![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
179 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Three branches of Cranial Nerve V.
|
Ophthalmic (V1), Maxillary (V2), Mandibular (V3)
|
|
|
|
Branches of Ophthalmic (V1) nerve
|
Supratrochlear, Infratrochlear, Supraorbital, External nasal branch of anterior ethmoidal nerve, Palpebral branch of Lacrimal nerve
|
|
|
|
Branches of Maxillary (V2) nerve
|
Infraorbital, Zygomaticotemporal, Zygomaticofacial
|
|
|
|
Mandibular (V3) nerve
|
Emerges from foramen ovale, Mental, Auriculotemporal (damage=Frey's), Buccal
|
|
|
|
Destruction of what nerve causes Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome?
|
CN V at the gasserian ganglion (surgery, encephalitis, or leprosy)
|
|
|
|
Name the branches of CN 7
|
Temporal, Zygomatic, Buccal, Marginal mandibular, Cervical
|
|
|
|
C2 sensation (lesser occipital)
|
scalp posterior to ear, superior portion of the posterior auricle
|
|
|
|
C2,C3 (greater auricular)
|
overlying the parotid, lower anterior ear, lower posterior ear, and mastoid process
|
|
|
|
C2 (greater occipital)
|
occipital scalp
|
|
|
|
C2,C3 (transverse cervical)
|
anterior portion of neck
|
|
|
|
C3, C4 (supraclavicular)
|
lower neck, clavicle and shoulder
|
|
|
|
C3, C4 (supraclavicular)
|
lower neck, clavicle and shoulder
|
|
|
|
Sural Nerve innervates:
|
posteriolateral sole
|
|
|
|
Posterior Tibial Nerve innervates:
|
anteromedial sole
|
|
|
|
Deep Peroneal Nerve innervates:
|
great toe and toe cleft b/tw 1st and 2nd toe
|
|
|
|
Superficial Peroneal Nerve innervates:
|
Dorsum of the foot
|
|
|
|
Name the six major arteries supplying the face
|
Facial, Superficial temporal, Maxillary, Posterior auricular, Occipital, Ophthalmic
|
|
|
|
Facial artery branches
|
Branches off in the following order: submental, inferior labial, superior labial, angular arteries
|
|
|
|
Superficial temporal artery branches
|
transverse facial, superficial temporal artery anterior & posterior branches, zygomatico-orbital artery, and frontal arteries
|
|
|
|
Maxillary artery branches
|
Infraorbital, buccal, inferior alveolar (mental) arteries
|
|
|
|
Ophthalmic artery branches (What is its origin?)
|
supraorbital artery, supratrochlear artery, palpebral artery, dorsal nasal artery, anterior ethmoidal artery, and lacrimal artery; OFF OF THE ICA
|
|
|
|
Where does the median nerve lie?
|
Within the carpal tunnel, deep and radial to the palmaris longus (PL) tendon and medial to the flexor carpi radialis (FCR) tendon
|
|
|
|
Where do you inject for a median nerve block?
|
between palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis; 2-3 cm proximal to the distal crease of the wrist
|
|
|
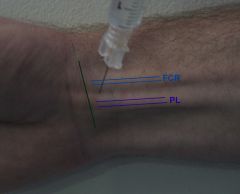
What is being demonstrated?
|
Median Nerve block (between palmaris longus and flexor carpi radii)
|
|
|
|
Name the sensory nerves to the plantar foot.
|
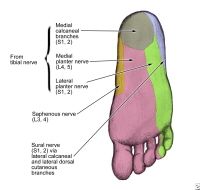
|
|
|
|
How do you anesthetize the ankle?
|
5 nerves are required: a line along the anterior ankle (superficial peroneal nerves), deep peroneal nerve), saphenous nerve, sural nerve, posterior tibial nerve.
|
|
|
|
What five nerves are involved with an ankle block?
|
5 nerves are required: a line along the anterior ankle (superficial peroneal nerves), deep peroneal nerve), saphenous nerve, sural nerve, posterior tibial nerve. See picture.
