![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define the term empirical formula
|
simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound.
|
|
|
Define the term molecular formula
|
actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule
|
|
|
Give the general formulas for:
-Alkane - Alkene -Alcohol -Cycloalkane -Cycloalkene -Haloalkane |
Alkane -CnH2n+2
Alkene CnH2n Alcohol CnH2n+1OH Cycloalkane CnH2n Cycloalkene CnH2n-2 Haloalkane CnH2n+1X |
|
|
Define the term Structural formula
|
the minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule
E.g. Butane: CH3CH2CH2CH3 or CH3(CH2)2CH |
|
|
Define the term displayed formula
|
the relative positioning of atoms and the bonds between them
EG. |
|
|
State the first 10 members of the alkanes homologous series
|
1 Methyl
2 Ethyl 3 Propyl 4 Butyl 5 Pentyl 6 Hexyl 7 Heptyl 8 Octyl 9 Nonyl 10 Decyl |
|
|
Define the term structural isomers
|
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
|
|
|
Define the term Stereoisomers
|
compounds with the same structural and molecular formula but with a different arrangement of atoms in space
|
|
|
Define the term E/Zisomerism as an example
|
restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group
|
|
|
Explain Cis and trans isomerism
|
EIZ isomerism in which two of the substituent groups are the same
|
|
|
Homolytic fission
|
(the same )The forming of two radicals from breaking of a covalent bond where one electron goes to each atom
|
|
|
Hetrolytic fission
|
(different types) formation of a cation and anion by breaking of a covalent bond where both electrons go to one atom
|
|
|
Draw an electrophilc addition reaction-between ethane and chlorine
|
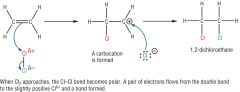
|
|
|
Draw a free radical substitution of chlorine and methane- and name each mechanism
|

|
|
|
Draw the nucleophilic substitution reaction
|
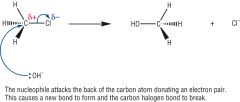
|
|
|
The equation for percentage yield
|
(Actual amount produced/Theoretical Amount produced) x 100 = Percentage Yield
|
|
|
The equation for atom economy
|
(Molecular Mass of desired products/Molecular mass of all products) x 100
|
|
|
How do addition and substitution reactions affect atom economy?
|
addition reactions have an atom economy of 100%, whereas substitution reactions are less efficient; x<100%
|

