![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
834 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A patient presents with acute pulmonary edema. Now what?
|
Tx:
1) Oxygen 2) Furosemide 3) Morphine 4) Nitrates Dx: 1) Chest xray 2) EKG 3) Pulsox/ABG 4) Echo **Treatment should with started WITH diagnostic maneuvers |
|
|
A pt comes in with dyspnea, S3 on exam and rales. What do you suspect
|
Acute pulmonary edema
|
|
|
Treatment for diastolic CHF
|
1) β-blockers
2) Diuretics |
|
|
What is an absolute contraindication to using β-blockers in CHF?
|
Symptomatic bradycardia
COPD should be considered but is not an absolute contraindication. Usually the benefit is greater than the risk. |
|
|
When is a biventricular pacemaker indicated in CHF?
|
Severe CHF with a QRS >120 msec
|
|
|
When is an ICD indicated in CHF?
|
When EF remains <35% on medical management
|
|
|
Which medications have been shown to have a mortality benefit in systolic CHF?
|
1) β-blockers
2) ACEIs/ARBs 3) Spironolactone No mortality benefit: digoxin, diuretics |
|
|
You float a right heart catheter in CHF. What do you expect?
|
Cardiac output: Down
Wedge pressure (L atrium): Up Right atrial pressure: Up Systemic vascular resistance: Up |
|
|
You float a right heart catheter in hypovolemic shock. What do you expect?
|
Cardiac output: Down
Wedge (L atrium): Down Right atrial pressure: Down Systemic vascular resistance: Up |
|
|
You float a right heart catheter in pulmonary hypertension. What do you expect?
|
Cardiac output: Down
Wedge (L atrium): Down Right atrial pressure: Up Systemic vascular resistance: Up |
|
|
You float a right heart catheter in septic shock. What do you expect?
|
Cardiac output: Up
Wedge (L atrium): Down Right atrial pressure: Down Systemic vascular resistance: Down |
|
|
Guidelines for cholesterol screening
|
Get fasting lipids (LDL, HDL, trigs) every 5 years in everyone over age 20.
Goals: LDL <200 (high is >240) Trigs <150 (high is >200) |
|
|
In lipid management, what are considered CAD equivalents?
|
1) Diabetes
2) Peripheral arterial disease 3) Symptomatic carotid artery disease 4) AAA |
|
|
In lipid management, what are the CAD risk factors?
|
1) Age: Men ≥45 yo and women ≥55 yo
2) Smoking: ≥1/2 ppd 3) Hypertension: ≥140/90 or on medication 4) HDL <40 (NB: HDL >60 is a protective factor) |
|
|
Mesenteric Ischemia
|
Etiology: Most often due to embolus in SMA, SMA thrombosis, venous thrombosis or nonocclusive ischemia
Hx: Sudden pain out of proportion to physical exam (at least initially); may have hematochezia or + FOBT Dx: increased WBC, increased amylase, late metabolic acidosis with increased lactate; angiography or CT angiography Tx: Surgery |
|
|
When should you transfuse platelets?
|
1) Active bleeding/needs surgery AND
2) Plts <50,000 |
|
|
How do you reverse elevated PT/INR?
|
If you have some time: Vit K
Emergently: FFP |
|
|
Initial Tx for Large Volume GI Bleeding
|
Bolus of Saline or LR
CBC Type and Cross PT/INR EKG Consult GI |
|
|
When should you suspect lithium toxicity?
|
Elderly patient on lithium with:
1) Renal failure and/or 2) Hyponatremia (may be caused by diuretics, nausea, vomiting, etc.) ***Well known interaction with thiazides! |
|
|
What is the treatment for lithium toxicity?
|
Dialysis
|
|
|
When should you suspect neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
|
Either:
1) Pt who recently started taking antipsychotics or 2) Parkinson's patient who has recently stopped levodopa Presentation: High fever, muscle rigidity, AMS, autonomic dysfunction, mutism, agitation, elevated CK and LFTs |
|
|
Treatment for neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
|
Transfer to ICU
Stop antipsychotic Bromocriptime to overcome dopamine receptor blockade Dantrolene or diazepam to reduce muscle rigidity Mortality 10-20%! |
|
|
When should you suspect serotonin syndrome?
|
History of SSRIs AND a migraine medication (triptan)/MAOI
Presentation: agitation, hyperreflexia, hyperthermia, muscle rigidity with volume contraction, myoclonus |
|
|
Treatment for serotonin syndrome
|
IV fluids
Cyproheptadine to reduce serotonin production Benzo to reduce muscle rigidity |
|
|
Possible sequelae of lithium toxicity
|
AMS
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Thyroid dysfunction Tremor |
|
|
When should you suspect MAOI-Induced Hypertension?
|
Acute hypertension, MAOI use AND: (one of the following)
- antihistamines - nasal decongestants - tyramine-rich foods (cheese, pickled foods) - TCA |
|
|
When should you suspect TCA toxicity?
|
Presentation: Hypotension, flushing, tachycardia, dilated pupils, dry mucous membranes, arrhythmia, urinary retention, constipation
[Think anticholinergic, sympathetic activation] |
|
|
What is the most serious complication of TCA toxicity?
|
Vtach, vfib, torsade de pointes
|
|
|
What are the most common side effects of lithium?
|
Weight gain
Acne Dose-related tremors GI distress Headaches Hypothyroidism (5%) ***Causes cardiac defects in the first trimester of pregnancy |
|
|
Depression Mimics
|
Hypothyroidism
Parkinson's Disease Medications: Beta blockers, steroids, antipsychotics, reserpine Alcohol abuse Amphetamine abuse |
|
|
Mania Mimics
|
Hyperthyroidism
Amphetamine use Pheochromocytoma |
|
|
Treatment of acute mania
|
Hospitalize
Mood stabilizer (lithium) Antipsychotics until the acute mania is controlled (risperidone) *Intramuscular depot phenothiazine may be considered in noncompliant patients |
|
|
How does invasive aspergillosis usually present?
|
Immunocompromised patient
Involves the respiratory tract, including lungs and sinuses |
|
|
What are the current screening guidelines for breast cancer (USPSTF)?
|
- Screen women ages 50-74 with mammogram q2yrs
- No proven benefit to self exam - Insufficient data to recommend clinical breast exam or mammogram after age 75 NB: ACS and NCI recommend yearly after age 40 |
|
|
Initial treatment for AMS of unknown etiology
|
Tx:
- Dextrose - Naloxone - Thiamine (give prior to dextrose to prevent Wernicke's) - Oxygen - Saline Dx: - Glucose - Tox screen - CBC, chemistries - UA |
|
|
Initial treatment for Overdose
|
Tx:
- Specific antidote (if known) - Otherwise --> thiamine, dextrose, naloxone - Charcoal - Psych consult, if intentional Dx: - CBC, chemistries - UA - Tox screen |
|
|
Antidote to acetaminophen
|
N-acetyl cysteine
|
|
|
"Antidote" to aspirin
|
Give bicarbonate to alkalinize the urine
|
|
|
Antidote to benzos
|
Flumazenil
BUT DO NOT GIVE IT! May precipitate a seizure |
|
|
Antidote to carbon monoxide
|
Oxygen (100% or hyperbaric)
|
|
|
Antidote to digoxin
|
Digoxin-binding antibodies
|
|
|
Antidote to methanol
|
Ethanol or fomepizole
|
|
|
Antidote to ethylene glycol
|
Ethanol or fomepizole
|
|
|
"Antidote" for Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
|
Dantrolene, bromocriptine
|
|
|
Antidote to narcotics
|
Naloxone
|
|
|
Antidote to organophosphates
|
Atropine, pralidoxime
|
|
|
"Antidote" to TCAs
|
Give sodium bicarbonate to protect the heart
|
|
|
Antidote to B-blockers
|
Glucagon
|
|
|
Antidote to heparin
|
Protamine sulfate
|
|
|
Antidote to warfarin
|
Vitamin K
Fresh frozen plasma (immediate reversal) |
|
|
Routine Prenatal Tests: Initial Visit
|
CBC
Blood type and screen (Rh incompatibility) UA with culture (treat asymptomatic bacteriuria) Pap smear (if due) Syphilis Rubella antibody screen (do NOT vaccinate while pregnant!) HIV Hepatitis serology (Hep B surface antigen) Optional: - Chlamydia and gonorrhea cultures, if <25 yo |
|
|
Rh negative mothers: When do they get Rhogam?
|
28 weeks and within 72 hours after delivery
Also after any procedures i.e. amniocentesis NB: This is useless if the mother has strongly positive Rh antibodies. |
|
|
Routine Prenatal Tests: Third Trimester
|
Gestational Diabetes screening
Group B strep cultures |
|
|
What are the options for prenatal genetic screening (Down's neural tube defects, aneuploidy)? When is each test available?
|
First trimester:
- Sequential screen - Full integrated screen - Serum integrated screen Second trimester: - Quad screen plus ultrasound |
|
|
Initial treatment for Tylenol overdose
|
1) N-acetyl cysteine (always do first, never wrong)
2) Acetaminophen level |
|
|
Presentation with Tylenol Overdose
|
N/V for 24 hours --> liver failure
|
|
|
Initial Treatment for Suspected Aspirin Overdose
|
Dx:
- CBC - Chem - PT/INT/PTT - ABG (respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis) - Salicylate level Tx: - D5W with bicarbonate to alkalinize the urine - Charcoal, if recent - Dialysis, if severe |
|
|
Alkalinizing the urine helps with excretion of which drugs?
|
Aspirin
TCAs Phenobarbitol Chlorpropamide |
|
|
What should you order on a tox screen?
|
Alcohol
Aspirin Acetaminophen Benzodiazepines |
|
|
Initial Treatment for Benzo Overdose
|
Dx: Standard overdose work-up
Tx: If benzos alone, let them sleep it off |
|
|
Presentation of Digoxin Overdose
|
Arrhythmia
Encephalopathy Seeing yellow halos around objects Blurred vision |
|
|
What is the difference (in presentation) between heat exhaustion and head stroke?
|
Heat Exhaustion: Think Mom
- Excessive sweating - Nausea/vomiting Heat Stroke: Can't compensate any more - Dry skin - ALTERED MENTAL STATUS |
|
|
How do you treat heat exhaustion?
|
IV fluids (room temp)
Get them out of the heat |
|
|
How do you treat heat stroke?
|
Spray with water
Ice packs/baths |
|
|
How does narcotic overdose kill you?
|
Respiratory depression
|
|
|
When should you suspect organophosphate poisoning?
|
Situation:
- Farm/crop duster exposed to insecticides - Nerve gas attack Presentation: Think cholinergic aka parasympathetic! - Salivation - Lacrimation -Urination - Diarrhea - Bronchospasm with wheezing |
|
|
Treatment for organophosphate poisoning?
|
- Toxin is absorbed through skin so remove clothes/wash patient
- Atropine (best initial) or pralidoxime (most effective) |
|
|
How does a TCA overdose kill you?
|
Arrhythmia
Seizures |
|
|
Initial treatment for TCA overdose
|
#1: Get an EKG
If widened QRS --> give bicarb and transfer to ICU NB: Giving bicarb has its own risks so get EKG first |
|
|
When should you suspect a black widow bite?
|
Abdominal pain withOUT tenderness
Rigidity Hypocalcemia *May look as if they have an abdominal perforation |
|
|
How do you treat a black widow bite?
|
Antivenin
|
|
|
When should you suspect a brown recluse bite?
|
Local necrosis
Bullae Dark lesions |
|
|
Treatment for a brown recluse bite
|
Debridement
Occasionally, steroids and dapsone help |
|
|
What is the most common early and late cause of death with burns?
|
Early: Carbon monoxide poisoning
Late: Infection |
|
|
Initial Treatment for Someone in a Fire
|
- Give oxygen
- Assess respiratory status: Is the patient wheezing, stridorous or hoarse? Do they have burns in the mouth or nose? --> Intubate if yes - Give fluids per the Parkland formula |
|
|
Parkland Formula:
What's it for? How do you calculate it? |
Calculates the amount of IV fluids needed by a burn patient in a 24 hour period to keep them hemodynamically stable
4 ml * Wt in kg * percentage of body with a 2nd or 3rd degree burn Ex: 75 kg pt with 30% burns would need 9000 mL of normal saline or LR |
|
|
How does hypothermia kill you?
|
Arrhythmia
|
|
|
Most important step in evaluation of hypothermia?
|
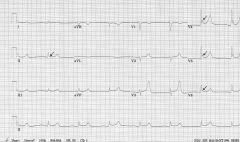
EKG: Look for "J waves of Osborn"
|
|
|
Treatment of hypothermia
|
Secure airway
Remove wet clothing and rewarm (blankets, warm IV fluids) EKG!! Monitor electrolytes, renal function and ABG |
|
|
How does treatment of electrical burns differ from thermal burns?
|
Most of the destruction is internal
Monitor: renal function, myoglobin, acid base status, EKG Treat aggressively with IV fluids to prevent renal failure Tx: - ABCs - IV fluids - Pain control - Tetanus prophylaxis - If they have myoglobinuria, give IV fluids to maintain urine output at 1.5-2 cc/kg/hr |
|
|
What are extrapyramidal symptoms?
|
Tremor, torticollis, trismus, rigidity, dysphonia, dysphagia
|
|
|
Describe anticholinergic effects
|
Sympathetic!
Fever Skin flushing Dry mucous membranes Tachycardia Dilated pupils Urinary retention Psychosis |
|
|
What medications tend to cause anticholinergic side effects?
|
Antihistamines
TCAs Scopolamine Antipsychotics Atropine |
|
|
Describe cholinergic effects
|
Parasympathetic!
