![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Structure Today |
1. Chain of command 2. Work Specialization 3. Formalization 4. Departmentalization 5. Centralization/De- 6. Span of Control |
|
|
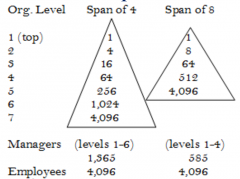
All things equal, the shorter the span, the taller the organization |
|
|
|
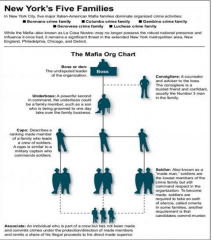
La Cosa Nostra: 10 Commandments |
1. 3rd must always introduce 2. Never look at a friends wife 3. Never be seen w/ cops 4. Don't go to pubs/clubs 5. Always be available, even if wife giving birth 6. Respect appointments 7. Respect wives 8. When asked for the info, tell the truth 9. Don't appropriate money for other family 10. No relations w/ police: 2 timing relatives, or family w/ no morals |
|
|
Plausible Deniability |
|
|
|
La Cosa Nostra's Structure |

|
|
|
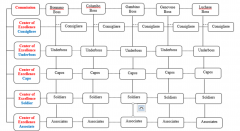
La Cosa Nostra's Matrix |
|
|
|
Mechanistic Structure |
-Advised for stable environment -Individual Specialization: employees work separately + specialize in 1 task -Organization is a network of positions w/ corresponding tasks -Centralization: decision making kept as high as possible, most communication is vertical -Standardization: extensive use of rules + standard operating procedures -Much written communication -Mostly pooled interdependence |
|
|
Organic Structure |
-Advised for unstable/turbulent environment -Joint specialization: employees work together and coordinate tasks -Organization is a network of person or team. People work in different capacities, simultaneously and over time -Decentralization: authority to control tasks is delegated. Most communication is lateral -Mutual Adjustment: face to face contact for coordination. work process tends to be unpredictable -Much verbal communication -Mostly sequential or reciprocal interdependence |
|
|
Task Interdependence |
Refers to the dependence of one organizational unit on another for materials or information 4 Types: -Pooled -Sequential -Reciprocal -Comprehensive |
|
|
Pooled Interdependence |
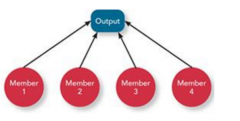
-cheapest form -describes a situation where each part renders a discrete contribution to the whole and supports the whole -group members complete their work independently and then work is piled up to represent the groups output ex: bank branches |
|
|
Sequential Interdependence |
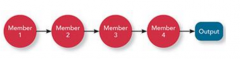
-between units and requires a direct relationship ordered in a serial fashion. -the input for one unit is the output for another -contrast with pooled, has both direct and order aspect -order matters, group is structured and specialized around ordered tasks ex: assembly line |
|
|
Reciprocal Interdependence |
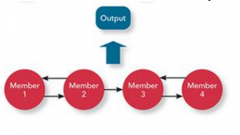
-members are specialized to perform specific tasks and interact w/ a subset of other members to complete the team's work -order does not matter -ex: building a house |
|
|
Comprehensive Interdependence |
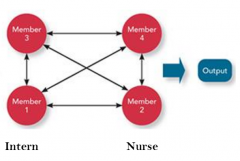
-the outputs of each component become the input for the others -key difference is that the input-output exchange can move in all directions -reciprocal because goes in input-output-input |
|
|
Bureaucracy |
5 Elements 1. Hierarchy: chain of command 2. Division of Labor: job + specs per individual 3. Formalization: written rules + regulations 4. Selection + Promotion by Competence 5. Separation of Individual + Office: equipment + information on the premises of organization belongs to the organization |
|
|
Bureaucracy Summary |
-predominant in western world (US, Germany) -control comes from above -contains division of labor (specialization) -selection/promotion is by competence -written rules/regulations enforced by boss -based on equity (get what you put in) -advantages: risk control, equity, effort coordination, standards -calls for rational authority: rests on the belief of the "legality of rules" and the right of superiors to issue commands -one word description: efficiency |

