![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why use regional anesthesia with general anesthesia
|
-decreased requirements for inhalation anesthetics
-improved muscle relaxation -preemptive analgesia |
|
|
Pre-emptive analgesia
-define |
-local anesthesia that prevents transmission of noxious stimuli to the spinal cord, thus preventing excitation of interneurons in the dorsal horn
|
|
|
Local anesthetic
-mechanism of action |
-prevent NA+ influx into nerve ---> prevents depolarization of propagation of action potential
|
|
|
Differential nerve blocks are important due to:
|
-Sympathetic > A-delta, C-fiber (sensory > A-alpha (motor)
-Size -Myelination -Rate of discharge |
|
|
Local anesthetic
-disposition |
-distribution
-absorption -elimination |
|
|
Local anesthetic
-efficacy of block depends on |
-concentration
-proximity to nerve -volume -distribution |
|
|
Local anesthetic toxicities
-general |
Systemic
-cardiovascular -CNS -Methemglobinemia Allergic Reactions (rare) -localized -systemic Local Tissue toxicity |
|
|
CNS toxicity
-common with |
-lidocaine
|
|
|
Cardiovascular toxicity
-occurs with |
-bupivicaine
|
|
|
Distal Limb block
-nerves blocked on forelimb |
-radial n.
-ulnar n. -median n. |
|
|
IVRA
- aka |
-IV Regional Anesthetic
-Bier Block |
|
|
IVRA
-how to perform |
-place tourniquet and inject drug IV to lose sensation in everything distal
-careful when removing tourniquet because drug can go systemic |
|
|
Brachial Plexus Block
-indications |
-procedures within or distal to the elbow
|
|
|
Brachial Plexus Block
-nerves blocked |
-radial n.
-median n. -ulnar n. -musculocutaneous and axillary nerves |
|
|
Brachial plexus block
-drugs |
-lidocaine
or -bupivicaine |
|
|
Brachial plexus block
-landmarks |
-point of the shoulder
-first rib -transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae |
|
|
Brachial Plexus Block
-downside to use |
-motor block too
|
|
|
RUMM Block
-purpose |
-distal forelimb
-possibly with fewer complications |
|
|
RUMM Block
-nerves |
-Radial n.
-Ulnar n. -Musculocutaneous n. -Median n. |
|
|
Epidural Anesthesia
-injection occurs where |
Lumbosacral space
-dorsal cranial iliac crest -dorsal spinous processes of L7 and S1 |
|
|
Epidural Local Anesthesia
-Extent of anesthesia is dependent on |
-volume
-concentration of drug injected |
|
|
Epidural Local Anesthesia
-surgerys (low to high drug concentratoin) |
-abdominal surgery
-hindlimb surgery -perineal surgery |
|
|
Knee Surgery
-what nerves get blocked -where are they on the spinal cord |
-Sciatic n. & Femoral n.
-L4 |
|
|
Epidural Local anesthesia
-advantages |
-frequently combined with epidural opioids
-good muscle relaxation -decreased requirement for inhalation anesthesia |
|
|
Epidural Local Anesthesia
-disadvantages |
-sympathetic blockade (hypotension, loss of motor tone, etc.)
-motor blockade |
|
|
Epidural Opioid
-advantages |
-prolonged segmental analgesia
-minimal sedation -reduced inhalation anesthetic requirement |
|
|
Epidural opioid
-disadvantages |
-requires technical expertise
|
|
|
Epidural Opioids
-drugs |
-Morphine*****
-Buprenorphine (not used due to preservative) -Fentanyl (not used due to short half-life) |
|
|
Epidural Opioids
-when to use |
-perioperative analgesia for the hind limb, abdomen, perineum
-pancreatitis -extensive soft tissue wounds -orthopedic trauma |
|
|
Epidural opioids
-side effects |
-pruritis (uncommon)
-urinary retention* -delayed respiratory depression? -vomiting |
|
|
Epidural opioids
-complications |
-ineffective analgesia
-epidural hematoma -epidural abscess |
|
|
Epidural opioids
-contraindications |
-sepsis
-coagulopathy -pyoderma |
|
|
Dental Nerve Block
-indications |
Analgesia for face and oral cavity
-dental extractions -skull fracture repair -maxillofacial surgery -inflammatory/ulcerative conditions |
|
|
Dental nerve blocks
-advantages |
-analgesia during dentistry (reduced MAC)
-pre-emptive analgesia? -post-op analgesia (improved recovery) -less stress at emergence |
|
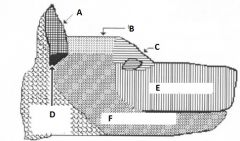
Label the sensory innervation to the head
|
-A) facial n.
-B) dorsal cutaneous n. -C) ophthalmic n. (V) -D) vagus n. -E) maxillary n. (V) -F) mandibular n. (V) - |
|
|
Dental nerve block
-nerves blocked |
-infraorbital n.
-mandibular alveolar n. -mental n. -maxillary n. |
|
|
Dental nerve blocks
-key anatomical sites of the skull |
-infraorbital canal
-infraorbital foramen -mandibular foramen -mental foramina |
|
|
Infraorbital nerve block
-function -where to inject |
-anesthesia for the maxilla rostrol to the molars
-palpate infraorbital foramen and insert needle caudally |
|
|
Mandibular n.
-branching pattern |
-exits skull at foramen ovale
-branches to lingual n. and buccal n. -enters mandibular foramen as mandibular alveolar n. -exits mandible at mental foramen as mental n. |
|
|
Mandibular Alveolar nerve block
-function -where to inject |
-anesthesia for mandible
-palpate the nerve (medial side) ---> insert the needle ventral to the mandible and cranial to the angular process |
|
|
Mental nerve block
-function -where to inject |
-anesthesia for mandibular incisors, canines, first 2 premolars
-direct caudally into the middle mental foramen |
|
|
Intercostal nerve block
-indications |
-lateral thorocotomy
-rib fracture |
|
|
Intercostal nerve block
-where to inject |
-2 rib spaces cranial and 2 rib spaces caudal to the injury site at the caudal border of the rib near the intervertebral foramen
|
|
|
Intercostal nerve block
-proposed mechanism of action |
-diffusion through pleura
or -direct blockage of intercostal nerves |
|
|
Intercostal nerve block
-blocked nerves |
-thoracic n.
-sympathetic chain -splanchnic n. |
|
|
Interpleural analgesia
-indications |
-thorocotomy
-rib fracture -thoracic wall, pleural, mediastinal metastasis -pancreatitis -cholecystectomy -renal surgery |
|
|
Interpleural analgesia
-drug use |
-bupivicaine
|
|
|
Interpleural analgesia
-comparison of buprenorphine and bupivicaine post-op |
Bupivicaine
-lower heart rate and respiratory rate -lower total pain score -higher partial pressure of oxygen |
|
|
Intraarticular local anesthetic
-indications |
-stifle surgery
-shoulder surgery -elbow surgery |
|
|
Intraarticular analgesia
-drug |
-bupivicaine
|