|
|
|
|
What five nerves are involved with an ankle block?
|
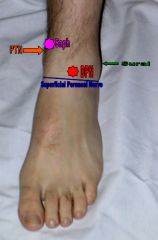
Posterior Tibial Nerve, Saphenous Nerve, Deep Peroneal Nerve, Superficial Peroneal Nerve, Sural nerve
|
|
|
|
Where do you inject for a posterior tibial block?
|
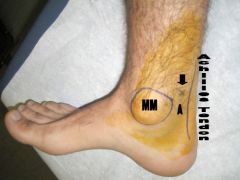
Between Medial Maleolus and Achilles tendon (medial aspect). The posterior tibial artery runs appx 1 cm from the site marked.
|
|
|
|
Purpose of a Basting stitch
|
Anchors tissue to bed of wound (ensures aposition of a FTSG to recipient bed)
|
|
|
|
Purpose of a running locked stitch
|
for wounds under tension and to provide hemostasis
|
|
|
|
Purpose of a suspension or tacking suture
|
holds skin to periosteum or perichondrium to permanently elevate an area, maintain concavity or alter tension vector near a free margin
|
|
|
|
Purpose of a vertical mattress suture
|
relieves tension to place other sutures, produces eversion and approximation of skin edges to eliminate dead space
|
|
|
|
Purpose of a horizontal mattress suture
|
remove tension from the edges of the wound; assists with hemostasis
|
|
|
|
Purpose of a running subcuticular stitch
|
reduces track marks; use prolene due to low coefficient of friction
|
|
|
|
Purpose of a tip stitch
|
half-buried horizontal mattress - aligns tissue and prevents vascular compromise
|
|
|
|
What does the number on the suture mean?
|
specifies the diameter of that suture material that is required to produce a certain tensile strength (smaller the diameter the higher the number assigned)
|
|
|
|
Branches of Maxillary Artery
|
Middle meningeal artery; Inferior alveolar artery --> MENTAL ARTERY (aka mental branch of inferior alveolar artery); Deep temporal arteries; Masseteric artery; INFRAORBITAL ARTERY; sphenopalatine artery; descending palatine artery;
|
|
|
|
What are the major arteries off the ECA supplying the face?
|
Facial, Maxillary, Superficial temporal, Posterior auricular, Occipital
|
|
|
|
What are the major arteries off the ICA supplying the face
|
Opthalmic (branches are supraorbital, supertrochlear, palpebral, dorsal nasal, lacrimal)
|
|
|
|
The ICA & ECA anastamose where?
|
Angular artery (ECA from Facial a) to Dorsal nasal branch (ICA from Ophthalmic)
|
|
|
|
Damage to temporal nerve causes what?
|
Inability to raise eyebrow (lid ptosis), visual field compromise, flattened forehead lines (loss of expression)
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Frontalis muscle
|
Temporal branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Corrugator supercilli muscle
|
Temporal br of facial n
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Orbicularis oculi muscle (upper portion)
|
Temporal br of facial n
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Auricular muscle (aka temporoparietalis, anterior and superior)
|
Temporal br of facial n
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Orbicularis oculi muscle (lower)
|
Zygomatic br of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Nasalis muscle
|
Zygomatic br of facial n (alar portion); Buccal does the rest
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Procerus muscle
|
Zygomatic br of facial n
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Upper lip muscles
|
Zygomatic & Buccal br of facial n
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: Levator anguli oris muscle
|
Zygomatic br of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: zygomaticus major muscle
|
Zygomatic br of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
What defect occurs when zygomatic branch of facial nerve is damaged?
|
Inability to tightly close eyelid
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: buccinator muscle (mastication)
|
Buccal branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
What innervates the: depressor septi nasi muscle?
|
Buccal branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Nasalis muscle (transverse portion) innervated by?
|
Buccal branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Zygomaticus major muscle?
|
Buccal branch of facial nerve & Zygomatic branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Zygomaticus minor muscle?
|
Buccal branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Orbicularis oris muscle?
|
Buccal branch & Marginal Mandibular branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Levator anguli oris muscle?
