![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
119 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the steps to engage the pump? |
1. Bring the appliance to a complete stop. 2. Apply handbrake 3. Transmission to neutral 4. Engage HP pump 5. Engage main pump 6. Count to 5 then put transmission into top gear |
|
|
Why do we use pumps in the MFS |
1. Control pressure of water 2. Control volume and flow of water 3. Transfer water to and from an appliance |
|
|
What is the purpose of the transfer case? |
Directs engine power from the drive wheel to the pump |
|
|
What do the gauges on the pump panel indicate? |
The condition of the engine, pump & water supply |
|
|
What does the compound gauge display? |
Water pressure entering the pump |
|
|
What is negative pressure on the compound gauge indicative of? |
A vacuum is present at the pump during priming or when the pump is operating from draft/lift |
|
|
What is a positive pressure on the compound gauge indicative of? |
Residual pressure when a pump is operating from a hydrant or receiving water through a supply line from another pump |
|
|
What does the main pressure gauge tell us? |
Water pressure leaving the pump but before it reaches the individual discharge line gauges |
|
|
What does the high pressure gauge tell us? |
Pressure delivered to the high pressure hose reels |
|
|
What side of the appliance is near side? |
Left side or passenger's side |
|
|
What side of the appliance is off side? |
Right side, or drivers side |
|
|
What are the functions of each part of a centrifugal pump? |
Impeller - heart of the pump. Rotates to create centrifugal force.
Eye - where the water is drawn in through an area of low pressure.
Vanes - throws the water outwards.
Volute - houses the impeller and directs the water spun from the impeller to reduce velocity and water turbulence. |
|
|
How does a centrifugal pump work? |
Energy is imparted by centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the impeller |
|
|
What is the purpose of the relief valve? |
A safety mechanism designed to protect branch operators from surges in pressure when using a 64mm hose. |
|
|
What causes pump damage? |
Cavitation Overheating Water hammer But also... (Not in our books)... Relief valve on when not required Operator error Poor water quality Dry running the pump |
|
|
Purpose of a pump operator? |
Responsible for supplying continuous, reliable and effective water for firefighting. Safety of the branch operator is the number 1 priority |
|
|
5 principals of Friction Loss |
1. Friction loss varies directly with the length of the hose
2. For the same velocity, friction loss decreases with the increase in diameter
3. Friction loss increases directly as the square of the velocity.
4. Friction loss increases with the roughness of the interior of the hose
5. Friction loss for all practical purposes, is independent of head pressure |
|
|
How do you work out pressure required as a pump operator? |
Branch requirements - 700 kpa or 500 kpa Elevation - 10 kpa loss/gain per altitude to account for head pressure Friction - 100 kpa loss for every 30m 64mm hose / 200 kpa loss for every 30m 38mm hose. |
|
|
What 10 items are in a high rise sling? |
1. 38mm hose 2. 10/100 Branch 3. Shove knife 4. Wheel valve 5. Door indicators 6. Brass olive 7. Square key 8. Hydrant key 9. Door wedges 10. Forestry adaptor |
|
|
What 5 things are on the water gear trolley |
1. Standpipe 2. Turncock key and bar 3. Heavy duty plate cover lifter 4. Safety torch 5. Combination key |
|
|
List 8 items in the tool roll. |
Universal shears Eclipse saw Shifting spanner Stanley knife Life hammer Hammer Screw drivers Cable cutter Pliers Spread strap Multigrips Windscreen remover Speed brace and socket |
|
|
When do you check the appliance? |
Commencement of shift Changing over appliance After an incident |
|
|
What stations and numbers are in the southern command? |
40 St Marys 41 Camden Park 42 O'Halloran Hill 43 Christies Downs 44 Glen Osmond 45 Brooklyn Park 46 Seaford |
|
|
What stations and numbers are in the central command? |
20 Adelaide 21 Beulah Park 24 Woodville 25 Port Adelaide 27 Marine 28 Largs North 37 Prospect |
|
|
What stations are in the Northern command? |
22 Paradise 30 Oakden 31 Golden Grove 32 Salisbury 33 Elisabeth 35 Gawler 36 Angle park |
|
|
What is a fire? |
