![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Effects of ETOH on developing fetus
|
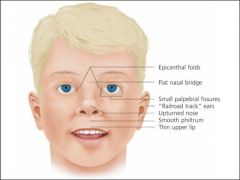
Fetal ETOH syndrome
1. Growth restriction 2. CNS involvement (structural, neurological, functional impairment) 3. Craniofacial dysmorphic features (short palperbral fissues, thin upper lip, abnormal philtrum, hypoplastic midface) |
|
|
Effect of smoking of the developing fetus
|
Lower average birth weight
Dose-dependent can be reversed if smoking is stopped early in pregnancy spontaneous abortion prematurity placental abruption premature rupture of membranes stillbirth increased risk of SIDS |
|
|
Effects of opiates on developing fetus
|
no teratogenic effects
risk of withdrawal Miscarriage, preterm delivery, and foetal death seizures |
|
|
Effect of cocaine on the developing fetus
|
Placental abruption
IUGR Preterm labour and delivery CNS complications and developmental delay Causes vasoconstriction and hypertension |
|
|
effects of amphetamines on developing fetus
|
Decreased head circumference, length, birth weight
increased rates of abruption, prematurity, growth restriction intracranial lesions - haemorrhage, infarction, cavitatory lesions |
|
|
What is the scoring system used for nenoatal abstinence syndrome
|
Modified Finnegan scoring system
Infants scoring 3 consecutive abstinence scores > 8 or > 12 for 2 scores should be treated for NAS Scoring 4 hourly until infant has stabilised |
|
|
Describe the Finnegan scoring system for NAS
|
CNS
High pitched cry Restlessness: sleep for < 1-3 hrs after feeding tremors increased mm tone excoriation myoclonic jerks generalised convulsions Metabolic/vasomotor/ respiratory disturbances fever frequent yawning nasal stuffiness sneezing > 3-4 times RR > 60/min with retractions GIT disturbances excessive sucking poor feeding regurgitation/ projectile vomiting loose stools |
|
|
When will an infant of a mother on heroine/methadone withdraw
|
heroin typically within 24 hrs of birth becoming more obvious over 3-5 days - can take up to 7 days to reach severity, can take up to 2 weeks to present
methadone 2-7 days after birth NAS can last from 1 week to 6 months |
|
|
Which infections may be associated with mothers with drug dependency
|
HIV
Hep C/ Hep B |
|
|
In what situations are infants born to Hep C mothers at risk of devloping Hep C infection?
|
anti-HCV +ve; HCV RNA -ve
Will not get infection only 5-10% of infants born to anti-HCV +ve; HCV RNA +ve mothers will develop HCV infection |
|
|
Can mothers with HCV breastfeed?
|
yes as long as they are asymptomatic
|
|
|
Does breastfeeding increase the risk of HIV transmission
|
yes
|
|
|
In what situations are infants born to Hep B mothers risk of getting hep B infection?
|
Without immunisation > 70% born to HBsAg+ve HBeAg +ve mothers
Without immunisation 5-10% born to HBsAg+ve HBeAg -ve mothers All infants born to HBsAg +ve mothers should receive hep B vaccination and immunoglobulin < 12 hr |
|
|
Can mothers with Hep B breastfeed
|
Yes as long as the infant has received hep B vaccination and immunoglobulin
|
|
|
How shoudl women with HBV deliver
NVD or CS |
There is no evidence to suggest that CS prevents maternal infant transmission
Therefore CS is not routinely recommended for HBV mothers NB: risk of transmission is related to the HBV replicative status of the mother i.e. HbeAg |
|
|
What is the risk of trasmission of HCV vertically?
|
5%
|
|
|
Should HCV mothers devlier vaginally or CS
|
There is no good evidence on the mode of delivery
Vertical transmission is higher when the mother is co-infected with HIV |

