![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
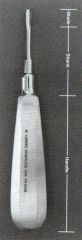
|
Straight elevator Uses: luxation and extraction of remaining posterior roots Working end has a concave (sometimes serrated) surface on one side which faces the tooth Lever action |
|
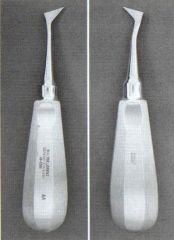
|
Cryer's elevator luxation and extraction of lower posterior teeth Used to remove remaining roots of multi-rooted teeth Wheel and axle action |
|
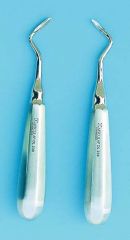
|
Apexo elevator
Mainly used to remove remaining root tips in both jaws
Wedge action |
|
|
Lever Principle |
In order to gain a mechanical advantage the effort arm on one side of the fulcrum has to be longer than the resistance arm on the other side |
|
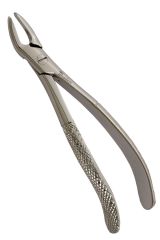
|
Maxillary anterior forceps Used for extracting upper incisiors and canines Straight handles |
|
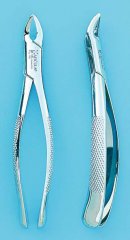
|
Maxillary premolar forceps
Used for extracting upper premolars
Symmetrical concave beaks (closed)
Curved handles |
|
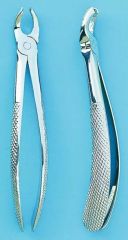
|
Maxillary right or left molar forceps
Used for extraction of maxillary posterior teeth
One for the left and one for the right
Asymmetrical beaks, concave palatal beak and pointed buccal beak (shows which side of the arch it's used for) Open beaks
Curved handles |
|
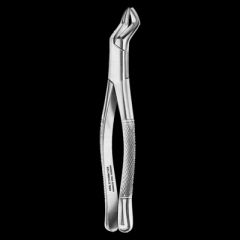
|
Jockey forceps Used for extraction of maxillary third molars |
|
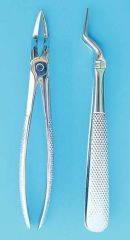
|
Bayonet forceps Used for extraction of maxillary posterior remaining roots Straight handles but angled beaks |
|

|
Mandibular anterior forceps Used for extraction of mandibular incisors Can also be used for extraction of lower remaining roots Closed beaks |
