![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of SCM?
|
SCM is a set of approaches utilized to efficiently integrate suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and stores so that merchandise is produced and distributed at the right quantities, to the right locations, and at the right time, in order to minimize systemwide costs while satisfying service level requirements.
|
|
|
Describe the information flow both to and from the customer
|
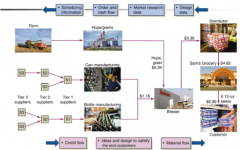
|
|
|
SUPPLY CHAIN INTEGRATION
What does vertical integration do? What does vertical integration require? What company is an example of it |
DO: Assures supply
Reduces cost REQUIRES: hugh investments Production risks Ford is an example |
|
|
SUPPLY CHAIN INTEGRATION
What is supply chain semi-integration? What company is an example of it? |
-Few suppliers
-Long-term agreements -Coordinated business processes Dell is an example (because does not own all its suppliers as part of vertical integration) |
|
|
What are the systemwide costs that SCM purports to minimize?
|
1. Acquisition
2. Transportation 3. Inventory 4. Materials handling |
|
|
What are ways SCM works to minimize system wide costs?
|
1. making decisions between global versus local optimization (the inventory / transportation tradeoff in that you either have holding costs or you have transportation costs)
2. Inventory is often seen as the greatest opportunity of cost reduction |
|
|
What is inventory turnover?
|
Inventory turnover = annual sales / average inventory level
The amount of inventory turnover is dependent on the sector |
|
|
What is service level?
|
the ability to satisfy customer's delivery date. So this could be measured by a % of all orders sent on or before delivery date
|
|
|
What is risk pooling?
What is a way in which risk pooling exists? |
Risk pooling aims to aggregate demand across locations in order to reduce demand variability and thus required stock
Risk pooling can be carried out through centralized distribution centers |
|
|
The case ML Fisher talks about "what is the right supply chain for your product." What are the major dimensions on which this decision is determined?
|
Cost versus responsiveness. So you select either primarily for cost/quality, or for speed/flexibility/quality
One is more focused on inventory turnover (costs) and the other is more focused on service level (responsiveness) |
|
|
What is the bullwhip effect and why does it exist?
|
Order variability increases as we travel up the supply chain. This happens because:
-supply chain stages don't see real demand -batch ordering -price fluctuations -inflated orders -high lead times amplify effect |
|
|
What are the consequences of the bullwhip effect?
|
– Higher inventory costs
– Lower service level – Inadequate capacity planning |
|
|
What are solutions to the bull-whip effect? Give an example of each kind.
|
– Reduce uncertainty
• Ex: Share point-of-sale (POS) data – Reduce variability • Ex: “Everyday Low Prices” – Reduce lead times – Strategic partnerships • Ex: Vendor-managed inventory |
|
|
How do firms decide what / how much to produce?
|
Push versus Pull
|
|
|
What is a push strategy and what are the problems associated with it?
|
– Production decisions based on long-term forecasts (“Make-to-stock”)
– Problems: • Inability to meet changing demand patterns • Obsolescence of inventories |
|
|
What is a pull strategy and what are the requirements, advantages, and problems associated with it?
|

|
|
|
Describe how a company knows when to use push or pull
|
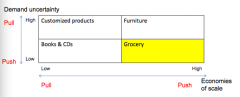
|
|
|
Explain Amazon's supply chain strategy and why
|
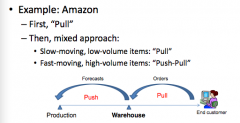
|
|
|
Describe Dell's supply chain strategy (what it's called, what it is, and why)
|
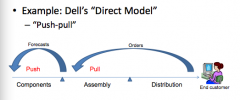
|

