![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Costs of production |
Labor, power, inputs |
|
|
Main goal of a firm |
Maximize profits |
|
|
Profit = ? |
Total Revenue- Total Cost |
|
|
Revenue= |
Price * Quantity |
|
|
T cost= |
what it takes to make products |
|
|
Explicit cost= |
direct cost |
|
|
Implicit cost |
no cash up front. Opportunity costs |
|
|
What is the explicit cost of borrowing 100k dollars with a 5% interest rate? |
5000 dollars for interest on loan |
|
|
What is the implicit cost of using 40kk of your own savings and borrowing the other 60k? |
2,000 dollars in interest that you could have accrued and 3000 you will pay in interest on the 60k |
|
|
Accounting profit= |
Revenue- Total explicit cost |
|
|
Economic profit= |
T (revenue)-T(cost) |
|
|
Marginal labor product formula : Note: When writing this out, MPL is in between the output and workers to show change |
MPL= deltaQ (quantity output) / deltaL (labor) |
|
|
Fixed cost |
Generally considered sunk cost. This cost is typically for building rent, machinery. |
|
|
Variable cost |
Vary with output. For example, wages, materials, and electricity used in production. |
|
|
Marginal cost= |
delta Total cost/delta Quantity |
|
|
Average fixed cost= |
FC/Q |
|
|
Average variable cost= |
VC/Q |
|
|
Average total cost= |
(VC+FC)/Q |
|
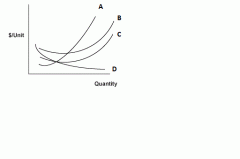
|
a: MC B: ATC C: AVG D: AFC |
|
|
Perfect competition market structure requirements |
1. many buyers/sellers 2. goods offered largely similar 3. firms can enter or exit freely |
|
|
Price takers |
Buyers and sellers in perfectly competitive market, they will pay for or sell goods based on the market price |
|
|
Revenue for a competitive firm |
TR= P*Q |
|
|
Marginal revenue in perfect competition |
change in total revenue/ change in quantity |
|
|
Minimum on the ATC |
efficiency scale |
|
|
ATC short run vs. long run |
short run: all costs are fixed long run: all costs are variable |
|
|
economies of scale |
any point found before the minimum (effeciency scale) of the long run ATC |
|
|
Diseconomies of scale |
any point after ATC minimum (effeciency scale) on the long run ATC curve |
|
|
In perfect competition Marginal Revenue= |
Price |
|
|
When MR>MC _____ Q to raise profit |
increase |
|
|
When MR<MC _____ Q to raise profit |
decrease |
|
|
When MR=MC what happens to profit |
maximized |
|
|
Marginal cost is a company's _____ curve |
supply |
|
|
Pro and cons of shutdown |
shutdown temporary decision to not produce goods. It costs TR (total revenue) but you save by not spending (VC) |
|
|
When to shutdown |
If MR<AVC then the company will shutdown. |
|
|
Exit if |
P<ATC |
|
|
Enter the market if |
TR>TC |
|
|
To find profit when given MC and MR curve.... |
(MC-MR)*Q |
|
|
Marginal product= |
change in quantity/change in hours |
|
|
Zero profit condition |
Economic 0 profit (not accounting), entering and exiting market keeps economic profit at 0 |
|
|
Intersection of MC and ATC is ___ |
Effecient scale |
|
|
Monopoly |
a firm sells a good that does not have a close substitute |
|
|
Market power is possessed by _____ |
monopolies
|
|
|
Monopolist demand curve is what type of curve? |
Downward sloping line |
|
|
In monopolistic markets MR has what relationship to P |
No correlation. MR DNE P |
|
|
How does increasing quantity effect output and price? |
Higher output means higher revenue Lower price reduces revenue |
|
|
At what point does profit maximization occur for monopolies |
MR=MC. Find difference in ATC and demand curve. They will always profit |
|
|
Firms spend money on advretising and the two cancel each other out and profits fall by price of advertising |
Ad wars |
|
|
Best off if both countries disarm, but each has dominant strategy of arming |
Arms race |
|
|
Conserving resources is good, sbut strategy involves using resources |
Common resources |
|
|
Differences in perfect competition and monopolistic competition |
products are differentiated in monopolistic competition. Monopolistic competition does not have market power. D curve in monopolistic competition is downward sloping |
|
|
Markup in monopolistic competition |
Different of LR price and MC |