Diarrhea Urination Salivation Lacrimation Pupils constricted Bradycardia Bronchospasm |
|
|
What medications tend to produce cholinergic effects?
|
Organophosphates
Pilocarpine Pyridostigmine |
|
|
Antidote to anticholinergics
|
Physostigmine
|
|
|
When should you treat for rabies with an animal bite?
|
If:
1) Animal is wild 2) The animal is domestic, acts unusual and has a positive direct immunofluorescent antibody study performed on their brain following sacrifice *No tx is necessary if the animal is observed to be normal for 10 days |
|
|
What are the most common organisms in a human bite?
|
Polymicrobial
- Aerobic gram positive i.e. strep - Eikenella |
|
|
What are the most common pathogens in cat bites?
|
Pasteurella
Bartonella |
|
|
What are the most common pathogens in dog bites?
|
Alpha-hemolytic strep
Staph aureus Pasteurella multocida Anaerobes |
|
|
What is the first choice of antibiotic for any human/cat/dog bite?
|
Amp/clavulanate
|
|
|
When would you consider giving tetanus immunoglobulin?
|
Contaminated wound AND
Patient had <3 doses of vaccine (or unknown) NB: Do not give if the pt has EVER completed vaccination i.e. even if it was >10 yrs ago |
|
|
When would you consider giving tetanus vaccine in the setting of a wound?
|
1) No vaccination
2) Unknown vaccination history 3) >10 years since completion of the 3 shots 4) Contaminated wound AND >5 years since vaccine |
|
|
Describe the rule of 9s in burns
|
Describes the percent body surface area involved:
9% per arm and head 18% per leg, front torso, back torso 1% for perineum NB: In children, the legs are 14% apiece and the head is 18%. |
|
|
When should a patient be referred to a burn center?
|
Partial thickness >25% BSA
Full thickness >10% Burns to face, hands, feet, perineum or joints Electrical or circumferential burns |
|
|
When should you suspect acute angle glaucoma?
|
Red eye
Fixed midpoint pupil** Rock-hard, painful eye Corneal haziness Haloes around lights Nausea/vomiting Headache |
|
|
How do you diagnose acute angle glaucoma?
|
Tonometry (IOP >30 mm Hg)
|
|
|
Treatment for acute angle glaucoma
|
Pilocarpine drops
Acetazolamide (reduces production of aqueous humor) IV Mannitol (osmotic diuretic) Latanoprost/travoprost (prostaglandin analogues) Timolol (topical beta blocker) Once resolved --> peripheral iridotomy to prevent recurrence |
|
|
When should you suspect retinal detachment?
|
Sudden loss of vision like "a curtain coming down"
Floaters/flashers Painless Unlateral |
|
|
Treatment for retinal detachment
|
Immediate referral to ophtho
Tilt head back Reattach with surgery, cryotherapy or injecting gas into the eye Last choice: Place band around the eye to get the retina close to the sclera |
|
|
Differential Diagnosis of Sudden, Unilateral, Painless Vision Loss
|
Retinal detachment
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Vitreous hemorrhage Optic neuritis Stroke/TIA |
|
|
When should you suspect central retinal artery occlusion?
|
Sudden, painless, unilateral vision loss
Cherry red spot in the macula |
|
|
Treatment for central retinal artery occlusion
|
Mostly supportive
Exception: In the case of temporal arteritis, give high dose steroids |
|
|
When should you suspect central retinal vein occlusion?
|
Sudden, painless, unilateral vision loss
"Blood and thunder" appearance on exam Retinal hemorrhages Often in the setting of HTN, diabetes, glaucoma, and increased blood viscosity |
|
|
Treatment for central retinal vein occlusion
|
Basically none
|
|
|
When should you suspect optic neuritis?
|
Unilateral vision loss
May be sudden or subacute Usually painful, but not always NB: Consider in the setting of MS, Lyme disease, or tumor |
|
|
Ddx for sudden, unilateral, painful vision loss
|
Optic neuritis
Closed angle glaucoma Migraine headache (consider with N/V, aura) Trauma |
|
|
Ddx for gradual vision loss
|
Cataracts
Macular degeneration Open angle glaucoma Presbyopia Diabetic retinopathy Uveitis (consider in autoimmune settings) Papilledema Corneal infection (CMV retinitis, HSV keratitis, corneal ulcer) Direct insult to brain |
|
|
Exam Findings in Macular Degeneration
|
Yellow-white drusen in the macular area
|
|
|
Exam Findings in Diabetic Retinopathy
|
Cotton wool spots
Dot-blot hemorrhages Microaneurysms Neovascularization |
|
|
Exam Findings in Optic Neuritis
|
Blurred disc margins
|
|
|
Exam Findings with hypertensive retinopathy
|
Arteriolar narrowing
Copper/silver wiring Cotton-wool spots Optic nerve edema (if severe) |
|
|
How does a CN4 palsy present?
|
Patient cannot look down when their gaze is medial
Often presents as diplopia when the pt walks down stairs |
|
|
How does a CN3 palsy present?
|
Eye is down and out
Can only move laterally May have ptosis |
|
|
When should you suspect corneal abrasion?
|
Pain out of proportion to exam
Photophobia Foreign body sensation Dx: Fluorescein staining |
|
|
Treatment for corneal abrasion
|
Topical broad spectrum antibiotics (gentamicin, bacitracin)
Tetanus prophylaxis Oral pain meds NB: Do NOT patch if caused by contacts. |
|
|
Ddx of a red eye
|
Uveitis
Glaucoma Conjunctivitis Abrasion |
|
|
Bacterial vs Viral vs Allergic Conjunctivitis: Presentation
|
Viral: Bilateral, watery discharge, irritated, preauricular lymphadenopathy
Bacterial: Unilateral, purulent discharge, eyelids stuck together Allergic: Bilateral, intensely itchy, watery discharge, cobblestone papillae under upper lid, history of atopy |
|
|
Treatment for Allergic Conjunctivitis
|
Cool compresses
Topical antihistamine/vasoconstrictors (naphazoline/pheniramine) Mass cell stabilizers (Cromolyn, olopatadine) |
|
|
Causative organisms in Bacterial Conjunctivitis
|
Staph
Strep Neisseria gonorrhoeae Chlamydia trachomatis |
|
|
Treatment for Bacterial Conjunctivitis
|
Staph or strep: topical 10% sulfacetamide or aminoglycoside
Gonorrhea: IV ceftriaxone AND topical erythromycin/tetracyline Chlamydia: Oral doxycycline or oral/topical erythromycin |
|
|
Treatment for Viral Conjunctivitis
|
Generally none
|
|
|
DDx and Timing of Neonatal Conjunctivitis
|
Within 24 hours: chemical
2-5 days: Gonorrhea 5-14 days: Chlamydia |
|
|
Primary Survey for Trauma
|
Airway and cervical spine control
Breathing with ventilation Circulation with hemorrhage control Disability (neuro) Exposure |
|
|
Primary Survey for Trauma: A
|
Airway and cervical spine control
- Check patency of airway - Oxygen - Intubate or create a surgical airway, as indicated |
|
|
Indications for Intubation in Trauma
|
Impending airway compromise
GCS <=8 Altered mental status Apnea Severe closed head injury |
|
|
When should you consider a surgical airway in trauma?
|
Significant maxillofacial injuries
|
|
|
What are the most common pulmonary pathogens seen in cystic fibrosis?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staph aureus H. flu |
|
|
What is the preferred empiric antibiotic regimen in a CF patient with a pulmonary exacerbation?
|
Tobramycin AND
Ticarcillin-clavulanate NB: Should cover staph, pseudomonas and H. flu. Single drug therapy is never appropriate in treatment of Pseudomonas. |
|
|
When should you suspect heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
|
Heparin exposure for 5-14 days AND:
- Thrombosis - Reduction in platelets >=50% - Necrosis at injection site - Anaphylactoid reaction after heparin |
|
|
How do you diagnose HIT?
|
Serotonin release assay
|
|
|
Treatment for HIT
|
- Stop all heparin products (including Lovenox)
- Serotonin release assay to confirm - Start alternative anticoagulation with direct thrombin inhibitor (argatroban, fondaparinux) - Start warfarin ONLY AFTER treatment with another anticoagulation AND recovery of platelet count >=150,000 |
|
|
Why shouldn't you start warfarin immediately in HIT?
|
Dropping Protein C --> prothrombotic state
|
|
|
What transient form of birth control has the lowest pregnancy rate?
|
Implantable or injectable contraceptives (<2-3%)
NB: Compared to OCPs, condom, cervical cap, diaphragm and spermicide. Check where this stands compared with regard to IUD! |
|
|
A minor presents to your office and asks you not to tell his/her parents. What topics can you generally talk about without consent?
|
Mental health
Contraceptives STDs Pregnancy Substance use |
|
|
How do you correct serum calcium for aberrant albumin?
|
For every decrease of 1 g/dL below 4, add 0.8 to the calcium.
Example: Uncorrected Ca 10.0 with albumin of 2.0 --> Corrected Ca of 11.6 |
|
|
What is the most common diagnosis with bilateral breast discharge?
|
Prolactinoma
Dx: Order prolactin and TSH levels |
|
|
Most Common Cause of Unilateral Nipple Discharge
|
Nonbloody: Intraductal Papilloma
Bloody: Cancer until proven otherwise |
|
|
When should you suspect intraductal papilloma?
|
Woman with unilateral, nonbloody nipple discharge
NB: A palpable mass, bloody discharge or involvement of more than one duct makes it more likely to be cancer. |
|
|
Workup for Unilateral Nipple Discharge
|
Mammogram
If negative --> Surgical duct excision If positive --> Biopsy |
|
|
Ddx for a Breast Mass
|
Cancer
Fibroadenoma Intraductal papilloma Mastitis Fat Necrosis Fibrocystic breasts Abscess |
|
|
When should you suspect fibrocystic breasts?
|
Setting: 20-50 yo woman
Presentation: Bilateral, nodular, painful breast lump(s) that vary with the menstrual cycle |
|
|
Treatment for fibrocystic breasts
|
OCPs
|
|
|
When should you suspect fibroadenoma?
|
Setting: Young woman
Presentation: Small, discrete, rubbery, unilateral, highly mobile mass. Usually slow growing. |
|
|
Treatment for fibroadenoma
|
Can observe. Surgery is curative but unnecessary.
NB: 30% will spontaneously resolve, but recurrence is common. |
|
|
Janeway lesions
|
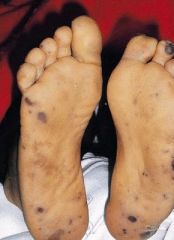
- Septic emboli --> nontender, hemmorhagic macules on the palms or soles
- Indicative of infective endocarditis |
|
|
Osler nodes
|
- Characteristic of infectious endocarditis
- Occur on finger pads |
|
|
What is phentolamine used for?
|
Mechanism: Vasodilation via alpha blockade
Indications: - Hypertensive emergency due to pheochromocytoma or cocaine - Erectile dysfunction (injected into penis) |
|
|
Initial treatment for cocaine-induced MI?
|
- Nitrates (or CCB)
- Oxygen - Aspirin - Benzodiazepine NB: If pt does not immediately improve, coronary angiography NB: Do NOT give beta blockers. Unopposed alpha activity may lead to worsened vasospasm. |
|
|
What is an appropriate nutrition goal (kcal and protein) for a patient with adequate baseline nutrition? i.e. not malnourished
|
30 kcal/kg/day with 1g/kg protein
|
|
|
In a setting suggestive of MI, how many troponins are needed to rule out?
|
2, spaced 6 hours apart
|
|
|
A patient on IV nutrition develops sudden hyperglycemia. What should you suspect?
|
Sepsis. Initiate an infection workup.
|
|
|
What BUN/Cr ratio is suggestive of a prerenal etiology of AKI?
|
>20
|
|
|
Describe the treatment paradigm for acute atrial fibrillation
|
1) Is the patient stable? If no --> urgent cardioversion
2) Rate control with a beta blocker (not in asthma) or calcium channel blocker (not in CHF or heart block) 3) Anticoagulate 4) If they don't spontaneously resolve w/in ~24 hours, cardiovert NB: Some sources suggest maintenance rate control with anticoagulation instead of cardioversion.... |
|
|
What are the preferred agents for rate control in acute atrial fibrillation?
|
Calcium channel blockers: IV diltiazem, IV verapamil
- Do NOT use in severe CHF or heart blocks Beta Blockers: IV metoprolol or IV propranolol - Do NOT use in asthma Others: amiodarone, digoxin (very slow onset) |
|
|
When should you suspect atrial fibrillation?
|
Setting: Patient with history of HTN, ischemia or cardiomyopathy
Presentation: Palpitations, irregular pulse |
|
|
Work-up for acute afib
|
EKG --> telemetry for dx
1) Is the patient unstable? (SBP<90, AMS, CHF, chest pain) If yes --> Emergent cardioversion If no: - TEE - TSH and T4 - Electrolytes: K, Mg, Ca - Troponin, if indicated |
|
|
Preferred anticoagulation in acute atrial fibrillation
|
Dabigatran or
Heparin bridge to warfarin |
|
|
Target INR in acute atrial fibrillation
|
2-3
|
|
|
Describe the CHADS score: What's it for? How do you calculate it?
|
Used to determine anticoagulation in afib
Congestive heart failure (1 pt) Hypertension (1 pt) Age 75 or older (1 pt) Diabetes (1 pt) Stroke or TIA (2 pt) Score 0 --> Aspirin Score 1 --> Aspirin or Warfarin Score 2 --> Warfarin or Dabigatra |
|
|
A mother with chronic Hep B gives birth. What should you do?
