![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Stream |
A body of running water that is confined in a channel and moves downhill under the influence of gravity. |
|
|
|
Stream Channel |
A long narrow depression eroded by the stream into rock or sediment. |
|
|
|
Sheetwash |
A thin layer of unchanneled water flowing downhill |
|
|
|
Drainage Basin |
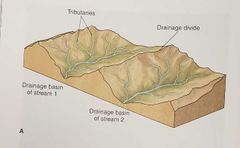
The total area drained by a stream and its tributaries (a small stream flowing into a larger one) |
|
|
|
Hydrologic Cycle |
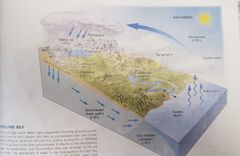
The interrelationship of the hydrosphere: Geosphere Biosphere Atmostsphere The movement and interchange of water between the ocean, atmosphere, and land. |
|
|
|
Divide |
A ridge or strip of high ground dividing one drainage basin from another. |
|
|
|
Drainage Pattern |
The arrangement, in a map view, of a river and its tributaries. Dendritic Radical Rectangular Trellis |
4 ct |
|
|
Dendritic Drainage Pattern |
Develop on uniformly edible rock or regolith and are the most common type of pattern. The pattern resembles branches of a tree or nerve dendrites. |
|
|
|
Radical Drainage Patterns |
The streams diverge outward like spokes of a wheel. |
|
|
|
Rectangular Drainage Pattern |
Tributaries have frequent 90 degrees bends and tends to join other streams at right angles. |
|
|
|
Trellis Drainage Pattern |
Parallel main streams with short tributaries meeting them at right angles. |
|
|
|
Stream Velocity |
The distance water travels in a stream per unit time. High Velocity = Greater Velocity Low Velocity = Lower energy |
|
|
|
Stream Gradient |
Downhill slope of the bed measured by ft; controls streams velocity. |
|
|
|
Discharge |
The volume of water that flows past a given point in a unit of time. Discharge (cfs) = Avg stream width (ft) x Avg depth (ft) x Avg velocity (ft/sec) |
|
|
|
Stream Erosion |
Hydraulic Action Solution Abrasion |
3 ways |
|
|
Hydraulic Action |
The ability of flowing water to pick up and move rock and sediment. |
|
|
|
Solution |
Can be a slow process. Rocks being dissolved by water through weathering and erosion. |
|
|
|
Abrasion |
The grinding away of the stream channel by the friction and impact of the sediment load. |
|
|
|
Potholes |
Depression that are eroded into the hard rock of a stream bed by the abrasive action of the sediment load. |
|
|
|
Stream Transportation of Sediment |
Bed Load Suspended Load Dissolved Load |
3 ways |
|
|
Bed Load |
The large or heavy sediment particles that travel on the stream bed. They are moved by either traction or saltation. |
|
|
|
Traction |
Movement by rolling, sliding, or dragging
Ref. Bed Load |
|
|
|
Saltation |
A series of short leaps or bounces off the bottom. Ref. Bed Loads |
|
|
|
Suspended Load |
Sediment that is light enough to remain lifted indefinitely above the bottom by water turbulence. |
|
|
|
Dissolved Load |
Soluble products of chemical weathering processes. |
|
|
|
Bar |
A ridge of sediment, usually sand and gravel, deposited in the middle or along the banks of a stream. |
|
|
|
Placer Deposit |
Are found in stream where the running water has mechanically concentrated heavy sediment. |
|
|
|
Braided Stream |
Flowing in a network of interconnected rivulets around numerous bars. Characteristically has a wide, shallow channel |
|
|
|
Meanders |
Rivers that carry fine-grained silt and clay in suspension tend to be narrow, and deep, and to develop pronounced, sinuous curves. |
|
|
|
Point Bar |
The low velocity on the inside of a curve promotes sediment deposition sandbars that have been deposited on the inside of curves because of the lower velocity there. |
|
|
|
Meander Cutoff |
A new, shorter channel across the narrow neck of a meander. |
|
|
|
Oxbow Lake |
The old meander may be abandoned as sediment separates it from the new, shorter channel. The cutoff meander becomes a crescent-shaped oxbow lake. |
|
|
|
Flood Plain |
A broad strip of land built up by sedimentation on either side of a stream channel. |
|
|
|
Natural Levces |
Low ridges of flood-deposited sediment that form either side of a stream channel and thin away from the channel. |
|
|
|
Delta |
A body of sediment deposited at the mouth of a river when the river's velocity decreases. |
|
|
|
Distributaries |
Small, shifting channels that carry water away from the main river channel and distribute it over the surface of the delta. |
|
|
|
Alluvial Fan |
A large, fan or cone shaped pile of sediment that usually forms where a stream's velocity decreases as it emerges from a narrow mountain canyon onto a flat plain. |
|
|
|
Downcutting |
The process of deepening a valley by erosion of the stream bed. |
|
|
|
Base Level |
It is a theoretical limit for erosion of the Earth's surface. Ref. Downcutting |
|
|
|
Graded Stream |
A stream that exhibits a delicate balance between its transporting capacity and the sediment load available to it. |
|
|
|
Lateral Erosion |
The erosion and undercutting of a stream's banks and valley walls as the stream swings from side to side across its valley floor. |
|
|
|
Headward Erosion |
The slow uphill growth of a valley above its original source through bullying, mass wasting, and sheet erosion. |
|
|
|
Stream Terraces |
Steplike landforms found above a stream and its flood plain. Formed may be benches cut in rock or they may be steps formed in sediment by deposition and subsequent erosion. |
|
|
|
Incised Meanders |
Meanders that retain their sinuous pattern as they cut vertically downward below the level at which they originally formed. |
|