|

|
Mandibular premolar forceps Used for extraction of mandibular premolars Can also be used to extract the mandibular canines Open beaks |
|

|
Mandibular molar forceps Used for extraction of mandibular molars Symmetrical pointed beaks and the sharp pointed tips engage the bifurcation at the buccal and lingual surfaces |
|
|
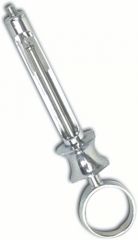
Aspirating dental syringe Contains hook or harpoon at the end of piston Used for medically compromised patients |
|

|
Self-aspirating dental syringe Does not contain hook/harpoon at end of piston Commonly used |
|
|
Components of Local anesthetic solution |
1) Local anaesthetic agent (lidocaine) 2) Vasoconstrictor (epinephrine) 3) Reducing agent (sodium metabisulphite) 4) Preservative (methyl paraben) 5) Fungicide (thymol) 6) Vehicle (modified Ringer solution) |
|
|
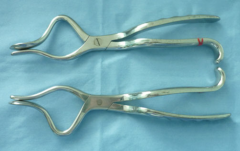
Rowe's disimpaction forceps |
|
|
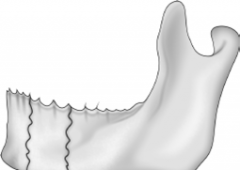
Simple Fracture |
|
|
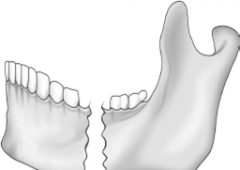
Compound Fracture |
|
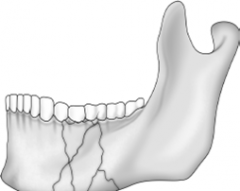
|
Comminuted Fracture |
|
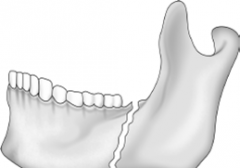
|
Horizontally favorable fracture |
|
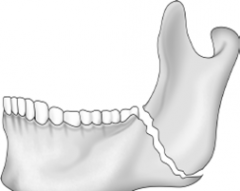
|
Horizontally unfavorable fracture |
|
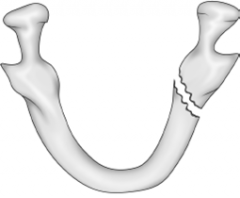
|
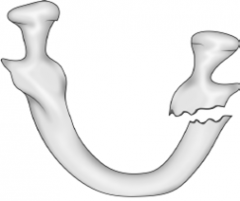
Vertically favorable fracture |
|
|
Vertically unfavorable fracture |
|
|
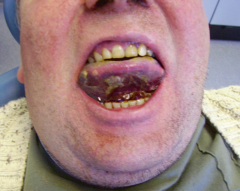
Coleman's sign |
|
|
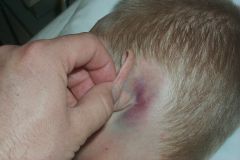
Battle's sign |
|
|
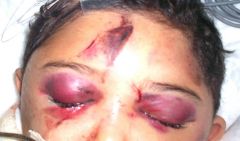
Racoon eyes |
|
|
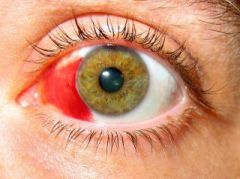
Subconjuctival hemorrhage |
|
|
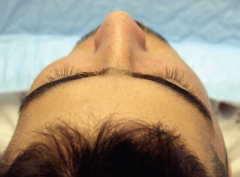
Flattening of malar prominence |
|
|