|
At birth: Hepatitis B immunoglobulin AND vaccine
1-2 mo: Hepatitis B vaccine booster 6 mo: Hepatitis B vaccine booster #2 Test serologies at 9-15 months |
|
|
Ddx for postpartum fever
|
7Ws:
- Womb - emdomyometritis - Water - UTI - Wind - Pneumonia, atelectasis - Walking - DVT, PE - Wound - Incision, lacerations - Weaning- Breast engorgement, mastitis, breast abscess - Wonder drugs- Drug fever |
|
|
What are the indications for a C-section?
|
Maternal:
- Prior C section with a vertical incision - Active genital herpes infection - Cervical cancer - Maternal death Fetal factors: - Malposition - Distress - Cord prolapse - Erythroblastosis fetalis Both: - Cephalopelvic disproportion - Placenta previa/placental abruption - Failed vaginal delivery |
|
|
When should you suspect 21-hydroxylase deficiency?
|
Setting: Newborn with ambiguous genitalia
Presentation: - Salt wasting (hyponatremia) - Hyperkalemia - Hypotension - Elevated ACTH - Increased 17-hydroxyprogesterone - Hirsutism in adults NB: Due to congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|
|
What are the three types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
|
21 hydroxylase deficiency (most common)
11 hydroxylase deficiency 17 hydroxylase deficiency |
|
|
Which patients in the ICU should get GI prophylaxis?
|
Coagulopathy or
History of GI bleed in the last year or Ventilation for >48 hours or Two of the following: Sepsis, ICU stay >1 week, occult GI bleeding >6 days, glucocorticoids |
|
|
Preferred agents for ICU GI prophylaxis
|
Enteral: PPI (omeprazole)
IV: H2 blocker (ranitidine) |
|
|
Preseptal (periorbital) cellulitis vs. Orbital (postseptal) cellulitis
|
Preseptal: Eyelid erythema, edema, tenderness, chemosis, fever and increased WBC
- Treat with oral abx Orbital: Above sx PLUS ophthalmoplegia, visual acuity changes, diplopia, proptosis - Treat with broad-spectrum IV abx +/- surgery |
|
|
What are possible complications of orbital cellulitis?
|
Abcesses (orbit or brain)
Cavernous sinus thrombosis Blindness |
|
|
When should you suspect PCP intoxication?
|
Agitation
Restlessness Disorientation Hypertension Tachycardia Nystagmus *** |
|
|
Treatment for PCP intoxication
|
Low stimulation environment
NB: Haldol or benzos can be used in the setting of aggression, seizures or agitation |
|
|
Good choices for treatment in a noncompliant schizophrenic
|
Haloperidol DECANOATE
Injectable risperidone Injectable fluphenazine |
|
|
Recommended interval for feeding a newborn
|
Q2-3 hours. 4 hours is the absolute maximum.
|
|
|
What is the rule of 2s?
|
Refers to characteristics of Meckel's diverticulum:
- 2 feet proximal to the ileocecal valve - 2 types of ectopic tissue (pancreatic, gastric) - 2% of the population - 2x as likely in males - Usually presents by age 2 - 2 cm in diameter |
|
|
When should you suspect Meckel's diverticulum?
|
Setting: Child under the age of 2 with painless rectal bleeding or intussusception
Dx: Tech-99 radionuclide scan ("Meckel scan") - Gold standard is a tissue biopsy |
|
|
Treatment for Meckel Diverticulum
|
- Stabilize with IV fluids +/- pRBCs as indicated
- Surgical exploration |
|
|
When should you suspect subclinical hypothyroidism?
|
Setting: Asymptomatic patient
Dx: TSH high, T4 normal |
|
|
When should you treat subclinical hypothyroidism?
|
Only if:
- Abnormal lipid profile - Symptomatic - Presence of antithyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies - Ovulatory or menstrual dysfunction - TSH >10 |
|
|
Thyroid Screening
|
Controversial
ATA: All pts >40 yo ACP: Women >50 yo with findings suggestive of thyroid disease |
|
|
What test is needed for definitive diagnosis of sickle cell?
|
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
NB: Peripheral blood smear is supportive but not definitive |
|
|
When should you suspect mucormycosis?
|
Setting: Patient with DKA
Presentation: Fever, facial flushing, maxillary pain and tenderness, nasal discharge, ophthalmoplegia, headache Dx: Biopsy |
|
|
Treatment for mucormycosis
|
Debride necrotic tissue
IV amphotericin B NB: Mortality remains high even with aggressive tx. |
|
|
Which pap results constitute a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)?
|
Moderate dysplasia
Severe dysplasia CIN 2-3 CIS |
|
|
What pap results constitute a low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL)?
|
Mild dysplasia
CIN 1 HPV-positive** |
|
|
Your pt has an ASCUS pap. Now what?
|
1) Repeat pap in 3-6 months with HPV DNA typing
2) Negative repeat --> routine screening Positive repeat --> colposcopy, ectocervical biopsies and endocervical curettage (ECC) NB: Do NOT perform an ECC in a pregnant patient. Also, if patient is not reliable, consider doing colposcopy upfront. |
|
|
Your patient has an abnormal Pap. Now what?
|
- Colposcopy, ectocervical biopsy and endocervical curettage
- If not diagnostic, consider CKC NB: Do NOT do ECC in pregnant patients. If age <20 and it's not HSIL, repeat Pap in one year. |
|
|
Treatment for LSIL
|
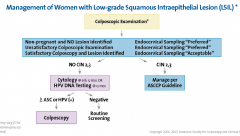
- Observation
- Follow-up Pap every 6 months |
|
|
Treatment for HSIL
|
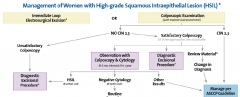
HSIL=moderate or severe dysplasia, CIN 2-3 or CIS
Dysplasia -->Colposcopy for diagnosis CIN 2-3 --> excision (LEEP) or ablation (CKC< last, cryotherapy) --> Pap in 6 months |
|
|
Treatment of choice for Pneumocystic pneumonia?
What if the patient has a sulfa allergy? |
IV trimethoprim-sulfamethaxazole (Bactrim)
Sulfa allergy: - Mild to moderate pneumonia--> oral atovaquone -Moderate to severe pneumonia --> IV pentamidine |
|
|
When should you suspect Pneumocystic pneumonia?
|
Setting: Patient with defects in cell-mediated immunity i.e. HIV/AIDs
Presentation: Insidious onset, low grade fever, cough ,dyspnea, tachypnea Imaging: Diffuse, BILATERAL, ground glass opacities |
|
|
Positive Psychotic Symptoms
|
Delusions (mostly bizarre)
Disorganized speech or behavior Hallucinations Agitation |
|
|
Negative Psychotic Symptoms
|
Flattened affect
Social withdrawal Anhedonia Apathy Poverty of thought |
|
|
What is needed for a diagnosis of schizophrenia?
|
POSITIVE psychotic symptoms
Impairment of social or occupational function Duration >6 months |
|
|
What is the difference between schizophrenia, schizophreniform disorder and a brief psychotic disorder?
|
Mostly duration
Schizophrenia: >6 months Schizophreniform disorder: 1-6 months Brief psychotic disorder: <1 month and resolves - Usually associated with a stressful life event |
|
|
A patient has peculiar thoughts/delusions without actual impairment of function. Ddx?
|
Delusional disorder: Delusions must be nonbizarre.
Personality disorder i.e. schizotypal Substance abuse Temporal lobe epilepsy |
|
|
Treatment for psychosis
|
1) Decide whether to hospitalize!
- Do so if paranoid or bizarre - Benzos for agitation - Antipsychotics for 6 months - Long term counseling - Consider long term antipsychotics only with repeat episodes |
|
|
Indications for an antipsychotic medication
|
Acute psychosis of any kind (schizophrenia, depression with psychotic features, mania, etc.)
- Has immediate quieting effect - Delays relapse Sedation with benzos are contraindicated Movement disorders to suppress tics and vocalization |
|
|
Pros and Cons of High Potency Conventional Antipsychotics
|
Examples: Haldol, fluphenazine
Pros: - Less sedating - Depot injections available - Fewer anticholinergic side effects - Less hypotension Cons: Greatest association with EPS |
|
|
Pros and Cons of Low Potency Conventional Anti-psychotics
|
Examples: Thioridazine, chlorpromazine
Pros: Less association with EPS Cons: - Greater anticholinergic side effects - More sedation - More postural hypotension |
|
|
Pros and Cons of Atypical Antipsychotics
|
Examples: Olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine, clozapine
Pros: - Greater effect on negative symptoms - Little risk of EPS Cons: - Clozapine associated with agranulocytosis |
|
|
Thioridazine: Class, Side effects
|
Low potency conventional antipsychotic
Side Effects: - Prolonged QT and arrhythmias - Long term retinal pigmentation (need eye exams!) |
|
|
Clozapine: Class, side effects, monitoring
|
Atypical antipsychotic
- Use only in refractory but compliant patients Side Effects: - Agranulocytosis (1%) - Seizures - Virtually NO risk of movement disorders/EPS Monitoring: - Must get CBC before therapy and weekly thereafter |
|
|
Common reasons for antipsychotic noncompliance
|
Men:
- Impotence - Inhibition of ejaculation Women: - Weight gain (hyperprolactinemia) - Galactorrhea - Amenorrhea |
|
|
Best medication choice for a schizophrenic with insomnia
|
Olanzapine
Quetiapine Aripiprazole Ziprasidone |
|
|
Best medication choice for a schizophrenic with sedation
|
Risperidone
|
|
|
Name the high potency conventional antipsychotics
|
Haloperidol
Fluphenazine |
|
|
Name the low potency conventional antipsychotics
|
Thioridazine
Chlorpromazine |
|
|
Name the atypical antipsychotics
|
Risperidone
Quetiapine Olanzapine Clozapine Ziprasidone Aripiprazole (Abilify) |
|
|
When should you suspect akathisia?
|
Setting; Patient on antipsychotics for at least several weeks
Presentation: - Whole body restlessness |
|
|
Treatment for akathisia
|
- Reduce dose of antipsychotic or
- Switch to a newer antipsychotic Consider adding beta-blocker or benzo |
|
|
When should you suspect acute dystonia?
|
Setting: Younger person who recently started an antipsychotic
Presentation: - Muscle spasms - Torticollis - Difficulty swallowing |
|
|
Treatment for acute dystonia
|
Reduce the dose of antipsychotic
Add an anticholinergic - Benztropine - Benadryl - Trihexyphenidyl |
|
|
When should you suspect bradykinesia?
|
Setting: Older patient on antipsychotic medications
Presentation: - Bradykinesia - Tremor - Rigidity - Other signs of parkinsonism |
|
|
Treatment for bradykinesia
|
Reduce dose of antipsychotics
Add anticholinergic - Benztropine - Benadryl - Trihexyphenidyl |
|
|
When should you suspect tardive dyskinesia?
|
Setting: Patient on antipsychotics for at least months
Presentation: - Repetitive, involuntary, purposeless movements such as lip smacking, tongue movements, grimacing, blinking NB: Can also be seen with long-term use of antiemetics (metoclopramide, prochlorperazine) |
|
|
Treatment for tardive dyskinesia
|
Stop older antipsychotic/dopamine antagonists
Switch to a newer antipsychotic Consider benztropine NB: Symptoms often worsen after discontinuation of the offending drug! |
|
|
Anxiety Mimics
|
Hyperthyroidism
Pheochromocytoma Excess cortisol Heart failure Arrhythmias Asthma/COPD Drugs: steroids, caffeine, amphetamines, cocaine, withdrawal from a depressant |
|
|
When should you suspect Panic Disorder?
|
REGULAR, brief attacks of intense anxiety
Autonomic symptoms (tachycardia, tachypnea, sweating, etc.) No obvious precipitant or underlying psych illness |
|
|
Treatment for Panic Disorder
|
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Relaxation training and desensitization Consider: SSRIs, benzos, imipramine MAOI |
|
|
When should you suspect OCD?
|
Obsessions: intrusive, anxiety provoking thoughts
Compulsions: Behaviors that reduce the anxiety NB: Generally have insight i.e. they know that the behavior is unreasonable and excessive |
|
|
Treatment for OCD
|
CBT
SSRIs or clomipramine |
|
|
When should you suspect acute stress disorder?
|
Setting: Patient who has experienced a LIFE THREATENING event within the last month
Presentation: - Re-experiencing the event - Avoidance of stimuli associated with the event - Numbing of general responsiveness - Increased arousal: Hypervigilance, anxiety, sleep disturbances, emotional lability, impulsiveness NB: Symptoms must last <1 month and occur within 1 month of the event |
|
|
When should you suspect PTSD?
|
Setting: Patient who has experienced a LIFE THREATENING event
Presentation: - Re-experiencing the event - Avoidance of stimuli associated with the event - Numbing of general responsiveness - Increased arousal: Hypervigilance, anxiety, sleep disturbances, emotional lability, impulsiveness NB: Symptoms last >1 month |
|
|
When should you suspect Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
|
Excessive, poorly controlled anxiety without any single focus
Must occur DAILY for at least 6 months |
|
|
Treatment for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
|
Supportive psychotherapy
Relaxation training Biofeedback Meds: SSRI, venlafaxine, buspirone, benzos short term |
|
|
When should you suspect cyclothymia?
|
Recurrent episodes of depressed mood and hypomania for at least 2 years
|
|
|
Treatment for cyclothymia
|
Psychotherapy
If function is impaired --> divalproex |
|
|
Indications for ECT
|
Major depression unresponsive to medications
High risk for immediate suicide Contraindication to antidepressant medications Good response to ECT in the past |
|
|
Side Effects of Bupropion
|
Modest weight loss
Seizures Tremor Fewer sexual side effects than other SSRIs |
|
|
Side Effects of Mirtazapine
|
i.e. Remeron
Weight gain Sedation |
|
|
Classic side effect of trazodone
|
Sedation
Priapism |
|
|
Antidepressants with sedative effects
|
Trazodone
Doxepin (TCA) Mirtazapine (also an appetite stimulant) Amitriptyline |
|
|
Indications for divalproex
|
First-line choice for rapid-cycling bipolar
When lithium is ineffective, not practical, contraindicated |
|
|
Significant side effects with carbamazepine
|
Sedation
Agranulocytosis |
|
|
Maintenance therapy for bipolar
|
First choice: Lithium
Second choice: Divalproex Third: Carbamazepine |
|
|
When should you suspect somatization disorder?
|
Multiple symptoms affecting multiple organs with no explanation
Dx: Need 4 pain symptoms, 2 GI, 1 sexual, 1 pseudoneurologic NB: Symptoms are not produced intentionally or feigned |
|
|
Treatment for somatization disorder
|
Limit care to a single PCP
Brief, monthly visits Limit diagnostic testing Psychotherapy |
|
|
When should you suspect conversion disorder?
|
At least one neurologic symptom that cannot be explained
Usually have psychologic factors associated with onset Generally not concerned with the impairment |
|
|
Treatment of conversion disorder
|
Supportive patient-physician relationship
Psychotherapy |
|
|
When should you suspect hypochondriasis?
|
- Pt belief that they have a SPECIFIC disease despite repeated negative work-up
- Symptoms for at least 6 months - Reassurance by a physician doesn't help |
|
|
Treatment for hypochondriasis
|
Single provider
Regular routine visits Psychotherapy |
|
|
What is the difference between factitious disorder and malingering?
|
Factitious Disorder: Pt generally presents to many doctors/hospitals, has a large body of medical knowledge and demands tx. Often it's more about the attention or there may be no clear motivation.
