![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hepatic blood supply
-% of cardiac output |
-25%
|
|
|
Hepatic artery
-blood flow |
-25% liver flow
-1/2 oxygen |
|
|
Portal vein
-blood flow |
-75% liver flow
-1/2 oxygen |
|
|
Liver
-function |
-protein synthesis
-glucose homeostasis -Bile (bilirubin, fat metabolism) -Immune (kuppfer cells) -Drug metabolism |
|
|
Protein synthesis by the liver is important for
|
-albumin
-coagulation factors (Vitamin K related) |
|
|
Albumin
-function |
-oncotic pressure
-drug protein binding |
|
|
Effect of albumin on propofol
|
-90% of dosed propofol bound to albumin, but free 10% causes anesthesia
-if low albumin, will get anesthesia with less dosed propofol |
|
|
Albumin
-indicator of |
-increased risk
|
|
|
Albumin
-drugs that are highly protein bound |
-opioids
-benzodiazepines -barbituates |
|
|
How should highly protein bound drugs be dosed?
|
-dose to effect
|
|
|
Effect of low albumin on oncotic pressure
|
-dec. oncotic pressure ---> fluid leaks out of vasculature ---> peripheral edema
|
|
|
Albumin
-size |
-70,000 daltons
|
|
|
Albumin
-production is regulated by: |
-peri-hepatic interstitial osmoreceptors working with hormonal control
|
|
|
Surgery effect on albumin levels
|
-tends to shift albumin to interstitium, which can be devastating in hepatically impaired patients
|
|
|
Hepatic insufficiency
-effect on coagulation |
Leads to inability to coagulate
-decreased production -increased use (anti-thrombin) |
|
|
Hepatic insufficiency
-effect on glucose levels |
liver normally produces glucose
-may need to supplement dextrose if hypoglycemic |
|
|
Exaggerated drug effects of liver dogs/cats due to
|
-hypoproteinemia
-decreased metabolism -increased sensitivity -altered blood flow |
|
|
Pathways of drug metabolism
|
-oxidation
-reduction -hydrolysis -conjugation |
|
|
Effect of decreased liver metabolism on drugs
|
-drug effects may be altered or prolonged
|
|
|
Reasons for increased drug sensitivity in liver cats/dogs
|
Unknown
Possibly: -altered blood-brain barrier -altered CNS receptor kinetics -circulating amines ***DOSE TO EFFECT |
|
|
Altered liver blood flow through liver can be due to:
|
-portal hypertension
-shunting -systemic hypotension -surgical manipulation |
|
|
Liver Cat/Dog
-pre-op testing |
-bile acids
-profile (ALB, CHOL, GLUC, BILI, BUN) -PT, PTT, Platelets, BMBT -assess volume status because dehydration can falsely elevate albumin and PCV |
|
|
BMBT
-how long in a normal patient |
-should clot within a few minutes
|
|
|
Childs-Hugh Classification
|
-bili
-alb -PT -Ascites -Encephalopathy |
|
|
Anesthesia for a liver animal
|
Cautious dosing
-premed benzodiazepine/opioid (probably won't need full dose) -induce propofol or inhalent (don't want to give a drug that may last a long time) -maintain inhalant Monitor -CVP, direct ABP, urine production |
|
|
Kidney
-normal function |
Maintain constant extracellular environment
-water balance -electrolytes -hydrogen and nitrogen excretion -acid-base balance Target for various hormones Secretion of erythropoietin, renin, etc. |
|
|
Renal blood supply
-% of cardiac output |
-25%
|
|
|
GFR
-% of renal plasma flow |
-20%
|
|
|
Ratio of urine produced to filtrate
|
1 mL urine / 100 mL filtrate
|
|
|
Amount of urine produced per hr
|
-0.5-1.0 mL/kg/hr
|
|
|
Effect of renal arterial pressure on:
-renal blood flow -GFR -urine flow rate |
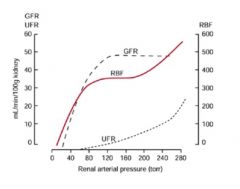
|
|
|
Effects of perfusion pressure and how the effect urinary output
|
-hypotension: reduced glomerular hydrostatic pressure---> reduced filtration
-increased sympathetic tone: constriction of renal artery ----> flow decrease -renin release: decrease renal blood flow -hemorrhage, dehydration, hypovolemia |
|
|
Nephrotoxicity
-typically caused by |
-anesthetics that are unavailable
|
|
|
Anesthetics that could cause nephrotoxicity
|
-sevoflurane
-compound a *but generally not a problem in semi-closed circuits |
|
|
Renal patient
-typical presentations |
-Post renal issue (obstruction)
-chronic renal disease (presented for other issues) -rare to see acute renal failure come through anesthetic service |
|
|
Renal patient
-pre-op testing |
-BUN, CR, Creatinine clearance (GFR tests)
-USG, urine osmolarity (renal tubular function tests) -Electrolytes -albumin (PLN) -hematocrit (no EPO production) |
|
|
Hyperkalemia
-treatment |
-dextrose +/- insulin
-hyperventilation -bicarbonate (rare, don't want to be chasing pH) -electrolytes? |
|
|
Band-aid for hyperkalemia
|
Calcium
-adjusts the resting membrane threshold |
|
|
Renal patient
-stabilization of obstruction |
-hydration status (volume replacement)
-treat hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremia, acidosis, uremia -peritoneal fluid? |
|
|
Renal patient
-stabilization of chronic renal disease |
-hydration status (volume replacement)
|
|
|
Renal patient
-goals of anesthesia |
-maintain hydration and blood volume
-maintain renal blood flow and GFR -avoid hypotension -avoid renal vasoconstriction -avoid hypovolemia |
|
|
Renal patient
-why is it important to treat hypovolemia early |
-don't want to get into a range where you can't autoregulate blood flow
|
|
|
Renal patient
-support |
-fluids (colloids, crystalloids)
-increase cardiac output??? (dobutamine, dopamine, ephedrine) -Increase resistance???? (phenylephrine, vasopressin) |
|
|
Renal patient
-monitoring |
-ECG (K+ concern ---> bradycardia)
-Blood pressure |
|
|
Renal patient
-drug selection for anesthesia |
-acepromazine?
-alpha-2 not a good idea (vasoconstriction) -opioids (benign) -ketamine (exclusively removed by the kidneys of cats) vs. propofol (short lived but profound hypotension) -avoid halothane and methoxyflurane |