|
Buccal branch of facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Lower lip muscle - orbicularis oris muscle innervation?
|
Buccal branch of facial nerve & Marginal mandibular branch
|
|
|
|
What defect occurs when Buccal branch of facial nerve is damaged?
|
Accumulation of food between teeth and buccal mucosa with chewing
|
|
|
|
Depressor anguli oris muscle innervation?
|
Marginal Mandibular branch of the facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Depressor labii inferioris muscle innervation?
|
Marginal Mandibular branch of the facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Mentalis muscle innervation?
|
Marginal Mandibular branch of the facial nerve
|
|
|
|
Risorius muscle innervation?
|
Buccal n of facial n (Marginal Mandibular branch of the facial nerve - per Bolognia)
|
|
|
|
Platysma (upper portion)
|
Marginal Mandibular branch of the facial nerve
|
|
|
|
What defect occurs with damage to the Marginal Mandibular branch of the facial nerve
|
Cannot form symmetric smile, not appreciated when patient is at rest. Inability to pull lower lip down/lateral, cannot evert vermilion border
|
|
|
|
Damage to both zygomatic and buccal?
|
Drooling, food accumulation between cheeks/gingivae, muffled speech
|
|
|
|
Temporalis muscle innervation?
|
Motor of Trigeminal (V3)
|
|
|
|
Masseter muscle innervation?
|
Motor of Trigeminal (V3)
|
|
|
|
CN7 supplies sensation to what?
|
Conchal bowl & Anterior tongue (chorda tympani)
|
|
|
|
What is the only nerve that supplies the muscle on the superficial surface?
|
Buccinator
|
|
|
|
What nerves are at Erb's point?
|
Greater auricular, lesser occipital, spinal accessory
|
|
|
|
Sutures ability to stretch and return to its original form?
|
Elasticity
|
|
|
|
Suture's ability to stretch and maintain its new length?
|
Plasticity
|
|
|
|
Defines stiffness of the suture and its inherent ability to return to its original shape after deformation
|
Memory
|
|
|
|
Force required to cause knot slippage (depends on the smoothness and memory of the suture)
|
Knot strength
|
|
|
|
Polygalactin 910?
|
Vicryl (braided, absorbable)
|
|
|
|
Polyglycolic Acid?
|
Dexon (braided, absorbable)
|
|
|
|
Poliglecaprone 25?
|
Monocryl (monofilament, absorbable) - highest initial strength and knot security of absorbables
|
|
|
|
Polglyconate: glycolide and trimethylene carbonate?
|
Maxon (monofilament, absorbable) - higher initial strength but absorbed faster than PDS
|
|
|
|
Polydioxanone?
|
PDS (monofilament, absorbable); slowest absorption; best tensile strength (more than vicryl, dexon & maxon).
|
|
|
|
Other names for Nylon?
|
Ethilon, Dermalon, Nurolon, Surgilon (monofilament, braided, nonabs)
|
|
|
|
Polybutester?
|
Novafil (monofilament, nonabs) - expansile and contractile elasticiy, good for swelling tissue
|
|
|
|
Polyester, uncoated?
|
Mersilene (braided, nonabs) - soft yet high tensile strength, second only to metal sutures
|
|
|
|
Polyester, coated?
|
Ethibond (braided, nonabs) - soft yet high tensile strength, second only to metal sutures; has less friction than mersilene.
|
|
|
|
Polypropylene
|
Prolene (monofilament, nonabs) - very low friction coefficient
|
|
|
|
Silk?
|
braided/twisted, non-abs; best for mucosal surfaces
|
|
|
|
Stainless steel?
|
Monofilament/braided/twisted
|
|
|
|
How are esters metabolized?
|
pseudocholinesterase in plasma
|
|
|
|
What do esters cross react with?
|
sulfa, thiazides, PABA, PPD
|
|
|
|
Longest acting ester? shortest acting?
|
Tetracaine is longest (2-3 hours); Procaine is shortest (15-60 min)
|
|
|
|
How are amides metabolized?
|
Cytochrome P450 3A4
|
|
|
|
Longest acting amides?
|
Bupivicaine/Levobupivacaine (2-4 hours); Etidocain (3 hours); Ropivacaine (2-4 hours)
|
|
|
|
Shortest acting amides?
|
Lidocaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine (0.5-2hrs)
|
|
|
|
What can prilocaine cause?
|
Methemoglobinemia (avoid use in children)
|
|
|
|
Does adding sodium bicarb increase its onset of action?