Malingering: Obvious gain results from the faked sxs i.e. shelter, medications, disability |
|
|
Treatment for Factitious Disorder or Malingering
|
Supportive psychotherapy
Minimize workup and tx |
|
|
When should you suspect anorexia nervosa?
|
Setting: Young person who is UNDERWEIGHT and amenorrheic
Criteria: 1) Restriction of intake relative to requirements 2) Intense fear of gaining weight or becoming fat 3) Disturbance in the way in which one’s body weight or shape is experienced NB: Up to 50% of anorexa patients may purge |
|
|
Treatment for Anorexia Nervosa
|
1) Chem7
- If electrolytes are abnl --> hospitalize SSRI Consider olanzapine for weight gain Behavioral psychotherapy |
|
|
When should you consider bulimia nervosa?
|
Setting: Young person in NORMAL weight range with binge eating, purging, diuretic and/or enema use
Presentation: - Painless parotid gland enlargement - Dental erosions - Electrolyte disturbances (hypokalemia, hypochloremia, metabolic alkalosis if puking, acidosis if laxatives) |
|
|
Criteria for Bulimia Nervosa
|
A.Recurrent episodes of binge eating.
B.Recurrent inappropriate compensatory behaviors in order to prevent weight gain C.The binge eating and inappropriate compensatory behaviors both occur, on average, at least once a week for 3 months. D.Self-evaluation is unduly influenced by body shape and weight. |
|
|
When should you suspect body dysmorphic disorder?
|
Setting: Young person who is preoccupied with an imagined or slight defect in appearance, causing impairment
|
|
|
Treatment for Body Dysmorphic Disorder
|
High doses of SSRIs
|
|
|
Prognostic Factors in Schizophrenia
|
Signifies a poor prognosis:
- Early age of onset - Negative symptoms - Poor premorbid functioning - Family history - Disorganized or deficit subtype |
|
|
When should you suspect intermittent explosive disorder?
|
Aggression out of proportion to the stressor
- Generally, the patient does not have insight - May have a history of head trauma NB: Rule out drug use first |
|
|
Treatment for intermittent explosive disorder
|
SSRIs
Mood stabilizers |
|
|
Your female patient is being abused by her husband. Do you report?
|
Reporting is not mandatory.
Provide information about counseling and local shelters. |
|
|
Cluster A Personality Disorders
|
Paranoid
Schizoid Schizotypal |
|
|
When should you suspect paranoid personality disorder?
|
Mistrustful, suspicious
Emotionally cold or distant Often take legal action against people Example: Old man who accuses his neighbors of stealing his mail and conspiring against him |
|
|
When should you suspect schizoid personality disorder?
|
Detached, emotionally distant
Absorbed in their own thoughts and feelings Example: Lighthouse keeper with no known contacts |
|
|
When should you suspect schizotypal personality disorder?
|
Discomfort with social relationships
Eccentric, magical thinking Example: Man living in a small town selling magical, healing herbs for a living, guided by spirits |
|
|
Cluster B Personality Disorders
|
Histrionic
Borderline Antisocial Narcissistic |
|
|
When should you suspect histrionic personality disorder?
|
Wants to be the center of attention
Exaggerated behavior with shallow expression of emotions Use of physical appearance to draw attention |
|
|
When should you suspect Borderline Personality Disorder?
|
Splitting
Mood swings Impulsivity Unstable relationships Intense anger if they feel abandoned |
|
|
When should you suspect Antisocial Personality Disorder?
|
Criminal acts
Inabililty to conform to social mores Lack of remorse Aggressive |
|
|
When should you suspect Narcissistic Personality Disorder?
|
Grandiose sense of self
Believes they're special and deserving of admiration Lack empathy Enraged when criticized |
|
|
Cluster C Personality Disorders
|
Avoidant
Dependent Obsessive-Compulsive |
|
|
When should you suspect Avoidant Personality Disorder?
|
Desirous of affection and acceptance but socially inhibited
Feel inadequate Hypersensitive to criticism Shy away from gatherings and new things |
|
|
When should you suspect Dependent Personality Disorder?
|
Submissive and clinging
Need to be taken care of Feel inadequate and helpless |
|
|
When should you suspect Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder?
|
Preoccupied with perfectionism and control
Consumed by details Overconscientious Inflexible |
|
|
CAGE Screening: What's it for? How is it administered?
|
Have you ever:
- Felt that you should Cut back? - Felt Annoyed by others who have criticized your drinking? - Felt Guilty about your drinking? - Needed an Eye-opener to steady nerves or alleviate a hangover? Two or more affirmative answers is suggestive |
|
|
Work-up in a patient with alcohol abuse
|
Tox screen for other substances (breath, blood and urine)
Screen AST, ALT, GGT, LDH If there's any suggestion of IV drug use, add: - HIV - Hep B - Hep C - PPD |
|
|
Treatment for Acute Alcohol Intoxication
|
IV or IM thiamine
Mg B12 Folate MVI Glucose Monitor for withdrawal - If concern --> chlordiazepoxide or diazepam NB: If the patient has a history of severe liver disease, use a short acting benzo (lorazepam or oxazepam) |
|
|
What drugs are available for treatment of alcohol dependence?
|
Naltrexone (NOT naloxone!)
Acamprosate |
|
|
When should you suspect DTs?
|
Setting: Alcoholic who hasn't had a drink for 48-96 hours
Presentation: - Hallucinations - Disorientation - Tachycardia - Hypertension - Low-grade fever - Agitation - Diaphoresis Classic scenario: Disorientation and hallucinations after 2 days in the hospital |
|
|
When should you suspect Wernicke-Korsakoff?
|
Setting: Chronic alcoholic
Presentation: - Ataxia - Nystagmus - Amnesia with confabulation |
|
|
When should you suspect alcoholic hallucinosis?
|
Setting: Alcoholic 12-24 hours after their last drink
Presentation: - Hallucinations (visual, auditory or tactile) - NO change in mental status |
|
|
Which drugs can cause withdrawal?
|
Alcohol
Benzodiazepines Opiates Cocaine Amphetamines Barbituates |
|
|
Which drugs generally do not cause withdrawal?
|
PCP
LSD Inhalants Hallucinogens Marijuana |
|
|
When should you suspect cocaine withdrawal?
|
Anxiety
Tremors Headache Increased appetite Depression Risk of suicide |
|
|
Treatment for cocaine withdrawal
|
Antidepressants
|
|
|
When should you suspect amphetamine withdrawal?
|
Anxiety
Tremors Headache Increased appetite Depression Risk of suicide |
|
|
Treatment for amphetamine withdrawal?
|
Antidepressants
|
|
|
When should you suspect LSD or mushrooms?
|
Hallucinations
Impaired judgment Dissociative symptoms ("out of body") Panic Pupil Dilatation Tremors Incoordination Ideas of reference |
|
|
Treatment for LSD Intoxication
|
Talk them down
Consider benzos or antipsychotics |
|
|
When should you suspect inhalant use?
|
Belligerence
Apathy Assaultive Impaired judgment Blurred vision Stupor Coma |
|
|
Treatment for inhalant use
|
Consider antipsychotics if agitated
|
|
|
When should you suspect opiate intoxication?
|
Respiratory depression
Miosis Dysphoria Slurred speech Drowsiness |
|
|
When should you suspect opiate withdrawal?
|
Fever/chills
Watery eyes and nose Abdominal cramps Muscle spasms Insomnia Yawning |
|
|
Treatment for opiate withdrawal
|
Clonidine
Methadone |
|
|
When should you suspect PCP use?
|
Panic
Assaultive Agitation Nystagmus Hypertension Seizures Hyperacusis |
|
|
Treatment for PCP use
|
Talk them down
Support respiratory function Consider benzos, antipsychotics |
|
|
When should you suspect benzo or barbiturate use?
|
Inappropriate sexual or aggressive behavior
Impaired memory Impaired concentration |
|
|
When should you suspect benzo or barbiturate withdrawal?
|
Autonomic hyperactivity (tachy)
Tremor Insomnia Seizures Anxiety |
|
|
Treatment for benzo withdrawal
|
Long-acting barbiturates i.e. chlordiazepoxide, phenobarbital
|
|
|
Drugs that cause sexual dysfunction
|
Beta blockers
SSRIs a1-blockers Trazodone (priapism) Dopamine agonists (increased libido) Neuroleptics |
|
|
When should you suspect a paraphilia?
|
Causes impairment
Lasts >6 months |
|
|
Treatment for paraphilias
|
Psychotherapy
Aversive conditioning If severe, antiandrogen or SSRI to impair libido |
|
|
When should you suspect subarachnoid hemorrhage?
|
Sudden onset of "worst headache of their life"
Stiff neck Photophobia Loss of consciousness (50%) Focal neurologic deficits (30%) |
|
|
Workup for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
|
Noncontrast head CT
If negative, LP (look for xanthochromia and RBCs) |
|
|
You have an elevated WBC on LP. How do you tell if it's due to infection or a traumatic tap?
|
Look at the WBC:RBC ratio
Normal ratio: 1 WBC: 500 RBCs To be an infection, the number of WBCs should be higher than this |
|
|
Treatment for subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
Angiography to determine source of bleeding
Embolize site of bleeding Consider PO nimodipine to reduce the risk of stroke secondary to vasospasm Blood pressure control NB: Shunt if hydrocephalus |
|
|
Name the different transfusion reactions
|
Acute hemolytic (ABO incompatibility)
Febrile nonhemolytic reaction Urticarial reaction IgA Deficiency Minor blood group incompatibility Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) |
|
|
When should you suspect an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction?
|
Time Course: During the transfusion
Presentation: - Hypotension - Dyspnea - Tachycardia - Dark urine - Chest, back and flank pain - Elevated LDH and bilirubin |
|
|
Treatment for Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction (ABO incompatibility)
|
Stop transfusion
IV fluids NB: Check for clerical error or blood mix-up. |
|
|
When should you suspect Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)?
|
Time Course: Within 6 hours of transfusion
Presentation: - Acute shortness of breath following a transfusion - Fever - Hypotension - "White lung" on CXR |
|
|
Treatment for TRALI
|
Supportive care
Oxygen Intubate, if indicated Will resolve spontaneously |
|
|
When should you suspect transfusion-related IgA deficiency?
|
Time Course: During the transfusion
Presentation: - Anaphylaxis (hypotension, tachycardia, dyspnea) |
|
|
Treatment for IgA Deficiency
|
Stop transfusion
??? If the pt needs a transfusion in the future, use blood from an IgA deficient donor or washed RBCs |
|
|
When should you suspect a transfusion-related febrile non-hemolytic reaction?
|
Time Course: Within a few hours of transfusion
Presentation: - Small rise in temperature - No evidence of hemolysis |
|
|
Treatment for transfusion febrile non-hemolytic reactions?
|
None needed
In the future, use filtered blood to remove white cell antigens. |
|
|
When should you suspect minor blood group incompatibility?
|
Time course: Delayed
Presentation: - Jaundice - Otherwise, largely asymptomatic |
|
|
Treatment for minor blood group incompatibility
|
No specific therapy
NB: Due to minor incompatibilities in Kell, Duffy, Lewis or Kidd antigens. |
|
|
When should you suspect HELLP Syndrome?
|
Setting: Third trimester or postpartum woman
Presentation: - Hemolysis - Elevated LFTS - Low platelets - RUQ or epigastric pain Complications: DIC, placental abruption, fetal demise, ascites, hepatic rupture |
|
|
Treatment for HELLP Syndrome
|
Immediate delivery
IV mag sulfate, for seizure prophylaxis IV dexamethasone when plts <20k or <50k if you're doing a C section - Continue until plts >100,000 and liver fxn normalizes |
|
|
When should you suspect preeclampsia?
|
Setting: Young black woman with her first child
Presentation: - Hypertension - Proteinuria - Swelling of hands/feet - Headache - Oliguria |
|
|
Mild vs Severe Preeclampsia
|
Mild:
- BP>140/90 - Proteinuria 1+ or >300 mg/24 hours Severe: - BP>160/110 - Proteinuria 3+ or >5g/24 hours - HELLP - Oliguria (<500 ml/24 hrs) - Pulmonary edema |
|
|
Treatment for Mild Preeclampsia
|
#1: Is the pregnancy near term?