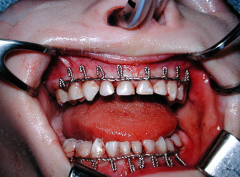
Ridson Cableused in pediatic maxillofacial trauma |
|
|
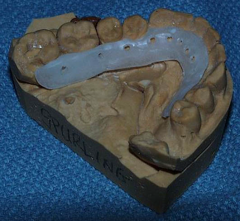
Acrylic splint |
|
|
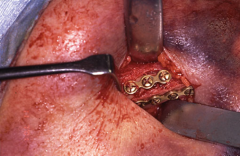
Internal fixation using miniplates |
|

|
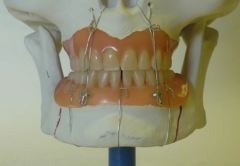
Gunning splint |
|
|
use of the patient’s dentures wired to the jaw, to splint the fracture, with intermaxillary fixation |
|
|
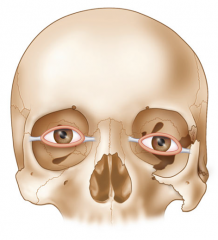
Antimongoloid slant |
|
|
Temporal approach Gillie's lift Presto elevator |
|

|
Malar Hook or Poswillo Hook used in percutaneous approach |
|
|
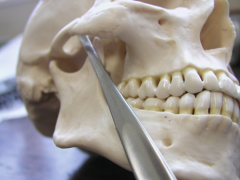
Intra-oral approach or Keen's approach |
|
|
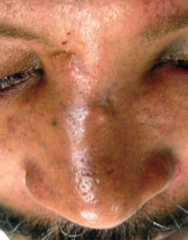
Nasal deviation |
|
|
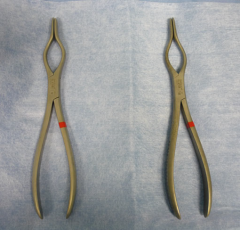
Walsham's septum straightening forceps |
|
|
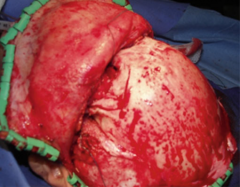
Coronal flap |
|
|
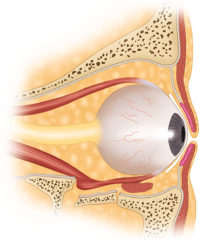
Blowout fracture |
|
|
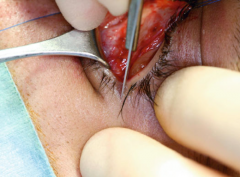
Lateral canthotomy for treatment of retrobulbar hematoma |
|
|
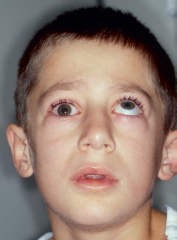
Trapdoor phenomenon |
|
|
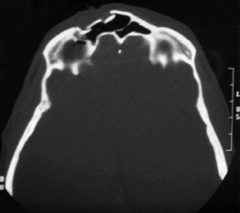
Type 1 Anterior table only |
|
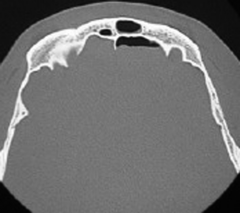
|
Type 2 Posterior table |
|
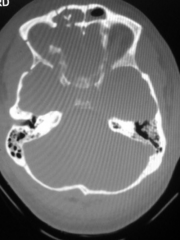
|
Type 3 Anterior and posterior tables |
|
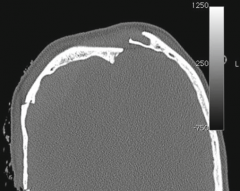
|
Type 4 Through and Through |
|
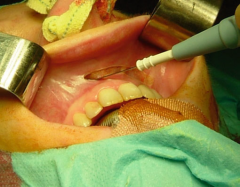
|
Maxillary gingivobuccal sulcus incision |
|
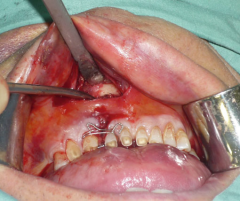
|
Mandibular vestibular incision |
|
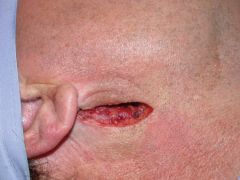
|
Periauricular incision/ approach |
|
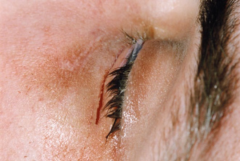
|
Subciliary midlid incision |
|
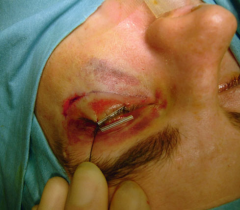
|