A chemical reaction where Oxygen is combined with a gaseous or vaporous fuel, producing heat and light as energy. |
|
|
List the numbers and appliance types |
1 1st G pumper 2 2nd G pumper 3 CAPA (combined aerial pump) 4 support tender 5 1st elevated platform 6 1st BA / hazmat 7 Hazmat Pump 8 4x4 pump 9 Rescue pump 11 3rd G pumper 14 4WD grassfire unit 15 2nd elevated platform 16 2nd Hazmat H01 1st hooklift 25 Marine 90 1st incident control unit 92 2nd incident control unit |
|
|
What is the fire triangle? |
Illustrates the 3 elements required for fire to exist. They are heat fuel and Oxygen. |
|
|
What are the stages of fire development? |
1. Ignition 2. Growth 3. Fully developed 4. Decay |
|
|
How do you extinguish a fire? |
Starve - take away fuel Smother - remove O2 Cool - remove heat |
|
|
What are the classes of fire and extinguishing agents used for each? |
A - solid combustible - cool - Water, foam, DCP, wet chem B - flam liquids - smother - foam , DCP, CO2 C - flam gases - starve - isolate D - flam metals - smother - TEC, sand E - electrical - smother - CO2, DCP F - cooking fats and oils - smother - wet chem |
|
|
What is the correct operating procedure for using a fire extinguisher? |
P in T est A im S queeze S weep |
|
|
What are the daily checks for extinguishers? |
1. Check gauges 2. Check maintenance tag 3. Check for obvious faults |
|
|
List 5 workplace hazards encountered by firefighters |
Wildfire
Electrical Biological Radiation Chemical
Hazardous atmospheres Extreme temperatures Structual collapse
Flammable liquids and gases Dust |
|
|
What are causes of structural collapse? |
1. Fire 2. Impact (MVA) 3. Explosion (gas/terrorist) 4. Poor workmanship 5. Flood 6. Earthquake 7. Landslide |
|
|
What are the ways chemicals can enter the body? |
Inhalation Absorption Injection Ingestion |
|
|
Where are SOPs & SAPs found |
On the member's only website |
|
|
What is the purpose of a SOP |
Standard Operating Procedure: Provide a number of known procedures that allows firefighting crews to operate in a manner that is SYSTEMATIC, EFFICIENT & PREDICTABLE when attending emergencies.
Applied when attending and normalizing an emergency incident What we do, why and how. |
|
|
What is the purpose of a SAP? |
Service Administrative Procedure: Provide practical information on the many administrative processes and procedures used by the MFS. Applied to day-to-day running of the MFS |
|
|
What is the number 1 rule with electrical hazards? |
Treat all downed wires as energised until proven otherwise by the relevant authorities.
(Includes TV cable and telephone cables) |
|
|
What is the safe distance from downed wires? |
8m |
|
|
What are the limits of high and low voltage? |
High - 1000 + volts Low - <650 volts |
|
|
Can you spray water onto solar panel fires? |
Water can be applied directly onto solar panels using a broken spray pattern (fog) and from a distance of 8 meters from all system components or adjoining conductive material. |
|
|
What are the 4 risk categories in the event of an alarm (SOP 4) and what they include - RISKS AND RESPONSE : |
Category A - 3 GP + capa 1. All individual buildings 4 floors and above 2. Oil and gas installations and storage facilities 3. Special target risks involving a very high hazard industrial or commercial life risk
Category B - 3 GP 1. Industrial buildings and complexes not specified in A. 2. Large shopping and commercial centres and supermarkets. 3. Health care facilities other than in A 4. Public buildings, grandstands, hotels and cinemas
Category C - 2 GP 1. Residential buildings 2. Small shopping and commercial buildings 3. Small industrial or public buildings in isolation up to 150sqm 4. Brush fire fences 5. Vehicle fires
Specific risk |
|
|
What are priority 1 & 2 incidents? |
1: immediate emergency response. Travel with warning device = sirens and alarms. Max 20kms over speed limits, following road work speeds and 20km/hr through intersections. 2: immediate emergency response. Comply with Aus road laws, no warning device. |
|
|
What are the rope lines and lengths |
Short line 5m Heaving line 30m Bucket line 30m Rescue line 50m Guide line 60m Personal line 4.75 + 1.25m |
|
|
MFS organisational structure |
CHIEF OFFICER: 1 large + 1 small impeller, 1 laurel wreath, 1 crown DEPUTY CHIEF OFFICER: 1 large impeller, 1 laurel wreath, 1 crown ASSISTANT CHIEF FIRE OFFICER: 2 Small impellers, 1 large impeller and laurel wreath COMMANDER: 1 small and 1 large impeller, 1 laurel wreath STATION OFFICER: 2 Small impellers SENIOR FIREFIGHTER: 2 red V FIREFIGHTER |
|
|
Can you still get electrocuted from solar panels that have been switched off at the isolator switch? |
Yes you can. The isolator switch only turns off the wires after the switch board. Before the switch the wires are still energised and can cause electrocution |
|
|
MFS vision |
A safer and more prosperous South Australia |
|
|
MFS mission |
Help protect South Australian lives, property, the environment and our economy |
|
|
What is the hierarchy of control fo hazards? |
1. Elimination 2. Substitution 3. Engineering 4. Administration 5. PPE |
|
|
What are the 3 heat illnesses |
1. Heat cramps 2. Heat exthaustion 3. Heat stroke |
|
|
What are the 2 main mechanisms of injury |
Overuse Overload |
|
|
What is the MFS risk identification model? (Also known as SPAR decision making model) |
S. Situation P. Plan A. Act R. Review |
|
|
What are the hose types, length and diameters, and the ADVANTAGES |
1. High pressure - 25mm, 30m - quick and easy get to work, low volume output. 2. Lay flat hose - 25mm (bushfire) - 38mm, 30m (Cleveland load) & high rise sling) - easy to manoeuvre - 64mm, 15+30m - 2 person hold and not easy to manoeuvre but the highest volume output. -150mm (High volume hose pod (FETCH)). 3. Rigid hoses - Feeds - 64mm, 2.4m - Suction - 140mm (2.4m), 150mm (3m) |
|
|
How do you avoid damaging the hoses? |
FACKT Avoid contact with flames Avoid abrasive surfaces Avoid contact with chemicals Avoid kinks Avoid traffic driving over the hose |
|
|
3 indicators of a fire plug? |
1. Blue cats eye 2. Indicator post 3. Yellow paint |
|
|
Ladder terminology: pitch, raise, underpin, extend, pawl, lower ladder, heel in/out, foot, strike, disengage pawls, house, make up, ladder secure, run the ladder. |
Pitch: erect a ladder against a building Raise: to lift the head of the ladder by underrunning Underrun: method of bringing the ladder from the ground to a vertical position or vise versa Pawl: secure the ladder law is on a round before ascending. Prevents accidental housing. Lower ladder: to lean ladder against a building. Heel in/out: to move the heel of the ladder towards or away from the structure Foot: to brace the heel of the ladder with one or two persons. No firefighter is to climb a ladder until it is safely footed or tied off correctly. Strike ladder: remove the ladder from the building Disengage pawls: to extend the sliding section of the ladder so that pawls are cleared for lowering. House: lower the sliding section of the ladder. Make up: replace the ladder on the appliance. Ladder secure: ensure the ladder is securely made up on the appliance. Run the ladder: the act of climbing the ladder |
|
|
4 command used when using ladders |
1. Stand-by to slip ladder 2. Slip ladder 3. Fingers 4. Far enough |
|
|
What is a knot, bend, hitch and dressing a knot? |
Knot: a rope intertwined Bend: 2 ropes joined together Hitch: a rope around an object Dressing: presenting (making the knot easily identifiable) and tightening (making sure all rope parts are touching firmly) |
|
|
What is the correct angle for pitching a ladder |
1/4 of the height of the building or 75 degrees |
|
|
What is the 2 ways to establish a ssfe driving distance when driving an appliance? |
1. 3 second rule 2. 1 appliance length for every 10km of speed |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
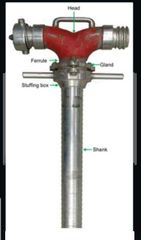
Lug ring and shoe at the bottom |
|
|
How do you practice good manual handling? |
Good base of support Maintain neutral spine Brace core Bend from the knees (use quads to lift not back) Keep arms at 90 degrees and close to the body |
|
|
What are some minor and major disciplinary breaches |
Minor: - being late - absent without notification - disruptive behaviour - untidy appearance - slothfulness - lack of respect to MFS staff Serious: - use of illicit drugs and alcohol at work - plagiarism - repeating minor offensive - offensive behaviour that damages the MFS reputation - purposeful damage to MFS or another person's property - theft - loss of licence - willful injury of another person |
|
|
What must you do if your uniform is damaged? |
Submit a requisition through the chain of command for a replacement |
|
|
When can you wear the MFS shorts |
Only around the station and under level 2 PPE. Never to be worn and seen in public |
|
|
What are the 12 knots used in the MFS? |
1. Figure 8 2. Figure 8 on the bight 3. Figure 8 loop 4. Bowline 5. Bowline on the bight 6. Yachtsman's purchase 7. Double sheet bend 8. Round turn and 2 half hitches 9. Clove hitch 10. Reef knot 11. Alpine butterfly 12. Rolling hitch |
|
|
What does SOP 01/2002 state regarding working in roof spaces? |
Power to the premises must be isolated |
|
|
What are 3 disadvantages of using water as an extinguishing agent? |
- High surface tension - Reactivity with certain materials and chemicals - Low viscosity - Will conduct electricity |
|
|
What are 3 advantages of using water as an extinguishing agent? |
Relatively cheap Relatively available and plentiful Readily absorbs quantities of heat Easily transported Expands when converted into steam 1700:1 @100degrees |
|
|
What SAP are appliance and equipment checks? |
SAP 29 |
|

|

|
|
|
Who is the incident controller? |
The first arriving officer |
|
|
What are the 2 types of incident management strategies? |
1. Offensive 2. Defensive |
|
|
What is the SPAR decision making model? |
Situation - ID known and unknown critical incident factors. Analyse situation and compare to experience Planning - set incident action plan. Conduct risk assessments Action - implement plan. Follow directions. Continually monitor health and safety of firefighters Review - continually monitor incident, evaluate operations, undertake post-incident review |
|
|
What are the 3 control zones at an incident? |
Hot, warm, cold |
|
|
What are the 3 systems of accountability? |
1. BA set tally = tactical 2. Nominal roll tally = strategic 3. Helmet accountability tags = task |
|
|
Where are the 2 places for the helmet accountability tags? |
Front of the incident management kit Nominal roll tally |
|
|
What does RIT stand for and who is involved? |
Rapid Intervention Team
Standby in a state of readiness to perform rescues firefighters where personnel are required to work under hazardous conditions 1 x station officer 3 x firefighters |
|
|
Who does the RIT report to? |
The incident controller |
|
|
What is PAR? |
Personal Accountability Report Ensures all firefighters are safe, okay and together |
|
|
What are k codes 0-5 |
0 - not available 1 - mobile to incident 2 - arrived at incident 3 - at incident but available for further assignments 4 - mobile in area 5 - at home station |
|
|
What is a CAN message? |
Conditions - fire and smoke conditions in a structure. Actions - what the crew is doing (I.e. search, ventilation, fire attack) Needs - what resources the crew needs (I.e. equipment) |
|
|
What are the 3 emergency messages? |
Abandon: abandon post, equipment and get out immediately Evacuate: abandon post and evacuate WITH equipment as quick as possible Mayday: used by firefighters to indicate their status as being lost, trapped, injured or in need of urgent assistance |
|
|
What does the 'yelp' sound signify? |
Communications are down, abandon |
|
|
What is the phonetic alphabet? |
A - Alpha B - Bravo C - Charlie D - Delta E - Echo F - Foxtrot G - Golf H - Hotel I - India J - Juliette K - Kilo L - Lima M - Mike N - November O - Oscar P - Papa Q - Quebec R - Romeo S - Sierra T - Tango U - Uniform V - Victor W - Whiskey X - X-ray Y - Yankee Z - Zulu |
|
|
What is the safe level of asbestos? |
There is not safe level! |
|
|
What are the asbestos control measures? |
- keep damp - PPE and BA - minimise release of fibres - double bag and yellow sticker PPE uniform |
|
|
What actions must you take if you suspect asbestos at an incident? |
- notify the incident controller - minimise disturbance |
|
|
What are some places you might find asbestos? |
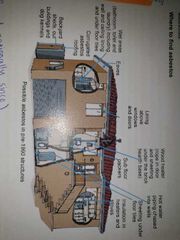
Cement sheeting Hot water pipes Insulation - heaters, stoves and wood fires Sub floor packers Eaves Lining under floors Corrugated roofing Sheds Dog kennels Imitation brick cladding Vinyl floor tiles Electrical meter boards |
|
|
What is BLEVE? |
Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapour Explosion |
|
|
What is flashpoint definition? |
The lowest temperature at which a volatile liquid can vapourise to form an ignitable mixture in air |
|
|