- If so --> stabilize mother and deliver If premature: - Hydralazine or labetalol for hypertension - Mag sulfate for seizure prophylaxis - Bed rest - Hospitalize |
|
|
Treatment for severe preeclampsia
|
#1: Stabilize mother (anti-hypertensives, MgSO4)
Deliver! NB: Continue mag for at least 12-24 hours after delivery |
|
|
When should you suspect magnesium toxicity?
|
Hyporeflexia
Respiratory depression CNS depression Coma Death |
|
|
Risk factors for preeclampsia
|
First pregnancy
Extremes in age Black Multiple gestation Hydatidiform mole Diabetes Chronic hypertension Chronic renal disease |
|
|
Workup for preeclampsia
|
CBC
UA with urine protein Chem12 PT/INR, PTT LFTs NB: Hemoconcentration with lead to an elevation in Hgb, Hct, BUN, Cr and uric acid |
|
|
What is the blood pressure goal in preeclampsia?
|
140-150/90-100
NB: Reducing the pressure below this may reduce uteroplacental blood flow. |
|
|
Medications for Blood Pressure Control in Preeclampsia
|
Acute elevation:
- IV hydralazine - IV labetalol Maintenance: - Methyldopa - B-blocker (may cause IUGR) NB: NEVER give thiazide diuretics or ACEIs. |
|
|
When should you suspect croup?
|
Age: 3 months-5 yrs
Presentation: - Upper respiratory symptoms - Barking cough*** - Low grade fever - Inspiratory stridor - Tachypnea - Worse at night - Steeple sign on frontal neck x-ray |
|
|
Treatment of croup
|
Humidified oxygen
PO dexamethasone Nebulized racemic epinephrine, if severe NB: Should resolve within 1 week. Rule out epiglottitis. |
|
|
Causative organisms in croup
|
Parainfluenza 1 or 3
Influenza A or B |
|
|
When should you suspect epiglottitis?
|
Setting: Sudden onset of symptoms in a 2-7 yo
Presentation: - Muffled voice - Drooling - Dysphagia - High fever - No cough*** - Sitting in tripod position - Inspiratory stridor |
|
|
Causative organism in epiglottitis
|
H. influenzae B (less common d/t vaccination)
S. pneumoniae S. aureus |
|
|
Treatment for epiglottitis
|
Hospitalize and send to OR
Consult ENT and anesthesia Intubate IV ceftriaxone Steroids Once stabilized: - Neck x-ray (thumbprint sign) - Blood cultures - Scope in OR - Epiglottic swab culture |
|
|
When should you suspect bacterial tracheitis?
|
Setting: Child <3 yo with a recent viral upper resp. infection
Presentation: - Brassy cough - Intermediate to high fever - Respiratory distress - NO drooling or dysphagia |
|
|
Workup for bacterial tracheitis
|
Blood cultures
Throat cultures Laryngoscopy Chest x-ray (subglottic narrowing and ragged tracheal air column) |
|
|
Treatment for bacterial tracheitis
|
Secure airway, if indicated
Antistaphylococcal antibiotics |
|
|
Causative organism in bacterial tracheitis
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
When should you suspect bronchiolitis?
|
Setting: Child under age 2 in fall or winter
Presentation: - Mild URI - Fever - Paroxysmal wheezy cough - Dyspnea - Tachypnea - Prolonged expirations - Expiratory wheezing NB: Ball-valve obstruction of the small airways leads to overinflation |
|
|
Workup for brochiolitis
|
Clinic diagnosis
CXR (hyperinflation with patchy atelectasis) Viral antigen testing of nasal secretions |
|
|
Causative organisms in brochiolitis
|
RSV (50%)
Parainfluenza Adenovirus NB: Viral!! |
|
|
Treatment for brochiolitis
|
Supportive:
- IV fluids - B-agonist nebulizer - Humidified oxygen Hospitalize if: - Severe tachypnea >60 rpm - Fever - Intercostal retractions |
|
|
When should you suspect viral pneumonia in a kid?
|
Setting: Age <5
Presentation: - URI symptoms - Low-grade fever - Tachypnea - CXR: Hyperinflation with bilateral interstitial infiltrates and peribronchial cuffing |
|
|
When should you suspect bacterial pneumonia in a child?
|
Setting: Age >5
Presentation: - High fever - Acute onset of shaking chills - Prominent cough - Pleuritic chest pain - Markedly diminished breath sounds - Dullness to percussion - CXR: Lobar consolidation |
|
|
When should you suspect a Chlamydia pneumonia in a child?
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
Setting: Infant 1-3 months in age Presentation: - Insidious onset - Staccato cough - Peripheral eosinophilia - No fever or wheezing - Conjunctivitis at birth - CXR: Unilateral lower lobe interstitial changes that look worse than the patient's presentation |
|
|
Work-up for Pediatric Pneumonia
|
Chest x-ray
Blood cultures CBC with diff IgM for mycoplasma/viral antigens NB: Do NOT get sputum cultures in children |
|
|
Treatment for Pediatric Pneumonia
|
Viral: Supportive.
- If they deteriorate, give abx as they may be coinfected with bacteria. Chlamydia/Mycoplasma: Erythromycin or another macrolide Bacterial: - Outpatient: Amoxicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanate or cefuroxime - Inpatient: IV cefuroxime. Add vancomycin for Staph aureus |
|
|
Most common initial presentation of CF
|
Meconium ileus
|
|
|
When should you suspect CF?
|
Meconium ileus
Failure to thrive Steatorrhea Vitamin A, D, E and K deficiencies Rectal prolapse Persistent cough Infertility (absent vas deferens) Undescended testes |
|
|
How do you diagnose CF?
|
Elevated sweat chloride test (>60 meq/L) x 2, obtained on different days
|
|
|
Inheritance Pattern in Cystic Fibrosis
|
Autosomal recessive
|
|
|
When should you suspect enuresis?
|
Bedwetting after age 5-7
At least twice a week for at least 3 months NB: Rule out UTI |
|
|
Treatment for enuresis
|
1) Behavioral therapy
- Sticker charts - Alarms If that fails --> TCAs, imipramine or desmopressin to reduce urine volume |
|
|
When is a family history of CAD significant?
|
Based on age.
Male relatives< 55 yo Female relatives< 65 yo |
|
|
What does an S3 gallop represent?
|
Dilated left ventricle
|
|
|
What does an S4 gallop represent?
|
Left ventricular hypertrophy
|
|
|
Describe a mitral regurgitation murmur
|
Holosystolic
|
|
|
What counts as a significant Q wave on EKG?
|
At least one little box wide or 1/3 of the entire QRS complex amplitude (height and depth)
|
|
|
What does a significant Q wave signify?
|
Necrosis
NB: Q waves are for life. |
|
|
Where should you look for an anterior infarct?
|
V1-V4
|
|
|
Where should you look for an inferior infarct?
|
II, III and AVF
|
|
|
Where should you look for a lateral infarct?
|
I, AVL
|
|
|
Where should you look for a posterior infarct?
|
V1 and V2
Looks like an inverted anterior MI so look for large R waves and ST depression |
|
|
When should you suspect a bundle branch block?
|
Widened QRS (at least 3 small squares)
R-R1 |
|
|
Left vs Right Bundle Branch Block
|
Left: Usually in leads V5-V6
- R-R1 may appear as two peaks "on the same mountain" or as a flattened peak Right: Usually in leads V1-V2 - Usually has two distinct R-R1 peaks with what looks like an S in between |
|
|
Why do we care about LBBB in the setting of possible ischemia?
|
EKG diagnosis of MI is generally not valid in the presence of LBBB (Q waves hide in the qRS complex)
|
|
|
What vessel is associated with a lateral MI?
|
Circumflex
|
|
|
What vessel is associated with an anterior MI?
|
LAD
|
|
|
What vessel is associated with a posterior infarction?
|
RCA or its branches
|
|
|
What vessel is associated with an inferior MI?
|
Left or right coronary artery, depending on dominance
NB: RCA more common |
|
|
What is the best test for reinfarction following an MI?
|
CK-MB
NB: CK-MB returns to baseline within 1-2 days after infarction whereas troponin stays elevated for 1-2 weeks. |
|
|
What is the first cardiac enzyme to elevate in the setting of MI?
|
Myoglobin
|
|
|
Absolute contraindications to exercise stress testing
|
Acute MI within the last 2-4 days
Acute aortic dissection Recent PE Myocarditis, pericarditis or endocarditis Critical aortic stenosis Severe CHF Unstable angina |
|
|
Relative contraindications to exercise stress testing
|
Anything that causes baseline EKG changes:
- LBBB - Digoxin - Paced rhythm - LVH HOCM High grade AV block |
|
|
When should you use a dipyridamole or adenosine stress test?
|
Patient can't exercise to a target heart rate of >85% of maximum
Baseline EKG changes |
|
|
When should you NOT use a dipyridamole or adenosine stress test?
|
Severe asthma or COPD (can cause bronchospasm)
Already on dipyridamole (Aggrenox for stroke prevention) Caffeine use in the last 24 hours (blocks adenosine) Second degree or higher heart block |
|
|
How do dipyridamole and adenoside stress the heart during a stress test?
|
Vasodilators
They work preferentially on the normal coronaries leading to "steal." |
|
|
How does dobutamine stress the heart during an echo?
|
Inotrope, increases contractility and heart rate
NB: Dobutamine is a beta agonist, so patients should be off of beta blockers on the day of the test. |
|
|
When should you consider a dobutamine stress echo?
|
Patient cannot exercise to >85% of maximum and
they cannot have a vasodilator stress test Example: Paraplegic with bad COPD |
|
|
What conditions make an EKG essentially unreadable for ischemia?
|
LBBB
Digoxin use Paced rhythm LVH Any baseline abnormality of the ST segment |
|
|
What is a thallium stress test good for?
|
Can localize non-perfused myocardium/infarcted tissue
Can be helpful with baseline EKG abnormalities (LBBB,etc.) |
|
|
Definition of acute coronary syndrome
|
Purely clinical!
Chest pain with features suggestive of ischemic disease |
|
|
First step in ACS
|
Morphine (if hypoxic)
Oxygen Nitrates Aspirin (only part that reduces mortality) Then --> EKG, CXR, cardiac enzymes, labs |
|
|
In STEMI, when should PCI occur?
|
Within 90 minutes (sx onset/door to balloon time)
|
|
|
Acute Treatment for STEMI
|
MONA
PCI within 90 minutes Gp IIb/IIIa inhibitor in cath lab (IV) Heparin IV or LMWH subQ Plavix (clopidogrel) Statin Beta blocker* ACEI or ARB, if EF<40% *CCB if cannot tolerate BB due to bronchospasm |
|
|
Which intervention has the greatest efficacy in reducing mortality in STEMI?
|
PCI
|
|
|
Post-MI, what medications should a standard patient go home on?
|
81 mg aspirin
Beta blocker (reduces mortality) Clopidogrel or prasugrel Statin (atorvastatin) ACEI, if EF<40% Sublingual nitro prn |
|
|
Lifestyle modifications post-MI
|
LDL <100
BP< 140/90 Smoking cessation Exercise/cardiac rehab |
|
|
What should you do if cath is delayed in a STEMI patient?
|
Consider TPA
|
|
|
Treatment for NSTEMI
|
MONA --> EKG, CXR, cardiac enzymes, labs
Heparin Clopidogrel Beta blocker Statin NB: If the patient does not go for cath, do an echo at some point. Add ACEI if EF <45%. |
|
|
Differences between the treatment between STEMI and NSTEMI?
|
STEMI: PCI, Gp IIb/IIIa inhibitor, TPA
- EF determined during cath NSTEMI: Get an echo if no cath |
|
|
Which therapies reduce mortality in ACS?
|
Aspirin
Beta blocker Statin Clopidogrel or prasugrel ACEI or ARB (only if EF<40%) |
|
|
When is a calcium channel blocker (diltiazem, verapamil) used in ACS?
|
Intolerance to beta blockers (severe asthma)
Cocaine-induced MI Prinzmetal's angina (coronary vasospasm) NB: CCB do NOT change mortality. |
|
|
When should you think about putting in a pacer post-MI?
|
AV blocks and severe brachycardia
- Mobitz II - Third degree AV block - Bifascicular block - NEW LBBB - Symptomatic bradycardia or brady <40 regardless of symptoms |
|
|
When should you consider giving amiodarone post-MI?
|
Vtach with a pulse AND is hemodynamically stable
NB: Vfib and pulseless vtach should be defibrillated. Unstable vtach with a pulse should be cardioverted. |
|
|
Post-MI Complications
|
Rhythm Changes:
- Sinus bradycardia - AV block - Vfib/vtach Anatomic: - Free wall rupture - Septal rupture - Papillary muscle rupture Cardiogenic shock Fibrinous pericarditis |
|
|
Duke's Criteria: What are they for? How many do you need?
|
For diagnosing infective endocarditis
Need: - 2 major - 1 major and 3 minor or - All 5 minor |
|
|
Roth spots
|
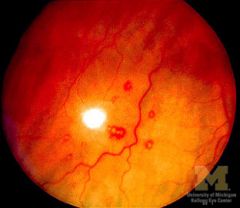
"White-centered" hemorrhages seen on the retina secondary to immune complex vasculitis
Associated with infective endocarditis (not specific) |
|
|
Duke Criteria: Major Criteria
|
1) TWO positive blood cultures with:
- Staph aureus - Viridans strep - Strep bovis/epidermis - Enterococci - Gram negative rods - Candida - HACEK organism 2) Abnormal echo - Intracardiac mass or vegetation - Abscess - New partial dehiscence of prosthetic valve |
|
|
HACEK organisms
|
Haemophilus aphrophilus/parainfluenzae
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Cardiobacterium hominis Eikenella corrodens Kingella kingae |
|
|
Duke Criteria: Minor Criteria
|
1) Fever >38 F
2) Presence of risk factors (IVDU, structural heart disease, prosthetic valve, dental procedures, hx of endocarditis 3) Vascular FIndings (Janeway lesions, septic pulmonary infarcts, arterial emboli, mycotic aneurysm, conjunctival hemorrhage) 4) Immunological Findings (Roth spots, Osler nodes, glomerulonephritis) 5) Positive blood cx without meeting major criteria |
|
|
Risk factors for endocarditis
|
Structural heart disease
Prosthetic heart valve IV drug use History of endocarditis Dental procedures that involve bleeding |
|
|
When should you suspect infective endocarditis?
|
Fever
New or changed heart murmur Vascular findings: Janeway, splinter hemorrhages, mycotic aneurysm, pulmonary infarcts Immunologic findings: Osler nodes, Roth spots, glomerulonephritis |
|
|
Workup for suspected endocarditis
|
1) Blood cultures
2) If positive --> echo |
|
|
What is the most common organism in endocarditis in the setting of IV drug use?