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
What is wrong with keeping pre-mixed solution of lidocaine with sodium bicarb around?
|
Epinephrine is stable only in an acidic environment (epinephrine activity is lost at a rate of 25% per week in neutral or alkaline environment)
|
|
|
|
Why do anesthetics work less in tissue with low pH?
|
Its all about the proportion of the anesthetic that is in the ionized form;
The HIGHER the pH – the HIGHER the proportion in the ionized form; HIGH pH correlates to FASTER onset of action; Alkalinization of the anesthetic solution increases the amount of base and the anesthetic’s onset of action |
|
|
|
What are the three portions of chemical structure of anesthetics? And, what do they determine?
|
1. Aromatic ring - onset of activity;
2. Intermediate (middle) chain - determines class (amide vs ester) 3. Amine - determines duration |
|
|
|
Loss of sensation/function occurs in what order with local anesthetic?
|
Temperature, pain, touch, pressure, vibration, proprioception, motor function
|
|
|
|
How many miligrams of lidocaine are in 1cc of 2% lidocaine?
|
2% = 0.02g/ml = 20mg/ml
|
|
|
|
Max total of 1% lido w/o or w/ epi (1:100,000)
|
Without: Adults 4.5mg/kg = 300mg/70kg (30cc); Child 1/3-1/2 mg/kg
With: Adults 7mg/kg = 500mg/70kg (50cc); Child 3-4.5mg/kg |
|
|
|
Recommended dose for tumescent anesthesia?
|
Recommended 35-55mg/kg;
Lidocaine 0.1% (klein's formula) with Epi (1:1,000,000) 1mg/L |
|
|
|
How many miligrams of lidocaine are in 1cc of 2% lidocaine?
|
2% = 0.02g/ml = 20mg/ml
|
|
|
|
Max total of 1% lido w/o or w/ epi (1:100,000)
|
Without: Adults 4.5mg/kg = 300mg/70kg (30cc); Child 1/3-1/2 mg/kg
With: Adults 7mg/kg = 500mg/70kg (50cc); Child 3-4.5mg/kg |
|
|
|
Recommended dose for tumescent anesthesia?
|
Recommended 35-55mg/kg;
Lidocaine 0.1% (klein's formula) with Epi (1:1,000,000) 1mg/L |
|
|
|
Class B or C? Bupivicaine, Lidocaine, Prilocaine, Mepivacaine, Etidocaine
|
Category C: Bupivicaine (cardiotoxic risk), Mepivacaine (BM is bad)
Category B: Lidocaine, Prilocaine, Etidocaine |
|
|
|
What is methemoglobinemia?
|
Hemoglobin Fe2+ gets oxidized to Fe3+ which reduces its oxygen carrying capacity
|
|
|
|
Treatment of methemoglobinemia?
|
< 30% removal of drug, O2, observe; >30% Tx with IV methylene blue 1-2mg/kg as a 1% solution (or Ascorbic acid 300-1000 mg/day iv in three to four doses for G6PD deficiency patients)
|
|
|
|
What drug prevents methemoglobinemia with Dapsone use?
|
Cimetidine (reduces hepatic oxidation of dapsone to hydroxylamine, thereby limiting methemoglobinemia formation)
|
|
|
|
Hexachlorophene
|
Phisohex
- Gram+ - Do NOT use on children or pregnant women - Potential neurotoxicity, therefore it was discontinued in 1970s (ex., Mohs fellow getting tingling in her fingers - Steifel question) - Teratogenicity |
|
|
|
Chlorhexidine
|
Hibiclens
- Gram +, Gram - - Keratitis & allergic rxn if direct ocular contact - Tympanic membrane damage |
|
|
|
Iodophor or Povidone-iodine
|
Betadine
- Gram +, Gram - - Allergic contact dermatitis |
|
|
|
What two topical medications have polymyxin B?