Subtarsalmid lid incision |
|
|
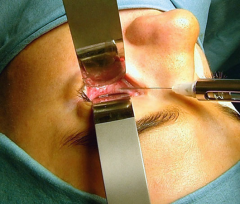
Transconjunctivalmid lid incision
|
|
|
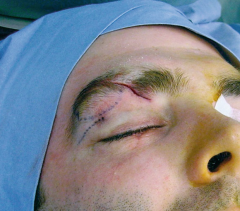
Upper lid incision |
|
|
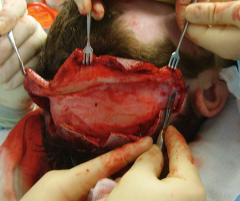
Coronal incision |
|
|
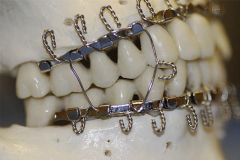
Arch bars |
|
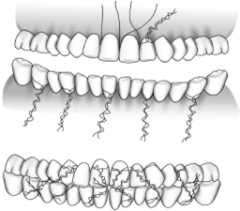
|
Gilmer method |
|
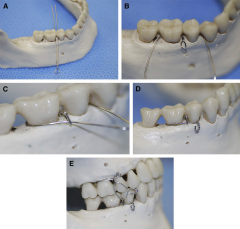
|
Eyelet method |
|
|
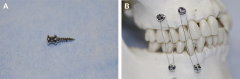
Intermaxillary fixation screw technique |
|
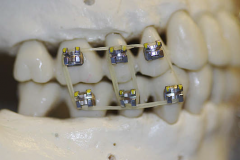
|
Bonded modified orthodontic bracket |
|
|
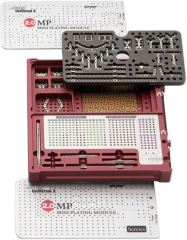
Miniplates |
|
|
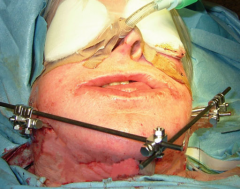
External fixation |
|
|
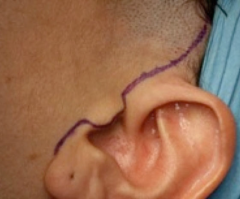
Retromandibular incision |
|
|
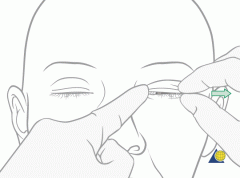
Bowstring test |
|
|
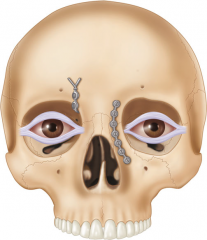
Canthopexy |
|
|
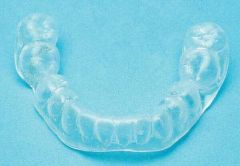
Occlusal Splint (therapy for TMJ/MPD) |
|
|
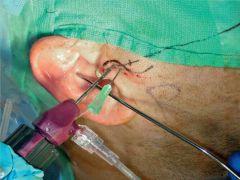
Arthrocentesis |
|
|
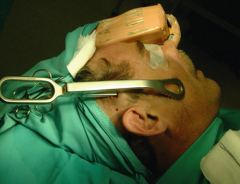
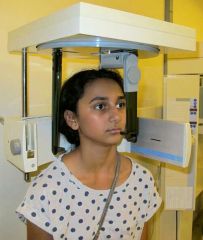
Cephalostate |
|
|
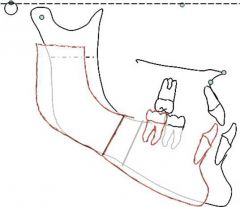
Visual treatment objective (VTO) Paper osteotomy |
|
|
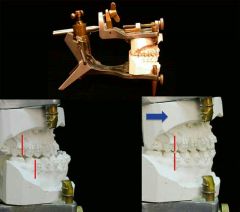
Dental Model surgery |
|
|
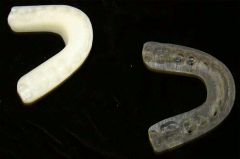
Occlusal Splint (orthognathic surgery) |
|
|
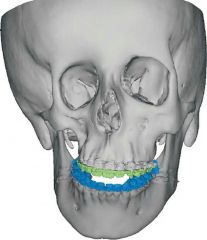
Computer Assisted Surgical Simulation |
|
|
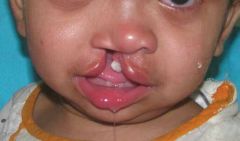
Cleft lip |
|
|
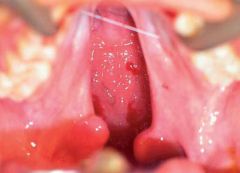
Cleft palate |
|
|
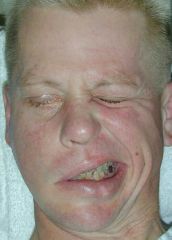
Facial nerve injury (Bell's Palsy) |
|
|
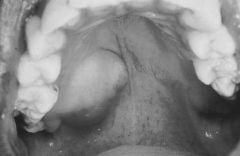
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma |