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Treatment in infective endocarditis
|
If any concern for MRSA: Vancomycin and gentamicin x 4-6 weeks
If no concern for MRSA: Nafcillin and gentamicin x 4-6 weeks Consider valve replacement for anatomic defects NB: If strep bovis, also consider colonscopy to rule out colon pathology |
|
|
When should you consider valve replacement in infective endocarditis?
|
Anatomic Defects:
- Valve rupture - Abscess - Prosthetic valve Fungal endocarditis Embolic Events once the patient is already on abx |
|
|
Who needs antibiotic prophylaxis for endocarditis?
|
High Risk Condition AND High Risk Procedure
Conditions: - Prosthetic valve - Unrepaired cyanotic heart disease - Previous endocarditis - Transplant pt with valve disease Procedures: - Dental procedures that CAUSE BLEEDING - Respiratory tract surgery - Surgery of infected skin |
|
|
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Endocarditis: Drug(s) of Choice
|
Amoxicillin PO
Penicillin allergy: Clindamycin or clarithromycin |
|
|
When should you supect sinus bradycardia?
|
Setting: Post-MI
Presentation: - BP<60 - Dyspnea - Chest pain - Hypotension - DIzziness |
|
|
Treatment for sinus bradycardia
|
1) Put in ICU and put on telemetry
2) Treat based on heart rate and symptoms 40-59 bpm and asymptomatic: Observe 40-59 bpm and symptomatic --> Atropine <40 bpm --> Atropine 3) If no response --> sedate with midazolam and place transcutaneous pacer pads 4) Transvenous or permanent pacer, if indicated |
|
|
When should you suspect first degree heart block?
|
PR interval >0.2 sec (one large square)
|
|
|
Treatment for first degree heart block
|
Atropine
|
|
|
When should you suspect Mobitz type I heart block?
|
PR interval gets progressively longer until a beat is dropped
|
|
|
Treatment for Mobitz type I heart block
|
Can try atropine (still has partial AV transmission)
Transcutaneous, transvenous or permanent pacer, as indicated |
|
|
When should you suspect Mobitz Type II heart block?
|
No change in PR interval
QRS complexes are dropped intermittently |
|
|
Treatment for Mobitz Type II heart block
|
Sedation --> transcutaneous pads
Consider transvenous or permanent pacer NB: Atropine is CONTRAINDICATED - Speeds up the SA node, which is not conducted |
|
|
When should you suspect 3rd degree heart block?
|
Complete AV dissociation
Ventricular rate is often 20-40 |
|
|
Treatment for 3rd heart block
|
Transcutaneous pacer --> permanent
|
|
|
Time Course for Electrical Complications following MI
|
Usually first 24 hours
|
|
|
Treatment for vfib
|
Defibrillate immediately
|
|
|
Treatment for vtach
|
1) Assess pulse
Pulseless --> Defibrillate 2) Assess blood pressure Unstable --> Synchronized cardioversion Stable --> Amiodarone |
|
|
Treatment for pulseless vtach
|
Defibrillation
|
|
|
Treatment for vtach with a pulse but hemodynamically unstable
|
Synchronized cardioversion
|
|
|
Treatment for hemodynamically stable vtach with a pulse
|
Amiodarone
|
|
|
When should you suspect papillary muscle rupture?
|
Setting: 3-5 days after MI
Presentation: - Hypotension - Acute mitral regurgitation --> holosystolic murmur - Dyspnea - Acute pulmonary edema - Cardiogenic shock (<90/65) |
|
|
Workup of papillary muscle rupture
|
Echo
|
|
|
Treatment of papillary muscle rupture
|
Nitroprusside (vasodilator, reduces afterload)
IABP (reduces afterload) Dobutamine or isoproterenol (inotrope) Call TCV for surgical repair! |
|
|
When should you suspect septal rupture?
|
Setting: 3-5 days after MI
Presentation: - Hypotension - Cardiogenic shock (<90/65) - JVD |
|
|
Workup for septal rupture
|
Echo
Right heart cath (saturation should increase from right atria to right ventricle d/t backflow) |
|
|
Treatment for septal rupture
|
Reduce afterload:
- Nitroprusside - IABP Inotropic Support: - Dobutamine or isoproterenol Definitive Management: Call TCV!! |
|
|
When should you suspect myocardial wall rupture?
|
Setting: ~5 days after MI
Presentation: - Cardiac tamponade - Muffled heart sounds - JVD - Pulsus paradoxus |
|
|
Workup for myocardial wall rupture
|
Echo
|
|
|
Treatment for myocardial wall rupture
|
Immediate pericardiocentesis
Transfuse Call TCV for repair! |
|
|
When is IABP contraindicated?
|
Aortic dissection
Severe aortic regurgitation Severe peripheral vascular disease |
|
|
Right vs Left Cardiogenic Shock: Quick differentiation
|
1) Listen to lungs: If crackles --> probably left
2) JVD present? : If yes, probably right |
|
|
Empiric treatment for right cardiogenic shock
|
IV fluids
|
|
|
Empiric treatment for left cardiogenic shock
|
Reduce afterload: nitroprusside, IABP
Increase contractility: Isoproterenol NB: IV fluids are CONTRAINDICATED |
|
|
When should you suspect fibrinous pericarditis?
|
Setting: 7 days after MI
Presentation: - Chest pain - Diffuse ST elevation on EKG - No bump in CK-MB (troponin is probably still elevated from MI) |
|
|
Treatment for fibrinous pericarditis
|
Aspirin
|
|
|
How do ACEI and ARBs affect potassium?
|
They both cause HYPERkalemia.
|
|
|
Treatment for stable angina
|
Aspirin (improves mortality)
Metoprolol (improves mortality) ACEI or ARB (if EF <40%) Sublingual nitro prn Statin (if LDL >70-100) NB: Clopidogrel can be added if the patient cannot tolerate aspirin. |
|
|
When might you do a cath in the setting of stable angina?
|
To determine eligiblity for CABG
|
|
|
CAD Equivalents
|
Diabetes
CAD Peripheral arterial disease Symptomatic carotid disease |
|
|
Indications for CABG
|
Left main stenosis >70%
Three vessel disease with >70% stenosis |
|
|
LDL goal in CAD
|
LDL <100
NB: Remember CAD equivalents! |
|
|
LDL goal with CAD and diabetes
|
<70
NB: Remember CAD equivalents! |
|
|
What is the most common side effect of statins?
|
Elevated transaminases
|
|
|
Monitoring for statins
|
Get LFTs at baseline and again at 3 months
NB: Don't stop the statin unless the transaminases are 3x the upper limit of normal |
|
|
Myalgias with a statin
|
Can be caused by rhabdomyolysis
Stop the statin. Restart at a lower dose and increase slowly. |
|
|
Treatment for isolated elevated triglycerides
|
Gemfibrozil
NB: Should not affect LDL or HDL |
|
|
Which statin should be used in HIV patients?
|
Pravastatin
NB: It's not metabolized by the p450 enzymes, so it should not interact with antiretroviral therapy. |
|
|
Treatment for isolated low HDL
|
Niacin (nicotinamide)
NB: Causes flushing and impaired glucose tolerance |
|
|
Treatment for Elevated LDL and Elevated Triglycerides
|
Fibrate: Fenofibrate or clofibrate
|
|
|
Triglyceride Goal
|
<150
|
|
|
HDL Goal
|
>40 in men
>50 in women |
|
|
BP Goal:
- Everyone - Diabetics - Diabetic Nephropathy (microalbuminuria) |
Everyone: <140/90
Diabetics: <130/80 Diabetic Nephropathy: <125/75 |
|
|
When should you suspect CHF?
|
DOE
Edema Rales on lung exam Ascites JVD S3 gallop (pathologic over age 40) Orthopnea PND Fatigue |
|
|
What is the worst manifestation of CHF?
|
Acute pulmonary edema
|
|
|
When should you suspect acute pumonary edema?
|
Acute, severe shortness of breath
Rales on lung exam S3 gallop Orthopnea PND |
|
|
You suspect acute pulmonary edema. Now what?
|
Dx and Tx AT THE SAME TIME
1) Oxygen, nitrates, morphine, furosemide Put in the ICU Dx: - Chest x-ray - EKG - Pulsox (consider ABG) - Echo |
|
|
What do you expect on a CXR in CHF?
|
Pulmonary vascular congestion
Cephalization of flow Cardiomegaly Effusions |
|
|
What medications should be given to a newborn at delivery?
|
1) 1% silver nitrate eye drops or 0.5% erythromycin ointment
2) 1 mg IM vitamin K |
|
|
Newborn: What needs to be done prior to discharge?
|
Hearing test
Neonatal screening tests: - PKU - Galactosemia - Hypothyroidism |
|
|
When should neonatal screening tests be performed?
|
After 48 hours
(More reliable at that time) |
|
|
When should you suspect Mongolian spots?
|
Setting: Newborn or very young child
Presentation: - Blue/gray macules on posterior thighs or presacral back |
|
|
Treatment for Mongolian spots
|
Usually spontaneously resolve
NB: Rule out abuse |
|
|
When should you suspect erythema toxicum?
|
setting: Newborn in first few days
Presentation: Firm, yellow or white pustules/papules on an erythematous base - Usually peak on day 2 of life |
|
|
Treatment for erythemia toxicum
|
Usually self-limited
|
|
|
When should you suspect a port wine stain (nevus flammeus)?
|
Setting: Child +/- Sturge Weber syndrome
Presentation: Permanent, unilateral vascular malformation on head and neck |
|
|
Treatment for port wine stain
|
Pulsed laser therapy
If associated with Sturge Weber: Also evaluate for glaucoma and give anticonvulsants |
|
|
When should you suspect Sturge Weber syndrome?
|
Port wine stain
Seizures Mental retardation Glaucoma |
|
|
When should you suspect strawberry hemangioma?
|
Setting: Child under the age of ~5
Presentation: - Red, sharply demarcated, raised lesion - Appears in first two months of life --> rapidly expands - Usually involutes by age 5-9 |
|
|
Treatment for strawberry hemangioma
|
Generally involutes on its own by age 5-9
Consider treating with steroids or pulsed laser if: - Large (can cause high output cardiac failure) - Deep and interfering with organ function |
|
A child presents with a preauricular pit. Now what?
|
Screen for hearing loss
Do renal ultrasound for GU abnormalities |
|

A child presents with a coloboma. Now what?
|
Screen for CHARGE syndrome:
- Coloboma - Heart defects - Atresia of the nasal choanae - growth Retardation - GU abnormalities - Ear abnormalities NB: Often have "deaf blindness" |
|
A child presents with aniridia. Now what?
|
Screen for Wilms
- Abdominal ultrasound Q3 months until age 8 |
|
|
When should you suspect branchial cleft cyst?
|
Neck mass lateral to midline
May become infected |
|
|
Treatment for branchial cleft cysts
|
If asx, leave it alone.
If infected --> antibiotics If large --> surgical removal |
|
|
When should you suspect a thyroglossal duct cyst?
|
Mass in midline
Moves with swallowing or tongue protrusion May become infected |
|
|
Treatment for thyroglossal duct cyst
|
Thyroid function tests
Thyroid scan (for thyroid ectopia) Then --> surgical removal |
|
|
When should you suspect omphalocele?
|
setting: Newborn. May be associated with trisomies 18, 13, 21.
Presentation: - Abdominal defect WITH a sac - Through the umbilicus - Absent umbilical ring - May have polyhydramnios in utero |
|
|
Treatment for omphalocele
|
Immediate surgery
Give TPN until healed Screen for trisomy 13, 18 and 21. NB: Small defects can be closed primarily. Large defects need a silastic "silo" to protect the bowel. Manually replace the bowel daily until closed (~1 week). |
|
|
When should you suspect gastroschisis?
|
Setting: Newborn
Presentation: - Abdominal defect lateral to midline - NO sac - Associated with intestinal atresia |
|
|
Treatment for gastroschisis
|
Immediate surgery
TPN for nutrition NB: Small defects can be closed primarily. Large defects need a silastic "silo" to protect the bowel. Manually replace the bowel daily until closed (~1 week). |
|
|
A child has an umbilical hernia. What screening should be done?
|
TSH, T4 (congenital hypothyroidism)
|
|
|
A child has an undescended testis. Now what?
|
Do nothing until at least one year of age (80% will descend)
Then: - B-hCG or testosterone injections or - orchidopexy (surgical removal) |
|
|
When should you suspect hypospadias?
|
Urethral opening UNDER the penis (ventral surface)
|
|
|
When should you suspect epispadias?
|
Urethral opening on TOP of the penis (dorsal surface)
|
|
|
A woman with diabetes has a baby. What might you expect in the infant?
|
Hypoglycemia
Hypocalcemia Hypomagnesemia HYPERbilirubinemia Polycythemia Macrosomia --> birth trauma Cardiac abnormalities Small left colon and abdominal distension Increased risk longterm of developing DM and childhood obesity |
|
|
Workup for respiratory distress in a newborn
|
#1: Chest x-ray
ABG Blood cultures Glucose CBC (anemia or polycythemia) Cranial ultrasound (hemorrhage) Exam for heart defects |
|
|
Initial treatment for a newborn in respiratory distress
|
Oxygen (keep SaO2 >95%)
Consider empiric antibiotics NB: If high oxygen requirements, consider nasal CPAP to prevent barotrauma. |
|
|
When should you suspect Respiratory Distress Syndrome in a neonate?
|
Setting: Premature neonate
Presentation: - Nasal grunting - Tachypnea - Intercostal retractions - Hypoxemia - Eventually hypercarbia and respiratory acidosis |
|
|
Workup for neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
#1: Chest x-ray (ground glass, atelectasis, air bronchograms)
Lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio on amniocentesis |
|
|
Treatment for neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome? What about prevention?
|
Oxygen
Nasal CPAP Exogenous surfactant (decreases mortality) Prevention: - Prevent prematurity with tocolytics - Betamethasone at least 24 hours prior to delivery if <34 weeks |
|
|
Complications of neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
Retinopathy of prematurity (secondary to hypoxemia)
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (prolonged high concentration O2) Intraventricular hemorrhage |
|
|
When should you suspect transient tachypnea of the newborn?
|
Setting: Term infant delivered by C section or rapid second stage of labor
Presentation: - Tachypnea - Air trapping, fissure fluid and perihilar streaking on CXR |
|
|
Treatment for Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
|
Oxygen support
Usually resolves rapidly in 24-48 hours |
|
|
When should you suspect meconium aspiration?
|
Setting: Term infant with hyposia or fetal distress in utero
Presentation: - Severe respiratory distress - Hypoxemia - CXR with patchy infiltrate, air trapping, flattening of the diaphragm |
|
|
Treatment for meconium aspiration
|
Airway suction of depressed infants immediately after delivery
Positive pressure ventilation High frequency ventilation Nitric oxide therapy ECMO |
|
|
Complications of meconium aspiration
|
Air leak (pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum)
Pulmonary hypertension Aspiration pneumonitis |
|
|
When should you suspect congenital diaphragmatic hernia?
|
Dyspnea at birth
Loops of bowel in left chest Scaphoid abdomen Respiratory distress Pulmonary hypoplasia |
|
|
Treatment for congenital diaphragmatic hernia
|
Intubate with low-pressure ventilation
Sedate NG suction Surgically repair after 3-4 days (for lung maturation) |
|
|
Ddx for meconium plugs
|
Small left colon (IODM)
Hirschprung disease Cystic fibrosis Maternal drug abuse NB: Plugs are usually found in the lower colon. |
|
|
What should you be thinking about with meconium ileus?
|
Cystic fibrosis
|
|
|
Workup for intestinal obstruction in a newborn
|
#1: Abdominal x-ray
|
|
|
Treatment for meconium ileus
|
Gastrografin enema
|
|
|
When should you suspect tracheoesophageal fistula?
|
Setting: Newborn
Presentation: - Choking and gagging with first feeding - Respiratory distress - Aspiration pneumonia - Drooling - Infiltrates on lung x-ray |
|
|
How to diagnose tracheoesophageal fistula
|
Place an NG tube (will be coiled in the chest on CXR)
NB: Remember to screen for other abnormalities (VACTERL syndrome) |
|
|
Ddx of the double bubble sign
|
Duodenal atresia
Annular pancreas Malrotation Volvulus |
|
|
When should you suspect intestinal atresia?
|
Often premature and/or Down's syndrome
Polyhydramnios in utero No respiratory distress Bilious vomiting Double bubble sign on chest w-ray |
|
|
Treatment for intestinal atresia
|
NG decompression
Screen for other VACTERL abnormalities Surgical correction |
|
|
VACTERL Syndrome
|
Vertebral defects
Anal atresia (imperforate anus) Cardiac abnormalities Tracheoesophageal fistula Esophageal atresia Radial and Renal abnormalities Limb Syndrome |
|
|
When should you suspect necrotizing enterocolitis?
|
Setting: Premature infant on formula feeds
Presentation: - Low APGAR scores - Bloody stools - Apnea - Lethargy - Abdominal wall erythema and distension - Pneumatosis on abdominal x-ray |
|
|
Workup for NEC
|
Abdominal x-ray and/or ultrasound
|
|
|
Treatment for necrotizing enterocolitis
|
STOP all feeds
Decompress gut Broad spectrum antibiotics Evaluate for surgery |
|
|
When should you suspect Hirschprung disease?
|
Setting: Newborn
Presentation: - Failure to pass meconium spontaneously - Voluminous stool passed after digital rectal exam |
|
|
Workup for Hirschprung's disease
|
#1: Rectal exam (looking for passage of voluminous stool afterward)
Barium enema (proximal megacolon) Rectal biopsy (absent ganglionic cells) |
|
|
Treatment for Hirschprung's disease
|
Surgery
|
|
|
When should you suspect kernicterus?
|
Setting: Jaundiced infant
Presentation: - Elevated indirect bilirubin - Posturing - Hypotonia - Seizures - Choreoathetosis - Delayed motor skills - Sensorineural hearing loss |
|
|
Treatment for kernicterus
|
Immediate exchange transfusion
|
|
|
When is neonatal hyperbilirubinemia pathologic?
|
- First day of life or after 2 weeks
- >12 mg/dL in a term infant - Direct bilirubin > 2 mg/dL at any time - If it rises > 5 mg/dL/day |
|
|
Ddx of direct, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia in a neonate?
|
Sepsis
TORCH infections TPN Hypothyroidism Galactosemia Tyrosinemia Cystic fibrosis Choledochal cyst |
|
|
Ddx of indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia in a neonate?
|
Rh/ABO incompatibility
Thalassemia minor Polycythemia Twin-twin transfusion Maternal-fetal transfusion Delayed cord IUGR IODM Spherocytosis Elliptocytosis G6PD deficiency Pyruvate kinase |
|
|
Ddx of Coombs-positive, indirect hyperbilirubinemia in a neonate?
|
Rh/ABO incompatibility
Thalassemia minor NB: All other indirect hyperbilirubinemias are Coombs negative. |
|
|
Workup for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
|
Total and direct bilirubin
Blood type of infant and mother: ABO, Rh Direct Coombs CBC Reticulocyte count Blood smear (look for hemolysis) UA and culture if elevated direct (look for sepsis) |
|
|
Ddx of prolonged (>2 weeks) jaundice in a neonate
|
Direct:
- Cholestasis Indirect: - Infection - Bilirubin conjugation abnormalities (Gilbert, Crigler-Najjar) - Hemolysis - Intrinsic red cell membrane or enzyme defects (G6PD, spherocytosis, pyruvate kinase |
|
|
Treatment for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
|
When bilirubin >10-12 mg/dL --> phototherapy
If phototherapy is ineffective or concern for kernicterus --> exchange transfusion |
|
|
How quickly should bilirubin decrease with phototherapy?
|
2 mg/dL every 4-6 hours
|
|
|
What are the most likely causes of early and late sepsis in a neonate?
|
Early=Within the first 24 hour
Early: Pneumonia Late: Bacteremia or meningitis |
|
|
Causative organisms in neonatal pneumonia
|
Group B Strep
E. coli H. influenzae Listeria monocytogenes |
|
|
Causative organisms in neonatal meningitis/bacteremia
|
Staph aureus
E. coli Klebsiella Pseudomonas |
|
|
Treatment for neonatal sepsis
|
If meningitis is possible: ampicillin and 3rd gen cephalosporin (NOT ceftriaxone)
If there is no evidence of meningitis: ampicillin and an aminoglycoside (-mycin) |
|
|
Third Generation Cephalosporins
|
Ceftriaxone
Cefotaxime Ceftazidime Cefpodoxime Cefixime Ceftibuten |
|
|
Aminoglycosides
|
Streptomycin
Gentamicin Tobramycin Amikacin |
|
|
When should you suspect a TORCH infection?
|
Setting: Congenital infection
Presentation: - IUGR - Hepatosplenomegaly - Jaundice - Mental retardation - Symptoms specific to individual infections |
|
|
TORCH Infections
|
Toxoplasmosis
Other (syphilis, varicella) Rubella CMV Herpes |
|
|
When should you suspect congenital toxoplasmosis?
|
Hydrocephalus
Intracranial calcifications Chorioretinitis |
|
|
Workup for a suspected TORCH infection
|
Review maternal history (sexual history, cats, etc)
Physical exam CBC and platelets LFTs X-rays of long bones Eye evaluation Hearing evaluation Neuroimaging Consider LP |
|
|
Best diagnostic test for congenital toxoplasmosis
|
IgM against toxo
|
|
|
When should you suspect congenital rubella?
|
Cataracts
Deafness Heart defects Blueberry muffin spots (extramedullary hematopoesis) |
|
|
Best diagnostic test for congenital rubella
|
Maternal rubella immune status (unknown or negative)
IgM against rubella |
|
|
When should you suspect congenital CMV?
|
Microcephaly
Periventricular calcifications Thrombocytopenic petechiae Sensorineural hearing loss |
|
|
Best diagnostic test for congenital CMV
|
Urine or saliva CMV culture (if negative, no CMV)
Serum IgM antibody |
|
|
When should you suspect congenital herpes?
|
First week: pneumonia and shock
Second week: Skin vesicles and keratoconjunctivitis Third-Fourth Week: Acute meningoencephalitis |
|
|
Workup for congenital herpes
|
Initial: Tzanck smear/culture (If neg, does not rule out)
Most specific: HSV PCR |
|
|
When should you suspect congenital syphilis?
|
Snuffles
Desquamating rash of palms and soles Osteochondritis and periostitis |
|
|
Workup for congenital syphilis
|
Initial test: VDRL screening
Most specific: IgM-FTA-ABS |
|
|
When should you suspect congenital varicella?
|
Neonatal pneumonia
Limb hypoplasia Cutaneous scars Seizures Mental retardation |
|
|
Workup for congenital varicella
|
Initial: IgM serology
Most specific: PCR of amniotic fluid |
|
|
When should you suspect neonatal seizures?
|
Subtle repetitive movements ie chewing, tongue thrusting, apnea, blinking
Ocular deviation Jitteriness |
|
|
Workup for neonatal seizures
|
EEG (may be normal)
Labs: CBC, lytes, Ca, Mg, phosphorus Glucose (especially in IODM) Amino acid assay and urine organic acids (errors in metabolism) Total cord blood IgM Urine culture Blood culture LP, if meningitis possible Ultrasound of head for hemorrhage (esp if premature) |
|
|
Ddx of neonatal seizures
|
Electrolyte abnormalities
Hypoglycemia Inborn errors of metabolism Infection Intracranial hemorrhage |
|
|
Treatment for neonatal seizures
|
Phenobarbital
Correct electrolyte abnormalities If seizures persist, phenytoin |
|
|
When should you suspect neonatal substance withdrawal?
|
Hyperactivity
Irritability Restlessness Fever Diarrhea Tremors/jitters High-pitched crying Vomiting Nasal stuffiness Poor feeding Seizures Tachypnea |
|
|
Which drugs cause neonatal withdrawal in the first 48 hours?
|
Cocaine
Heroin Alcohol Amphetamines |
|
|
Which drugs cause neonatal withdrawal after the first 48 hours?
|
Methadone (96 hours-2 weeks)
|
|
|
Possible complications with an addicted mother: Neonatal? Prenatal?
|
Low birth weight
IUGR Congenital abnormalities SIDS STDs Placental abruption Intraventicular hemorrhage (cocaine) |
|
|
Treatment for neonatal withdrawal
|
Generally opioids and phenobarbital
|
|
|
Which drugs have teratogenic effects?
|
Anesthetics
Barbituartes Mag sulfate Phenobarbital Sulfonamides NSAIDs ACEIs Isoretinoin Phenytoin DES Tetracycline Lithium Warfarin Valproate Carbamazepine |
|
|
Workup for Down's Syndrome
|
Hearing exam
Echo (endocardial cushion defects) TSH High index of suspicion for: GI defects (duodenal atresia, fistula), ALL, early onset Alzheimer's |
|
|
When should you suspect Edwards Syndrome?
|
Low set- malformed ears
Microcephaly Micrognathia Clenched hand Rocker bottom feet Hammer toe Omphalocele NB: Trisomy 18 |
|
|
Workup for Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)
|
Echo
Renal ultrasound (polycystic kidneys, ureter abnormalities) NB: Often die within first year |
|
|
When should you suspect Patau syndrome?
