![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Fontanelles |
Sphenoid Anterior Posterior Mastoid |
SPAM |
|
|
Sinusus |
Frontal Ethmoid Maxillary Sphenoid |
FEMS |
|
|
Mamalian features of the skull |
Nasal conchae 3 Bony oscicles in the middle ear Palate which seperates mouth from nasal cavity Single mandible Heterodont,Diphedont, Thecodont teeth |
|
|
|
1st secondary curvature |
3 months When the baby tries to keep the head straight |
|
|
|
2nd secondary curvature |
7 to 8 month When the baby starts to walk |
|
|
|
Movements of the spine |
Flexion Extension Lateral flexion Rotation Swinging of pelvis |
|
|
|
Parts of the sternum |
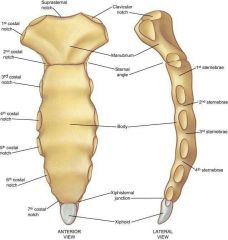
Manubrium Body or mesosternum Xiphoid process |
|
|
|
# Ribs # true ribs # false ribs # floating ribs |
12 pairs 7 pairs 5 pairs 2 pairs |
|
|
|
Shoulder Girdle |
2 scapula 2 clavicles |
|
|
|
Scaupala |
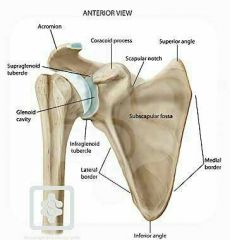
|
|
|
|
1. Coranoid process 2. Coracoid process 3. Corronoid fossa |
1. Ramus of the mandible 2. Scapula 3. Distal part of the humerus |
|
|
|
Head of Ulna |
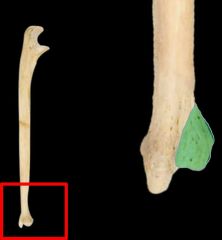
|
|
|
|
Radius wrist articulation |
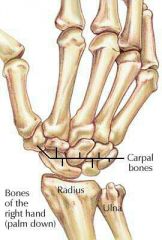
Metacarpals only articulate with the radius |
|
|
|
# of Carpel bones |
8 Two rows of 4 bones |
|
|
|
Innominate bone parts |
Illeum Ischium Pubis |
|
|
|
Pelvis |
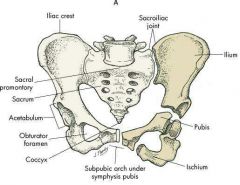
Sacroiliac joint - Synovial Pubic symphysis - Cartilaginous |
|
|
|
Arches of the foot |
2 transverse 1 longitudinal |
|
|
|
Types of joints |
Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
|
Fibrous joint |
Dense regular connective tissue rich in collagen Eg. Sutures of the skull |
|
|
|
Cartilaginous joint |
Cartilage Eg. Pubic symphysis |
|
|
|
Synovial joint
|
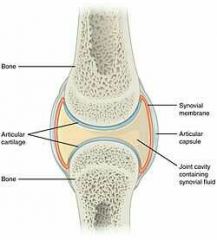
Bones aren't directly joined Synovial cavity filled with dense irregular present Eg. Sacroiliac joint |
|
|
|
Types of locomotary movements |
Pseudopodia Flagellar movement Cilliary movement Muscle movement |
|
|
|
Sliding fillament theory and Power stroke |
https://youtu.be/jUBBW2Yb5KI |
|
|
|
Levels of arrangement |
Actin and myosin fillaments Sarcomere Myofibrill Muscle fibre Fasicle Muscle |
|
|
|
Hydrostatic skeleton |
Nematoda Annelida |
|
|
|
Exoskeleton |
Coelenterates - Calsified (Some Anthozoa) Molluscs - Calsified Arthrapods - Chitinous Unicellular - Radiolaria, Foraminifera |
|
|
|
Endoskeleton |
Vertebrate Radiolaria Molluscs Echinodermates Multicellular sponges |
|