|
Polysporin (Bacitracin/Polymyxin B) and Neosporin (Neomycin/Bacitracin/Polymyxin B)
Polymyxin B has pseudomonas coverage (vs the others - neomycin, bacitracin, bactroban, erythromycin) |
|
|
|
Name three topical antibiotics with Gram negative coverage
|
Gentamicin (resistance seen), Neomycin (no pseudomonas coverage), Polymyxin B (pseudomonas coverage)
|
|
|
|
What is in polysporin?
|
Bacitracin & Polymyxin B
|
|
|
|
What is Neosporin?
|
Neomycin, bacitracin, polymyxin B
|
|
|
|
What are some side effects of silvadene?
|
Neutropenia, kernicterus, ACD with sulfa allergies
|
|
|
|
Thin Film Dressing Uses?
|
Skin tears, STSG donor site, laser resurfacting, Mohs
|
|
|
|
Foam dressing uses?
|
Chronic wounds, dermabrasion, burns, mohs, laser resurfacing; AVOID IN DRY WOUNDS
|
|
|
|
Hydrogel dressing uses?
|
Ulcers, dermabrasion, laser resurfacing, superficial thermal burns, chemical peels, graft donor sites; AVOID IN INFECTED WOUNDS
|
|
|
|
Alginate dressing uses?
|
Chronic highly exudate wounds, Full thickness burns, surgical wounds, STSG donor sites, Mohs
|
|
|
|
Hydrocolloid uses?
|
Chronic ulcers, burns, trauma wounds, surgery wounds, dermabrasion, bullous dz, inflammatory disease; AVOID IN INFECTED WOUNDS
|
|
|
|
What is the temperature of liquid nitrogen?
|
Temp: -196 C (or -320 F)
|
|
|
|
What is goal for temperature at the periphery of the ice ball in cryosurgery?
|
Temp: - 50-60C
|
|
|
|
What is resistance? what makes it higher or lower?
|
Resistance = ability of conductor to impede passage of electric current (ohms W)
- Proportional to length of substance - Inversely proportional to its x-sectional area - Fat has high resistivity - Muscle has low resistivity - Skin has variable resistivity Ex., Dry skin 100 000 W and Wet skin 200 W |
|
|
|
What is Ohm's Law?
|
Voltage = IR (current x resistance)
|
|
|
|
Biterminal?
|
Low resistance; Low voltage needed for adequate current
|
|
|
|
Monoterminal?
|
High resistance, requries high voltage for adequate current
|
|
|
|
Undamped wave?
|
Pure tissue separation with minimal hemostasis
|
|
|
|
Damped wave?
|
Marked tissue destruction - greater damping means increased tissue damage and hemostasis; lesser damping - less hemostasis/better healing
|
|
|
|
Continuous vs Discontinuous wave?
|
continuous wave results in greater tissue heating
|
|
|
|
Best waveform for pure cutting
|
Continuous, undamped (may also use discontinuous, undamped)
|
|
|
|
Best waveform for cutting and coagulation
|
Continuous, damped
|
|
|
|
Best wave form for desiccation and coagulation
|
Discontinuous, damped
|
|
|
|
Name the monoterminal circuits
|
Electrofulguration, Electrodessication (remember DEF Va (high voltage, low amperage)
|
|
|
|
Name the Biterminal circuits
|
Electrocoagulation, Electrosection with coagulation, Electrosection without coagulation (low voltage, high amperage)
|
|
|
|
Which electrosurgical technique has not circuit?
|
Electrocautery
|
|
|
|
What is the most important cell in the vascular phase of wound healing?
|
platelets
|
|
|
|
What is the most important cell for the inflammatory phase of wound healing?
|
Macrophages - the only cell that can tolerate low O2
|
|
|
|
What is a Life Tenant obligated to do?
