![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
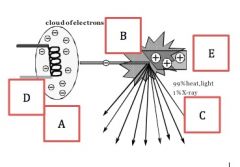
Determine the labels
|
A: mA
B: Kv C: s D: Cathode E: Anode |
|
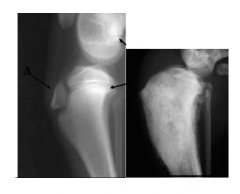
What does the right hand side picture show?
|
Increased radiopacity; sclerosis (thickening of bone tissue)
|
|
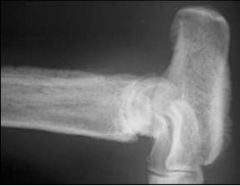
What does this picture show?
|
Periosteal reaction (columnar)
|
|
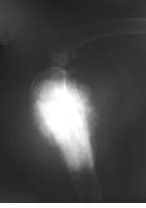
What is this picture an example of?
When does this occur? |
Sunburst periosteal reaction.
Osteo or chondro-sarcomas. |
|
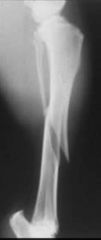
Type of fracture?
|
Oblique
|
|
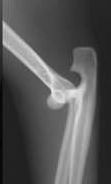
Name given to this type of injury?
|
Luxation of joint
|
|
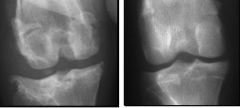
What does the left hand picture show if the right picture is to be taken as healthy?
|
Degenerative Joint Disease (arthrosis)
|
|
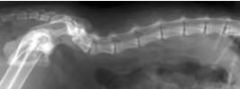
What deformity is shown?
|
Lordosis
|
|
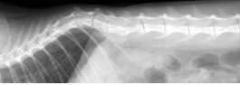
What deformity is shown?
|
Kyphosis
|
|
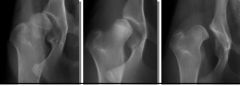
These are all an example of X?
From left to right name the types of X |
X= incongruence
1. Shallow acetabulum 2. Deformed femoral head 3. subluxation |
|
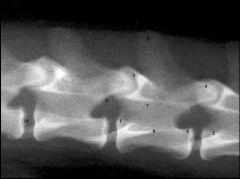
Label the structures 1 through to 10
|
1. end plate crane
2. trans proc 3. articular process cran 4. articular process caud 5. spinous process 6. end plate caud 7. spinal canal (canalis vertebralis) 8. Vertebral body 9. intervertebral foramen 10. intervertebral space |
|
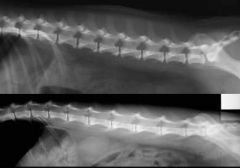
Which is an x-ray of a cat?
|
The bottom; vertebrae are closer to skin
|
|
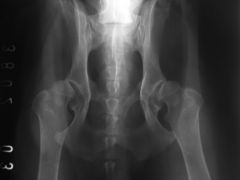
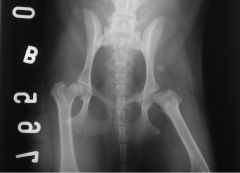
This x-ray is an example of?
|
Hip dysplasia
|
|
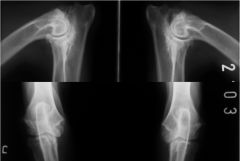
What does the x-ray show?
|
Elbow arthrosis
|
|
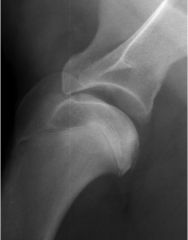
Which joint?
What developmental anomaly? |
Shoulder
Osteochondrosis dissecans |
|
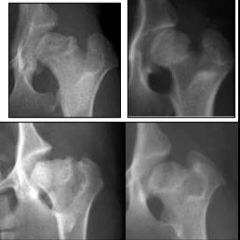
Which disease?
|
Perthe's Disease:-
- decrease radiopacity in fem head - deformed fem head |
|
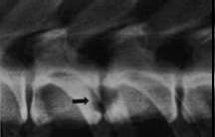
What does the arrow indicate?
|
Dyscospondylitis; osteolytic endplates rounded by sclerotic zone
|
|
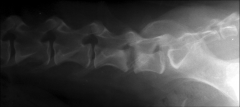
What can be seen in the x-ray?
