![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anesthesia systems
-functions |
-deliver oxygen
-deliver anesthetic gas -remove CO2 -Provide means of IPPV |
|
|
IPPV
-definition |
Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation
|
|
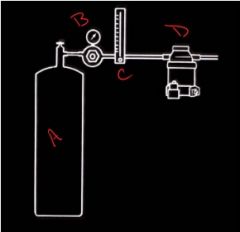
|
A = gas source
B = Pressure Regulator C = Flow meter D = Vaporizer |
|
|
Gas sources
|
-high pressure cylinders
-medical gas piping system -liquid oxygen bulk tank |
|
|
How to differentiate high pressure cylinders
|
-color coded
-pin coded -thread diameter and sizing code |
|
|
Medical gas
-color scheme |
-green = oxygen
-yellow = medical air -blue = nitrous oxide |
|
|
Oxygen cylinder
-physical state |
-compressed gas
|
|
|
Medical air cylinder
-physical state |
-compressed gas
|
|
|
Nitrous oxide cylinder
-physical state |
-liquid/gas interface
|
|
|
Pressure gauge for gas cylinder measures what?
|
-gas quantity for compressed gas (oxygen, medical air)
-can't measure quantity of liquid/gas interface (nitrous oxide) |
|
|
Noninterchangeable safety system
-located where |
-b/n cylinder and regulator
|
|
|
Noninterchangeable safety system
-uses what |
-unique threaded outlets
-varied thread sizes -different seat and nipple sizes -pin code |
|
|
Pin code is used for what kind of cylinders?
|
-E cylinders
|
|
|
Pin code
-components |
-2 pins on each yolk
-2 hols on each tank stem -unique pin location for each medical gas |
|
|
Type of wall outlets used
|
-Ohio style quick connects
|
|
|
Pressure regulator
-location -function |
-b/n high pressure system and intermediate pressure system
-decreases pressure to 37-55 psi |
|
|
Flowmeter assembly
-function |
-controls, measures, and indicates rate of flow of gas passing through the flow meter
|
|
|
Oxygen Flush Valve
-function |
-provides a high flow of oxygen to the breathing circuit that bypasses the vaporizer in order to dilute and flush anesthetic gases from the breathing circuit
|
|
|
Oxygen Flush valve
-rate |
-35-75 L/min
|
|
|
Low pressure system
-components |
-vaporizers
-common gas outlet -circle or non-circuit breathers |
|
|
Low pressure system
-pressure |
-slightly above atmospheric pressure
|
|
|
Pressure relationships
-1 psi --> airway pressure -1 psi --> blood pressure |
-airway pressure = 70 cmH20
-blood pressure = 52 mmHg |
|
|
What should the pressure in the breathing circuit never be greater than?
|
-20 cmH2O
|
|
|
vaporizer
-function |
-change liquid anesthetic into a vapor and add a controlled amount of the vapor to the flow of oxygen and other carrier gases
|
|
|
Vaporizer methods of regulating output concentration
|
-variable bypass*
-measured flow |
|
|
Methods of vaporization
|
Flow over
-with or without wick Bubble through Flow over or bubble through |
|

Vaporizer type
|
Flow over vaporizer
|
|

Vaporizer type
|
Bubble Through Vaporizer
|
|
|
Vaporizer locations
-difference |
Inside breathing system
Outside breathing system: only gas going through the vaporizer is O2, non from the patient |
|
|
Safer vaporizer location for IPPV
|
outside the breathing system
|
|
|
Outside breathing system vaporizer
-requirement |
-precision vaporizer
|
|
|
Inside the breathing system effect
|
increased patient ventilation increases anesthetic concentration
|
|
|
Vaporizer location inside the breathing system
|
-inspiratory arm
|
|
|
Vaporizers
-methods of temp compensation |
-none
-supplied heat (room air, electric heated) -flow alteration |
|
|
Why does a vaporizer need to stay within a temperature range?
|
-If outside of the recommended temp range, the vaporizer will not deliver the correct anesthetic gas conc.
|
|
|
Vaporizer
-specificity |
-unique agents
-multiple agents |
|

Vaporizer type
|
-liquid vaporizer into vaporization chamber (able to know max concentration)
|
|
|
Circle breathing system
-components |
-Y-piece
-breathing tubes -uni-directional valves -fresh gas inlet -absorber -relief valve -rebreathing bag -pressure gauge |
|
|
Y-piece
-sizes |
-endotracheal tube: 15 mm female
-breathing tubes: 22 mm male |
|
|
Why are the breathing tubes corrugates?
|
-keep them from twisting and kinking
|
|
|
Uni-directional valve
-function |
-2 valves that direct gas flow toward the patient in one breathing tube and away from the patient in the other breathing tube
-both need to function properly for unidirectional gas flow |
|
|
Canister/Absorber
-has to hold how much air |
-at least 2x the tidal volume
-intragranular air space must be greater than the max tidal volume |
|
|
Canister/absorber
-chemical |
-soda lime
|
|
|
Surgivet soda lime canister
-characteristics |
-U shaped
-narrow -long and skinny with limited capacity -high resistance -not for animals >20kg |
|
|
Soda lime
-absorbes what? |
-CO2
|
|
|
Soda lime
-components |
-sodium hydroxide
-water (need humidity for soda lime to work) -calcium hydroxide -ethyl violet indicator -doesn't regenerate after use |
|
|
Soda lime
-when to change |
-if 1/3 canister is violet after surgery
|
|
|
Reservoir bag
-size |
-must exceed patients largest tidal breath
|
|
|
Reservoir bag
-what happens when a larger bag is used |
-more total gas will be put in the system, so gas concentration will take longer to change
|
|
|
Breathing circuit manometer
-function |
-indicated pressure in the breathing circuit in mmH2O
|
|
|
Pop-off valve
-function |
-relieves the breathing system of excess gas if input exceeds uptake by the patient
|
|
|
Pop-off valve
-location |
-expiratory side
|
|
|
Pop-off valve
-size |
-19 mm scavenging outlet
|
|
|
Carrier gas flow
-closed circle |
3-5 ml/kg/min
-just enough to make sure animals metabolic needs are met -pop-off valve open |
|
|
Carrier gas flow
-semi closed circle |
30 mL/kg/min
-flow greater than metabolic requirement -higher flow at beginning of anesthetic to more easily change anesthetic conc. |
|
|
Carrier Gas Flow
-non-rebreathing |
-200 ml/kg/min
|
|
|
Non-rebreathing system
-function |
-rebreathing of expired gas is eliminated if appropriate fresh gas flows are supplied
|
|
|
Non-rebreathing system
-advantages |
-low resistance to breathing
-simple design -no valves -light weight -inexpensive |
|
|
Non-rebreathing system
-disadvantages |
-high gas flow (cost, dec. body temp, loss of humidity)
-rebreathing of CO2 occurs if appropriate gas flow not used |
|
|
Types of Non-rebreathing circuits
|
-bain circuit
-modified Jackson rees -arye's T-piece -Norman elbow |
|
type of non-rebreathing circuit
|
-Bain circuit
|