(4 things - physical and financial): |
(i) preserve the land and structures in a reasonable state of repair,
(ii) pay interest on mortgages (not principal); (iii) pay ordinary taxes on the land; (iv) pay special assessments for public improvements of short duration (improvements of long duration are apportioned between the life tenant and future interest holder). |
|
|
|
What are the four stages of successful graft?
|
Imbibition, Inosculation, Neovascularization, Maturation (I'm In No Mood)
|
|
|
|
Explain in detail the stages of successful graft healing?
|
Imbibition (first 48 hours, graft sustained by RECIPIENT bed)
Inosculation (day 2-3, blood vessels from the GRAFT establish connection with the wound bed) Neovascularization (Day 7 - ingrowth of new vessels INTO the graft) Maturation (Months - sensory innervation) |
|
|
|
Name the wavelengths of light
|
Gamma rays
X-rays UVC = 200-290 UVB = 290-320 UVA = 320-400 Visible light = 400-760 IR > 760-1400 Microwaves Radiowaves |
|
|
|
What are the three important features of LASERs?
|
Coherent – waves of light are in phase in time & space
Represents uniform wave front --> allows energies to be ADDITIVE Monochromatic – 1 wavelength ONLY Collimated – Parallel, NON-divergent waves I.E., Diameter of the beam changes minimally over distance focused High Intensity (as per Dr. Ross) |
|
|
|
Definition of:
Energy (Radiant Exposure) |
Fundamental unit of work
Unit: Joules |
|
|
|
Definition of:
Power |
Rate at which energy is delivered
Unit: Watts = (J/s) |
|
|
|
Definition of: Fluence
|
Amount of energy delivered per unit area
Unit: Joules/cm2 |
|
|
|
Definition of: Irradiance (Power density)
|
Power delivered per unit area
Watts/cm2 |
|
|
|
Definition of: Pulse Duration / Width
|
Laser exposure duration
Units: seconds |
|
|
|
Definition of: Spot Size
|
Diameter of the laser beam on skin surface
Unit: mm |
|
|
|
Definition of: Chromophore
|
Medium that absorbs light
|
|
|
|
Definition of: Thermal Relaxation Time
|
Time required for heated tissue to lose 50% of its heat through diffusion
Unit: seconds |
|
|
|
Name the wavelengths of light
|
Gamma rays
X-rays UVC = 200-290 UVB = 290-320 UVA = 320-400 Visible light = 400-760 IR > 760-1400 Microwaves Radiowaves |
|
|
|
What are the three important features of LASERs?
|
Coherent – waves of light are in phase in time & space
Represents uniform wave front --> allows energies to be ADDITIVE Monochromatic – 1 wavelength ONLY Collimated – Parallel, NON-divergent waves I.E., Diameter of the beam changes minimally over distance focused High Intensity (as per Dr. Ross) |
|
|
|
Definition of:
Energy (Radiant Exposure) |
Fundamental unit of work
Unit: Joules |
|
|
|
Definition of:
Power |
Rate at which energy is delivered
Unit: Watts = (J/s) |
|
|
|
Definition of: Fluence
|
Amount of energy delivered per unit area
Unit: Joules/cm2 |
|
|
|
Definition of: Irradiance (Power density)
|
Power delivered per unit area
Watts/cm2 |
|
|
|
Definition of: Pulse Duration / Width
|
Laser exposure duration
Units: seconds |
|
|
|
Definition of: Spot Size
|
Diameter of the laser beam on skin surface
Unit: mm |
|
|
|
Definition of: Chromophore
|
Medium that absorbs light
|
|
|
|
Definition of: Thermal Relaxation Time
|
Time required for heated tissue to lose 50% of its heat through diffusion
Unit: seconds |
|
|
|
Wavelength of:
Argon? Argon pumped tunable dye? Copper Vapor / Bromide? KTP? Nd:YAG? Pulsed dye? Ruby? Alexandrite? Krypton? |
Argon? 488, 514
Argon pumped tunable dye? 577, 585 Copper Vapor / Bromide? 510, 578 KTP? 532 Nd:YAG? 532 Pulsed dye? 510, 585 Ruby? 694 Alexandrite? 755 Krypton? 568 |
|
|
|
What is wavelength of:
Woods Lamp Blu U Diode Nd:YAG Erbium CO2 Excimer Red U Light therapy for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia |
Woods Lamp 366nm
Blu U 400-410 Diode 810, 1450 Nd:YAG 1064 Erbium 2940 CO2 10,600 Excimer 308 Red U 630 Light therapy for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia 460 |
|
|
|
Fraxel Wavelength?