What could it indicate? |
Osteophyte (bony projection) on vertebral body
Indication of spondylosis |
|
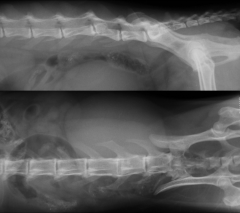
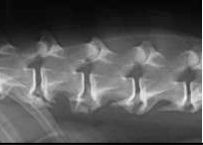
What is seen in both pictures?
|
Vertebral column fracture
|
|
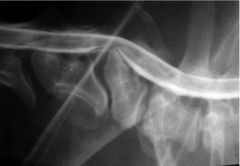
What does the x-ray show?
What is it an indication of? |
Disc protrusion C6-7
Wobbler syndrome |
|
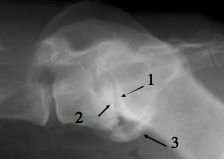
What can be seen at arrow 1?
What does it indicate? |
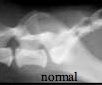
Collapsed lumbosacral intervertebral space
Cauda Equina Compression syndrome (2. sclerotic endplates, 3. LS spondylosis deformans) |
|
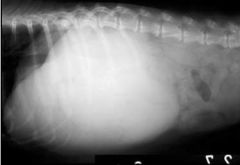
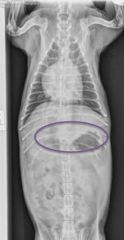
Abnormality shown by this abdominal x-ray?
|
Hepatomegaly
|
|
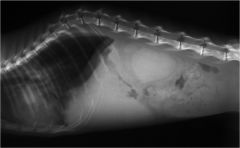
What is the radiographic sign indicating pancreatitis?
|
soft tissue radiopacity in the epigastrium
|
|
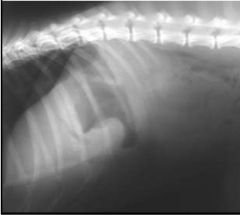
Organ indicated and therefore which species?
|
Stomach; J-shaped therefore cat
|
|
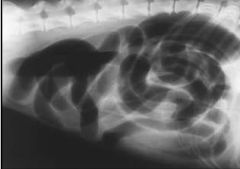
Organ indicated and therefore which species?
|
Stomach; U shaped across midline therefore dog
|
|
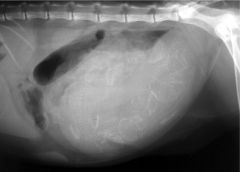
Abnormality shown?
|
Mesenteric volvulus
|
|
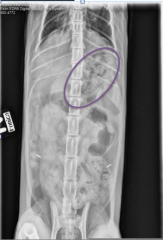
What can be seen in this abdominal x-ray?
|
Foetal skeleton; Gravid >45 days
|
|
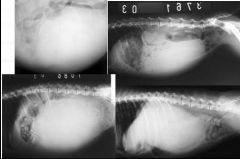
What is shown in all the x-ray's?
|
Abdominal masses
|
|
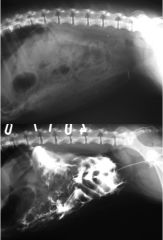
What is shown in the x-ray's?
|
Rupture of urinary bladder
|
|
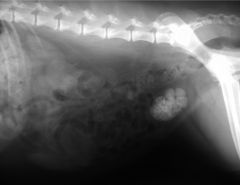
What is shown?
|
Cystolithiasis
|
|
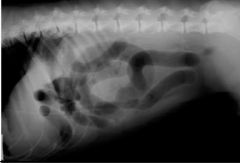
What can be seen?
Indication of? Type of radiography? |
Gas accumulation (increase radiopacity)
obstruction survey/plain |
|
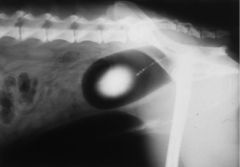
What type of radiography was used for this x-ray?
|
Double contrast urography
|
|
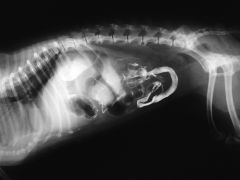
What type of radiography is this x-ray an example of?
|
Contrast radiograph
|
|
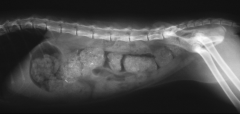
What can be seen?
What is indicated? |
Accumulation of dense, firm contents
Constipation |
|
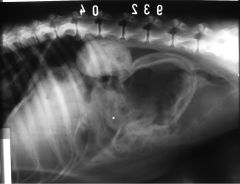
What can be seen?
What is indicated? |
Gas in the peritoneal cavity
Pneumoperitoneum |
|
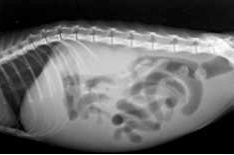
What can be seen?
What is indicated? |
Fluid accumulation
Intestinal perforation |
|
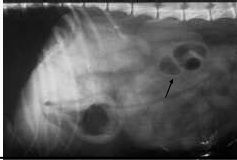
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Caecum
|
|
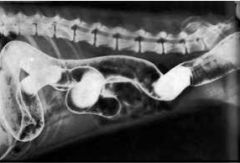
What type of study?
What is shown? |
Double contrast study
Large intestine |
|
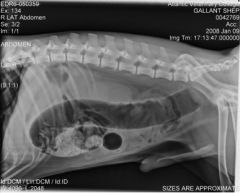
What abnormality can be seen?
|
Megacolon
|
|
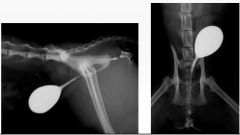
What type of radiography?
|
Positive contrast retrograde cystography
|
|
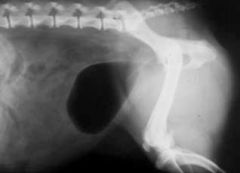
Type of radiography?
|
Pneumocystography
|
|
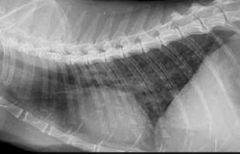
Which lung pattern is shown?
|
Interstitial
|
|
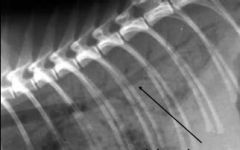
What lung pattern can be seen?
What is indicated by the arrow? |
Alveolar
air bronchogram |
|
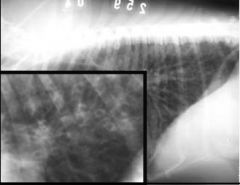
Which lung pattern can be seen?
|
Bronchial
|
|
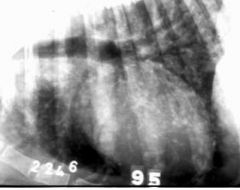
What type of lung pattern can be seen?
|
Nodular- micronodular
|
|
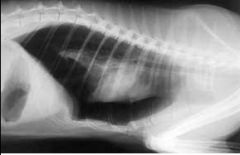
Which pulmonary anomaly?
|
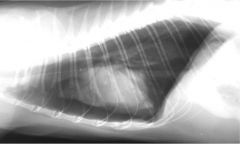
Pneumothorax
|
|
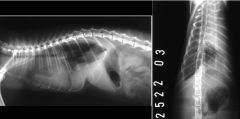
Which species?
What can be seen? Which pulmonary anomaly? |
Cat
Pleural fluid Haemothorax |
|
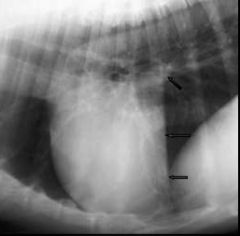
Which side is the cardiac enlargement?
|
Left;
(Elevated trachea, straight caud margin of heart, secondary pulmonary oedema) |
|
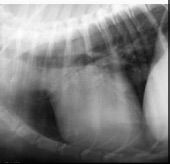
Which side is the cardiac enlargement?
|
Right;
(Rounded cranial margin of heart, longer contact with sternum) |
|
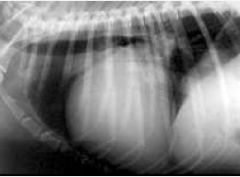
What cardiac anomaly is shown?
|
Cardiomegaly (generalised enlargement)
|
|
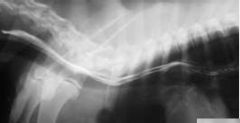
Oesophagus of which species?
|
Dog
(longitudinal folds) |
|
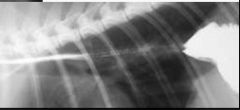
Oesophagus of which species?
|
Cat
(herring bone pattern) |
|
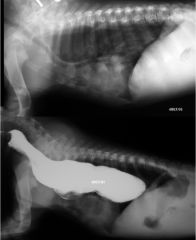
What is shown?
Which types of radiography? |
Megaoesphagus totalis
Survey (top) and contrast |
|
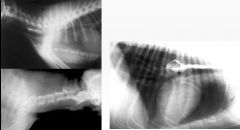
What is shown in all of the x-ray's?
|
Oesophageal foreign body
|
|
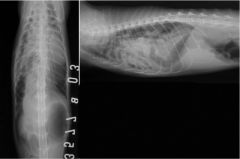
What condition is shown?
|
Diaphragmatic hernia
|
|
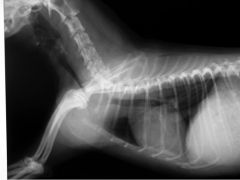
What is shown?
|
Tracheal collapse
|
|
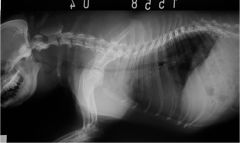
What is seen?
Which syndrome is this characteristic? Which breed is most susceptible to this? |
Tracheal hypoplasia
Brachycephalic syndrome Boxers |
|
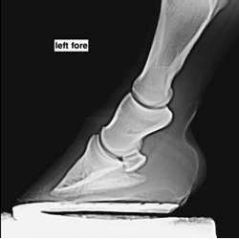
Which view?
|
Lateromedial
|
|
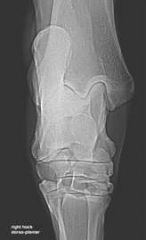
Which view?
|
Dorsopalmar/plantar
|
|
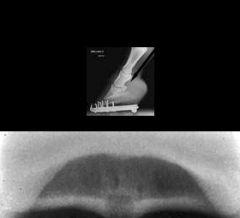
Which view?
|
Craniocaudal
|
|
Which view?
|
Palmaroproximal-palmarodistal oblique
|
|
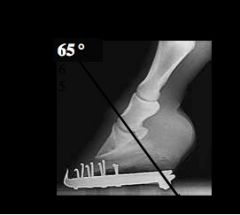
Which view?
|
Dorsoproximal-palmarodistal oblique
|
|
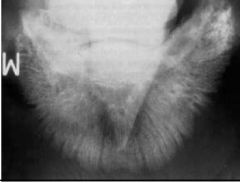
What pathological change?
Which anatomical structure? |
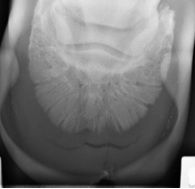
Osteitis
Solar surface, distal phalanx |
|
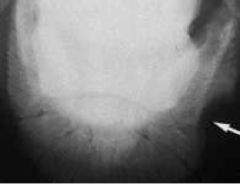
What is indicated by the arrow?
|
Keratoma
|
|
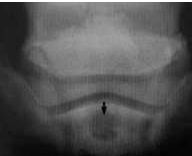
What is indicated by the arrow?
Which anatomical structure? |
Cyst
Distal phalanx |
|
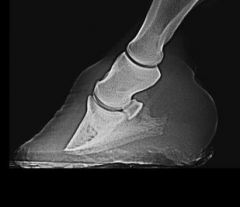
What diagnosis can be made from the x-ray?
|
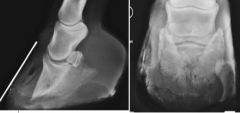
Laminitis
|
|
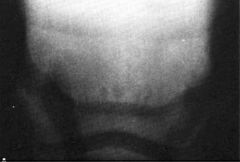
Which view?
Usually used for what anatomical structure? |
Oxspring
Navicular bone |
|
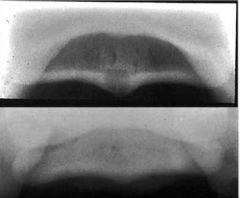
Which view?
|
Skyline (palmar prox palmar dist oblique)
|
|
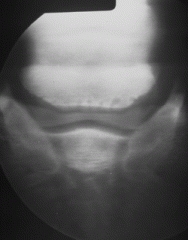
What can be seen in the x-ray?
What does this suggest? |
"lollipop" structures in navicular bone
Navicular degeneration- osteolytic change |
|
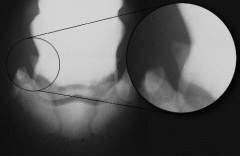
What can be seen in the x-ray?
What is this an indication of? |
Spur formation of wing of navicular bone
Proliferative navicular degeneration |
|
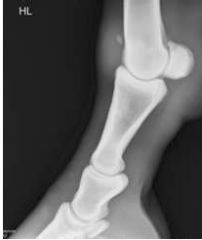
Which anatomical feature has been x-rayed?
What can be seen? |
Fetlock
OCD |
|
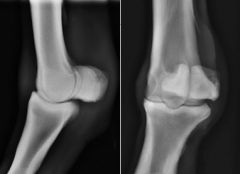
What can be seen?
|
Increased opacity of sesamoid bones
Prominent and increased vascular channels Remodelling of smooth margins Cyst formation ------> sesamoiditis |
|
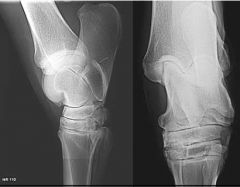
What is indicated?
|
DJD of tarsus/ Spavin
|
|
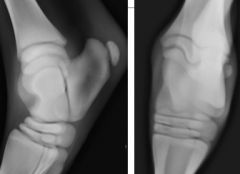
What developmental anomaly?
|
Tarsal collapse
|
|
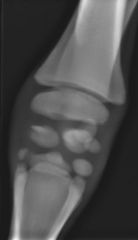
Which developmental anomaly?
|
Cuboidal disease; incomplete ossification
|
|
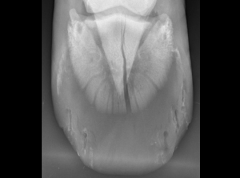
What does the x-ray show?
|
Fracture of the distal phalanx Eq
|
|
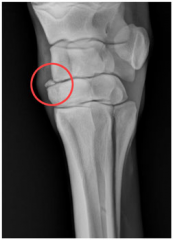
What does the x-ray show?
|
Chip fracture of carpus
|
|
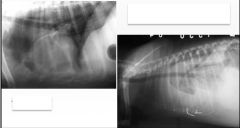
What abnormality?
|
Effusion (pleural)
- homogenous opacities with sharp margins |
|

What is shown?
|
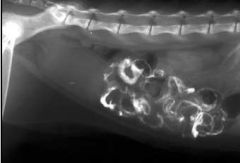
Ileus; linear foreign body
(picture above is another example) |
|
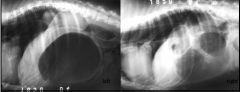
What is shown?
|
Gastric dilation & volvulus
|
|
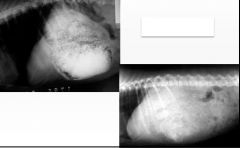
What is shown?
|
Gastric dilation due to food
|
|
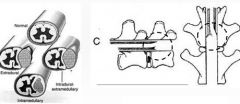
What does this schematic show?
|
Intradural-extramedullary compression
|
|
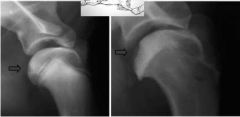
The arrows show an irregularity which is characteristic of which disease?
Which joint? |
Osteochondrosis dissecans
Shoulder |
|
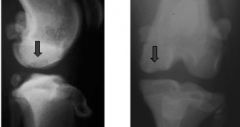
Which developmental abnormality?
Which structure is indicated with the arrows? |
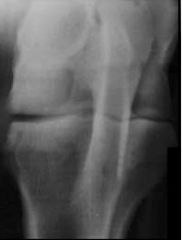
Osteochondrosis dissecans
Medial femoral condyle |
|
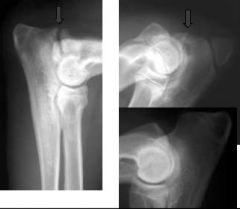
What is indicated with the arrows?
|
Ununited anconeal processs
|
|
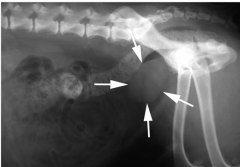
What is indicated by the arrows?
|
Prostate
|
|
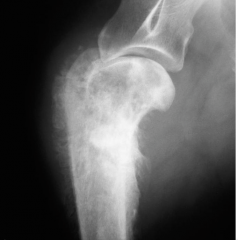
What abnormality?
|
Bone tumour
|
|
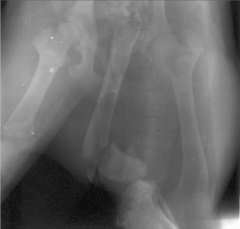
Which technical error?
|
Double exposure
|
|
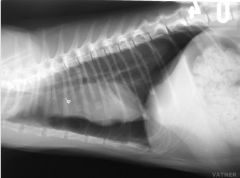
What abnormality is seen?
|
Pneumothorax
|
|
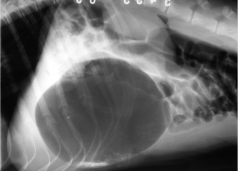
Which abnormality?
|
Gastric Torsion
|
|
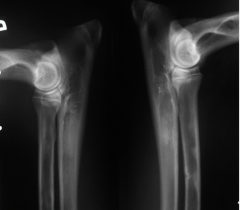
Which abnormality?
|
Panosteitis
|
|
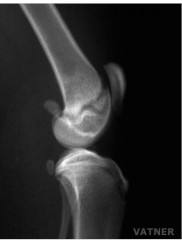
Which type of injury?
|
SH II
|