What are the ways you can identify a car with LPG? |
1. Green badge 2. Red diamond on number plate 3. Visually see the cylinder 4. Duel fuel refill points |
|
|
What are the 6 steps to preserving a scene? |
1. Do not disturb any more than necessary 2. Get tape up and police it 3. Do not turn over 4. Do not overhaul 5. Do not salvage 6. Do not ADMIT |
|
|
What are 8 points that can be noted by firefighters to assist in fire investigations? |
1. Door open/closed/locked 2. Demeanour of owner/occupier 3. Missing personal items I.e. family photos 4. Fire spread pattern 5. Presence of accelerator 6. Window smash: forced/heat break inside/outside 7. Structual damage prior to fire 8. Removal of valuable items 9. Hindered entry of MFS 10. Booby traps |
|
|
What do you do if you find a fatality on a scene and it is obviously dead? |
Leave in situ Do not disturb Do not cover with salvage sheet |
|
|
What are the risk categories as defined in SOP4? |
Risk A Risk B Risk C Specific risk |
|
|
What is priority 1 and priority 2 as defined by SOP4? |
Priority 1: immediate emergency response - travelling using emergency warning devices (lights and sirens) Priority 2: immediate emergency response. Complying with Australian road rules, no emergency device |
|
|
What are the 3 ways the MFS are notified of incidents? |
1. Phonecall from public 2. Referral from another agency i.e. SAPOL 3. Monitored automatic alarms |
|
|
What are the 3 things that comprises an incident action plan? |
Strategy Objectives Tactics |
|
|
What is the optimal pressure when working with a high pressure line? |
2400 kpa |
|
|
Name the 3 components of the Cleveland load |
Gated Y 38mm lay flat hose 10/125 TFT branch |
|
|
What colour are fire calls recorded in the occurance book? |
Red pen |
|
|
When arriving on shift what are the 3 things recorded in the occurance book? |
1. Book yourself on duty 2. Book off the person you are relieving 3. Time of change over |
|
|
What are the 4 pieces of information recorded in the occurance book? |
1. Duty personnel 2. Fire calls 3. Appliance movements 4. Station visitors |
|
|
What does the network GRN stand for? |
Government radio Network |
|
|
What are the 2 methods of data transmission over radios? |
Simplex - TACTICAL radio to radio. Line of sight. Short range Trunked - COMMAND via repeater tower, long range, recorded |
|
|
What is the alpha side of the building? |
The street fronting side. If on a corner it's the side the appliance is parked on. |
|
|
What must you do if you encounter an acetylene cylinder on fire? |
1. Move away from the area 2. Do not move the cylinder (it increases decomposition of gas) 3. Inform the incident controller 4. Get everyone to evacuate the area 5. If a cylinder is venting it will increase the rate of decomposition 6. Set up cooling lines if quick to do so. |
|
|
What does the command "haul away" mean? |
The command given when taking gear aloft with the aid of a rope line |
|
|
What does the command " stand from under" mean? |
The command given by anybody who has to drop or lower equipment from a height, where there is risk it might strike someone standing below |
|
|
What are the six sensors included in the MultiRAE lite atmospheric detector? |
1. Oxygen (LA =19.5% HA =23.5%) 2. Carbon monoxide 3. Hydrogen sulfide 4. LEL 5. PID sensors - measure volatile organic compounds 6. Hydrogen cyanide |
|
|
What is the aim of salvage |
PREVENTION: when the fire is in progress - simultaneous with firefighting- minimal damage with fixed entry- using sufficient water only for fire extinguishment- ventilation PROTECTION: when the fire is under control - reduce water damage- protect goods: use salvage sheets- secondary ventilation RECOVERY: when fire is extinguished - making up hose outside- removal of excess water - secure premises- preserve fire scene- remove/cover roofing |
|
|
What is the systematic approach at a road crash rescue? |
1. Readiness and preparation 2. Call out and response 3. Arrival at incident 4. Scene ad vehicle safety 5. Assess rescue requirements 6. Vehicle stabilisation 7. Gain access 8. Release and remove casualty 9. Conclude rescue 10. Maintain equipment and debrief |
|
|
What is an inner and outer assessment at a RCR? |
OUTER: 30m perimeter, searching for casualties, hazards, debris INNER: above, inside, around and under the vehicle within 10m perimeter |
|

|

|