|
1550nm
|
|
|
|
What is Gold STD laser for vascular lesions?
|
PULSED DYE
585-95nm (PDL), 510nm (Pigmented PDL) Green / Yellow Vascular (red color), scars/striae, NON-ablative dermal remodeling - GOLD STD for VASCULAR LESIONS 510nm --> Epidermal Pigment & Tattoos - Red/orange/yellow tattoos (ROY) |
|
|
|
What is Gold Standard for Hiar removal in types I-4 skin?
|
ALEXANDRITE
755nm Borderline of Visible & Near IR spectrum QS: Dermal pigment, Epidermal pigment, & **GREEN**/blue/black tattoos PREFERRED LASER FOR GREEN TATTOO REMOVAL Normal mode: hair removal, leg veins (blue color) GOLD STD OF HAIR REMOVAL IN TYPES 1-4 SKIN |
|
|
|
Best Tatoo for GREEN tatoos?
|
ALEXANDRITE
755nm Borderline of Visible & Near IR spectrum QS: Dermal pigment, Epidermal pigment, & **GREEN**/blue/black tattoos PREFERRED LASER FOR GREEN TATTOO REMOVAL Normal mode: hair removal, leg veins (blue color) GOLD STD OF HAIR REMOVAL IN TYPES 1-4 SKIN |
|
|
|
Best laser for Nevus of OTA?
|
RUBY
694nm Red QS: Dermal pigment, Epidermal pigment green/blue/black tattoos GOLD STD FOR NEVUS OF OTA TREATMENT Normal mode: hair removal & leg veins |
|
|
|
Name the substance that creates the following tatoo pigment:
Red? Blue? Black? Green? Yellow? Brown? Violet/Purple? White? |
Red? Cadmium Selenide, Mercury, Cinnabar
Blue? Cobalt Black? Carbon, Iron Oxide Green? Chromium/Chromate, Cyanide Yellow? Cadmium Sulfide Brown (Ferric hydrate)? Ochre Violet/Purple? Manganese White? Titanium and Zinc Oxide |
|
|
|
Best Laser for tatoo removal?
|
KTP = Red
Pigmented PDL = Yellow *archaic laser seldom used today* Alexandrite = Green Nd:Yag = Blue, Black |
|
|
|
Laser choices for Tatoo pigment?
|
Black/Blue:
Q-switched ruby (694) Q-switched Alex (755) Q-switched Nd:Yag (1064)*** Green Q-switched Alex (755)*** Q-switched Ruby (694) Red - Freq doubled Q-switched Nd:Yag (532nm)*** -Pigmened pulsed dye (510) Yellow - Pigmented pulsed dye (510) |
|
|
|
What is Jessner’s made of (4 components)?
|
Resorcinol, sal acid, lactic acid, ethanol
|
MN – JESS & SALI LACked the RESORces to buy EtOH
|
|
|
What is the Baker-Gordon Formula?
|
Deep Depth Peels:
Baker-Gordon Formula = most widely used Contains 88% phenol, croton oil, septisol, H2O Croton oil is keratolytic/epidermolytic that enhances phenol penetration Variations: Littons = glycerin for septisol Beeson McCollough formula which uses defatting & heavier application of Baker-Gordon |
|
|
|
Which chemical peel requires Neutralization?
|
Glycolic acid:
Can be neutralized with H2O or Sodium Bicarb |
|
|
|
What is the active ingredient in sunless tan lotion?
What epidermis layer does it stain? |
Dihydroxyacetone (DHA);
Stratum Corneum |
|

