr virus, Cytomegalovirus) A - autoimmune disease (Polyarteritis nodosa, Systemic lupus erythematosus) S - scorpion sting (e.g. Tityus trinitatis), and also snake bites H - hypercalcemia, hyperlipidemia/hypertriglyceridemia and hypothermia E - ERCP D - drugs |
|
|
What are Ranson's Criteria?
|
At admission:
age in years > 55 years white blood cell count > 16000 cells/mm3 blood glucose > 10 mmol/L (> 200 mg/dL) serum AST > 250 IU/L serum LDH > 350 IU/L At 48 hours: Calcium (serum calcium < 2.0 mmol/L (< 8.0 mg/dL) Hematocrit fall > 10% Oxygen (hypoxemia PO2 < 60 mmHg) BUN increased by 1.8 or more mmol/L (5 or more mg/dL) after IV fluid hydration Base deficit (negative base excess) > 4 mEq/L Sequestration of fluids > 6 L |
|
|
How shall we treat acute pancreatitis?
|
IV flues (monitor BUN, UO)
electrolyte correction (Ca++) glucose management blood gases nutrition antibx for abscess monitor mental status |
|
|
What is the role for surgery in acute pancreatitis?
|
elective chole surg
correctable lesions: pancreas divisum, obstruction |
|
|
What is the treatment of pancreatic pseudocst?
|
< 5 cm watch
> 5 cm ERCP, percutaneous drainage if noncommunication surgery at 6 weeks if communication with duct |
|
|
What is and what is the treatment for pancreatic abscess?
|
infected pseudocyts or necrotizing pancreatitis
debris in cyst, positive cultures Tx: wide surgical excision, debridement and antibx |
|
|
What are the s/s of chronic pancreatitis?
|
persistent pain
epigastric to back, worse with food/alcohol malabsorption (late) |
|
|
What is the best way to Dx chronic pancreatitis?
|
ERCP
NOT lipase/amylase |
|
|
What are the indications for surgery of chronic pancreatitis? What are the possibilities?
|
for intractable pain
pancreatojejunostomy pancreatic resection if in tail/body whipple if pancreatic head involvement |
|
|
How are body fluids distributed?
|
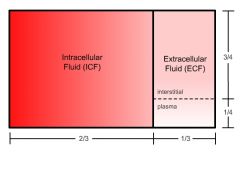
60% of BW
|
|
|
What is the risk for resuscitation with normal saline?
|
too much > 5ml causes
hypercholoremic metabolic acidosis |
|
|
What are the considerations when resuscitation with LR solution?
|
has 4 mEq of K so not if renal failure
lactate - HCO3 - alkalosis but bad if Liver failure |
|
|
What is the advantage of D5W for resuscitation?
|
distributed in all body water compartments
|
|
|
How many gm of dextrose in D5W? How many calories?
|
1000 ml
50 gm dextrose 4 kcal/g = 200 kcal |
|
|
What is needed for fluid maintenance?
|
4 cc/kg/hr for 1st 10 kg
2 cc/kg/hr for 2nd 10 kg 1 cc/kg/hr thereafter |
|
|
What is the goal for urine output during resuscitation?
|
min 30 cc/hr
720 cc/day for a 60 kg person or 1/2 cc/kg/hr |
|
|
What are the consequences of hyponatremia?
|
ileus
fatigue, confusion, seizure, coma |
|
|
What is the consequence of quickly correcting hyponatremia?
|
central pontine myelinolysis
|
|
|
What is the Rx for hypernatremia?
|
D5W
|
|
|
How do you calculate water deficit?
|
0.6 x wt x (Na-145)/145
|
|
|
What is the consequence for hypokalemia?
|
ileus
tetany, paresthesia |
|
|
What are the signs on EKG of hypokalemia?
|
T wave flattening
U waves |
|
|
How do you treat hypokalemia?
|
KCl
|
|
|
What are the s/s of hyperkalemia?
|
decreased DTR, weakness, paresthesia, paralysis
EKG - T wave peaking, QRS widening, V tach, V fib |
|
|
How do you treat hyperkalemia?
|
Ca+
HCO3 insulin/D5 furosemide albuteral dialysis |
|
|
What EKG changes are seen in hypocalcemia/ What is the Rx?
|
long QT, delayed repolarization
Ca++ gluconate |
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen in hypercalcemia? What is the Rx?
|
short QT, long PR
NS and furosemide |
|
|
What are the causes of hypercalcemia?
|
CHIMPANZEES
Ca++ HPT HT Hypocalciuric hypercalcemia Iastrogenic (thiazides) Mets Paget's dz Addison's Neoplasm ZE Excess D Excess A Sarcoid |
|
|
What can hypomagnesemia cause?
|
hypokalemia
|
|
|
What is the treatment of hypermagnesemia?
|
Ca++
insulin/D5 furosemide dialysis |
|
|
What is the treatment of hyperphosphatemia?
|
aluminum hydroxide
|
|
|
What are the protein requirements for a person?
|
1-2 g/kg/day
|
|
|
What size of breast tumor make sit T3?
|
> 5 cm
|
|
|
What is the necessary time from MI to elective surgery?
|
6 mo
|
|
|
Most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism?
|
parathyroid adenoma
|
|
|
Which vein limits the ability to resect during the Whipple procedure?
|
SVM
|
|
|
Patient with perforation of duodenal ulcer exanguinates, what happened?
|
penetrated into gastrodudodenal artery
|
|
|
Patient undergoing AAA repair, postop develops exanguination, what happened?
|
aortoduodenal fistula
|
|
|
I say Budd-Chiari syndrome, you think?
|
thormbosis of the hepatic vein
|
|
|
What is a spigelian hernia?
|
herniation lateral and ventral
through semilunaris semicircular line of douglas |
|
|
Most common cause of acute anal pain?
|
anal fissure
|
|
|
Most likely cause of thrombocytopenia in a person with history of ITP post-splenectomy?
|
accessory spleen
|
|
|
Causes of midline incision dehiscence?
|
infection
tension hematoma |
|
|
What is the workup for a lower GI bleed?
|
R/O UGI bleed
Rectal Exam TRBC or angiogram sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy |
|
|
Man from Honduras with fever, leukocytosis, and RUQ mass?
|
amebic abscess
|
|
|
Artery most commonly damaged during cholcystecomty?
|
right hepatic
|
|
|
Child with bilious vomit?
|
must R/O midgut volvulus
|
|
|
What are the best indicators of tissue perfusion?
|
color
pulse capillary refill abscence of acidosis urination mentation |
|
|
DDX of distended neck veins?
|
Tension pneumothorax
massive hemothroax cardiac tamponade myocardial injury with heart failure |
|
|
What are the causes of diabetic foot ulcer?
|
decreased sensation
decreased perfusion decreased neutrophils function |
|
|
What is the most irritating suture? Least irritating?
|
non-absorbable braided suture - least
monofilament absorbable - least irritating |
|
|
Survival rates for Duke's A, B, C, D?
|
A - 94-97%
B - 56 - 83% C - 15-86 % D - 5 % |
|
|
What is Adamkiewicz syndrome?
|
occlusion of radicular artery
|
|
|
What is the Edward's procedure?
|
replacement of aorta and aortic valve in aortic dissection
|
|
|
What is Mondor's Dx?
|
thrombophlebitis of thoracoepigastric veins and also thrombophlebitis of superficial breast veins
|
|
|
What is Belsey Marks IV procedure?
|
270 degree fundoplication
|
|
|
What is Battle's sign?
|
ecchymosis over mastoid process in basilar skull fracture
|
|
|
What is mitotane?
|
durg that kills cortisol producing cells
|
|
|
What is metyrapone?
|
11 beta hyroxylase inhibitor
|
|
|
What is Nelson's syndrome?
|
hypersecretion of pituitary hormones
|
|
|
What is the organ of Zuckernadl?
|
chormoaffin cell near aorta
|
|
|
What is the breast tissue in the axilla called?
|
tail of Spence
|
|
|
What is whipples traid?
|
hypoglycemia
vasomotor sx relief of sx with administration of glucose in insulinoma |
|
|
What is Beck's triad?
|
increased JVD, hypotension, faint heart sounds
cardiac tamonade |
|
|
MEN 1 aka?
|
Wermer's syndrome
|
|
|
MEN 2a aka?
|
Sipple's syndrome
|
|
|
What is Ogilvies syndrome?
|
paralytic dialation of colon
treat with colonscopy and physostigmine |
|
|
Early wound infection?
|
group A strep - erysipelas
clostridia dirty dishwater discharge, crepitance |
|
|
Tumor marker AFP?
|
testicular or hepatoma
|
|
|
Most common cause of maetabolic gap acidosis in surgery?
|
lactic acidosis
|
|
|
Telangictasis around lips?
|
Peutz-Jeghers
|
|
|
Diffuse telangictasias?
|
Osler-Rendu-Weber
|
|
|
Hammond's sign?
|
crunching, rasping sound, synchronous with the heartbeat,[3] heard over the precordium in spontaneous mediastinal emphysema.
|
|
|
How do you treat hypercalcemic crisis?
|
saline, furosemide, bisphosphonates, mithramycin, plicamycin, calcitonin.
|
|
|
How do you treat hypercalcemic crisis?
|
saline, furosemide, bisphosphonates, mithramycin, plicamycin, calcitonin.
|