|
Defects of midface, eye and forebrain development
Holoprosencephaly Microcephaly Microphthalmia Cleft lip/palate Single umbilical artery NB: Trisomy 13 |
|
|
Workup for Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)
|
Echo
Renal ultrasound (polycystic kidneys) |
|
|
What is WAGR Syndrome?
|
Wilms tumor
Aniridia GU abnormalities mental Retardation |
|
|
When should you suspect Klinefelter Syndrome?
|
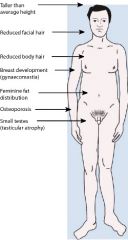
Usually present as male with:
Low IQ Behavioral problems Slim with long limbs Gynecomastia NB: XXY |
|
|
Workup for Klinefelter's Syndrome?
|
Testosterone levels (hypogonadism, hypogenitalism)
NB: Replace testosterone at 11-12 yo |
|
|
When should you suspect Turner Syndrome?
|
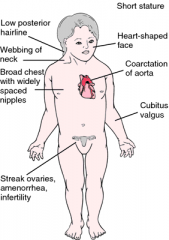
Female
Small stature Gonadal dysgenesis Low IQ Congenital lymphedema Webbed posterior neck Broad chest with wide-spaced nipples NB: X0 |
|
|
Workup for Turner Syndrome
|
Renal ultrasound (horseshoe kidney, double renal pelvis)
Echo (coarctation, bicuspid aortic valve) TSH (hypothyroidism) NB: Consider replacement of estrogen, growth hormone and/or anabolic steroids |
|
|
When should you suspect Fragile X Syndrome?
|
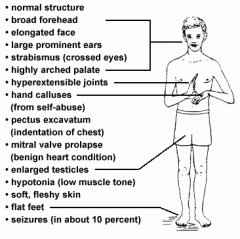
Macrocephaly in childhood
Large ears Large testes Elongated face Mental retardation ADHD |
|
|
When should you suspect Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome?
|
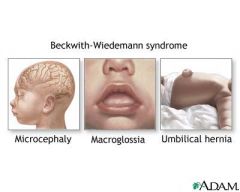
Multiorgan enlargement:
- Macroglossia - Pancreatic beta cell hyperplasia (leads to hypoglycemia) - Large kidneys Neonatal polycythemia Hemihypertrophy |
|
|
Workup for Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome?
|
AFP and abdominal ultrasound Q6 mo until age 6
NB: Increased risk of Wilm's and hepatoblastoma |
|
|
When should you suspect Prader-Willi syndrome?
|
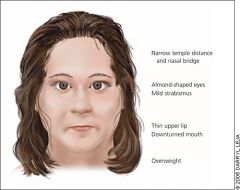
Morbid obesity
Mental retardation Binge eating Small genitalia |
|
|
What is the genetic defect in Prader Willi?
|
Deletion of the PATERNAL 15q11q13
|
|
|
When should you suspect Angelman Syndrome?
|

Mental retardation
Inappropriate laughter Sparse or absent speech Ataxia Jerky movements Recurrent seizures (80%) NB: Deletion of MATERNAL 15q11q13 |
|
|
When should you suspect Pierre Robin or Robin sequence?
|
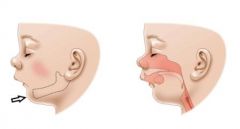
Mandibular hypoplasia
Cleft palate Tongue falls back --> high risk for airway obstruction |
|
|
First step in diagnosing abnormal growth
|
How does the height/length compare to the weight? Is it proportional?
|
|
|
Growth Abnormalities: Ddx if weight gain is more affected than height
|
Basically anything that prevents use of calories
Undernutrition Inadequate digestion Malabsorption (infection, celiac, CF, protein-losing enteropathy) |
|
|
Growth Abnormalities: Ddx when weight and height are proportional
|
Systemic illness:
- Heart failure - Inflammatory bowel disease - JRA - Renal insufficiency - Hepatic insufficiency Genetic short stature Constitutional growth delay |
|
|
Growth Abnormalities: Ddx when height is affected more than weight
|
Growth hormone deficiency
Thyroid hormone deficiency Skeletal dysplasia Excess cortisol |
|
|
Contraindications to breastfeeding
|
Absolute:
- Chemo - Iodide - Lithium - Chloramphenicol - Nicotine - Alcohol Relative: - Meuroleptics - Sedatives - Metronidazole - Tetracycline - Sulfonamides - Steroids |
|
|
Newborn Reflexes
|
Moro
Grasp Rooting Tonic neck (fencer reflex) NB: Appear at birth and should disappear by 4-6 months |
|
|
Parachute reflex
|

Extend arms when turned upside down
Appears at 6-8 months and persists |
|
|
Milestones at 9 months
|
Pincer grasp
Creeps and crawls Knows name |
|
|
Milestones at 12 months
|
Cruises
1+ words Plays ball |
|
|
Milestones at 15 months
|
Builds 3 cube tower
Walks alone Makes lines and scribbles |
|
|
Milestones at 18 months
|
4 cube tower
Walks down stairs 10 words Feeds self |
|
|
Milestones at 24 months
|
7 cube tower
Runs well Goes up and down stairs Jumps with 2 feet Threads shoelaces Handles spoon 2-3 sentences |
|
|
Milestones at 3 years
|
Walks downstairs with alternating feet
Tricycle Knows age and sex Understands taking turns |
|
|
Milestones at 4 years
|
Can hop on 1 foot
Throws a ball overhead Tells stories Participates in group play |
|
|
First line treatment for uncomplicated otitis media in a child
|
Amoxicillin x 10 days
|
|
|
Most common cause of acute diarrhea in an infant?
|
Rotavirus
|
|
|
What organisms cause bloody diarrhea in a child?
|
Campylobacter
Amoeba (E. histolytica) Shigella E Coli Salmonella |
|
|
Workup for acute diarrhea in a child
|
Ova and parasites
Stool culture Enzyme immunoassays for viruses If concern for HUS: CBC, blood smear, Coombs, UA If recent antibiotics: C difficile toxin |
|
|
Initial therapy for acute diarrhea in a child
|
Hydration
Fluid and electrolyte replacement Antibiotics only in specific cases NB: Do NOT use antidiarrheals in children |
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics in E. coli?
|
No! Especially in cases of E. coli 0157:H7, antibiotics increase the risk of HUS.
|
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics in Shigella?
|
Yes, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.
|
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics in Campylobacter?
|
Maybe. Give erythromycin if severe or dysentery.
|
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics in Salmonella?
|
Only if:
- <3 months old - Toxic - Disseminated disease - Salmonella typhi Then, amoxicillin, ampicillin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or ceftriaxone |
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics in C. difficile?
|
Yes. Stop all other antibiotics first.
Then, PO vancomycin or metronidazole. |
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics in amoebiasis?
|
Yes, metronidazole.
|
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics with Giardia?
|
Yes, metronidazole.
|
|
|
Acute pediatric diarrhea: Do you give antibiotics in cryptosporidium?
|
Yes, antiparasitics.
|
|
|
When should you suspect hemolytic uremic syndrome?
|
Setting: Child 5-10 days after bloody diarrhea
Presentation: - Pallor - Anemia - Weakness - Oliguria - Acute renal insufficiency |
|
|
Workup for HUS
|
CBC (anemic, elevated WBC, thrombocytopenia)
Blood smear (burr cells, helmet cells, fragments) Coombs test (negative) UA (microscopic hematuria and proteinuria) |
|
|
Treatment for HUS
|
Supportive care
Treat hypertension Dialysis, if indicated |
|
|
Benign causes of chronic diarrhea in children
|
Too much fruit juice
Carbonated beverages Low fat intake NB: Weight and height should be normal. No fecal fat. |
|
|
Which infection can cause chronic malabsorption?
|
Giardia
|
|
|
Workup for pediatric malabsorption
|
Fat:
- Sudan black - 72 hour fecal fat - Serum trypsinogen Carbohydrate: - Clinitest screening - Breath hydrogen test (most specific) Protein: - Spot stool alpha-1 antitrypsin level Vitamins/Minerals: - Serum iron - Folate - Ca - zinc - Mg - B12, D, A |
|
|
When should you suspect celiac in a child?
|
Chronic diarrhea
Failure to thrive Growth retardation Anorexia |
|
|
Workup for celiac
|
Antiendomysial antibodies
Antigliadin antibodies Biopsy (most specific) |
|
|
When should you suspect GERD in a child?
|
Wheezing
Apnea after feeds Recurrent spitting up |
|
|
Treatment for pediatric GERD
|
1) Change feeding technique and thicken feeds
2) H2 receptor blocker (ranitidine) 3) PPI or surgery only for severe cases and esophagitis |
|
|
When should you suspect pyloric stenosis?
|
Setting: 2-6 week old, first born, Caucasian male
Presentation: - NONbilious vomiting - Hypochloremia - Metabolic alkalosis - Firm, mobile mass in epigastrium on exam |
|
|
Diagnostic test for pyloric stenosis
|
Abdominal ultrasound
|
|
|
When should you suspect malrotation or volvulus?
|
Setting: Infant
Presentation: - Bilious emesis - Recurrent abdominal pain - Acute small bowel obstruction |
|
|
Workup for suspected malrotation or volvulus
|
Abdominal ultrasound
Barium enema Upper GI series |
|
|
When should you suspect intussusception?
|
Setting: Child <2 yo
Presentation: - Currant jelly stools - Paroxysms of colicky abdominal pain - Lethargy - Fever - Shock NB: May have a history of GI infection, Meckel's, polyp, Henoch-Schlonlein purpura |
|
|
Workup for intussusception
|
Abdominal x-ray
Air enema (diagnostic and therapeutic) |
|
|
Treatment for pediatric UTI
|
1) Amoxicillin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
2) Repeat urine culture 1 week after stopping abx to confirm sterile urine 3) Consider VUR workup in boys, febrile UTI, girl under 5 and girls >5 with their second UTI NB: Do NOT give quinolones to children under 16 |
|
|
Which children should be screened for vesicoureteral reflux?
|
UTI and:
- Male - Female under 5 - Female over 5 (second UTI) - Fever |
|
|
Workup for suspected vesicoureteral reflux
|
Voiding cystourethrogram
Renal ultrasound |
|
|
What is the danger of vesicoureteral reflux?
|
Predisposition to pyelonephritis
Renal scarring Reflux nephropathy (HTN, proteinuria, ESRD, impaired kidney growth) |
|
|
Treatment for vesicoureteral reflux
|
Antibiotic prophylaxis for one year after diagnosis
Surgery if: breakthrough UTI, renal scarring, failure to resolve |
|
|
Antibiotics for prophylaxis in VUR
|
Amoxicillin
Trimpethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Nitrofurantoin |
|
|
Treatment for pediatric pyelonephritis
|
IV ceftriaxone or
Ampillin + gentamicin |
|
|
Age cut-off for tetracyline in children
|
Do NOT use in children under 7
|
|
|
Age cut-off for quinolones in children
|
Do NOT use in children under 16
NB: ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, etc. |
|
|
When should you suspect acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis?
|
Setting: 5-12 yo child a few weeks after strep or impetigo
Presentation: - Hypertension - Edema - Hematuria |
|
|
Workup for acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
|
Urinalysis: RBCs, RBC casts, protein, PMNs
C3 (low) Throat culture Streptococcal antibody titer Anti-DNase antigen (most specific) |
|
|
Treatment for acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
|
Treat the underlying infection: Penicillin
- Erythromycin if pen-allergic Supportive care: Sodium restriction, diuresis, electrolyte management NB: Do NOT give antihypertensives or steroids |
|
|
Ddx for pediatric hematuria
|
Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
IgA Nephrophathy (Berger's Disease) Alport Syndrome |
|
|
When should you suspect IgA Nephropathy (Berger's DIsease)?
|
Setting: Teenager or in 20-30s with a recent GI or upper respiratory infection
Presentation: - Gross hematuria - Mild proteinuria - Hypertension - NORMAL C3*** |
|
|
Treatment for IgA Nephropathy
|
Control blood pressure
|
|
|
When should you suspect Alport Syndrome?
|
Setting: Young boy with positive family history of hearing loss and renal issues
Presentation: - Hearing trouble - Asymptomatic microscopic hematuria - Intermittent gross hematuria after URIs - Eye abnormalities |
|
|
When should you suspect Polycystic Kidney DIsease (autosomal recessive type)?
|
Setting: Infant
Presentation: - Bilateral flank masses - Hypoplasia - Hypertension - Oliguria - Acute renal failure |
|
|
Workup for Polycystic Kidney Disease
|
Renal ultrasound (cysts through medulla and cortex)
Liver ultrasound (Fibrosis, bile duct proliferation) |
|
|
Treatment for Polycystic Kidney Disease (autosome recessive)
|
Dialysis
Kidney Transplant |
|
|
Ddx for pediatric proteinuria
|
Orthostatic
Transient: - Fever - Exercise - Dehydration - Cold exposure Glomerular or tubular disorders (more likely if >1 g/24 hours or associated with HTN, hematuria, etc.) |
|
|
When should you worry about pediatric proteinuria?
|
>1 g protein per 24 hours
Associated with hypertension, hematuria or renal dysfunction |
|
|
What is orthostatic proteinuria?
|
Benign condition in school-aged children and teens
Proteinuria is increased when UPRIGHT and normal when supine |
|
|
When should you suspect pediatric nephrotic syndrome?
|
Setting: Age 2-6 with a recent minor infection
Presentation: - Edema - Proteinuria (>40 mg/m2/hour) - Hypoalbuminemia (<2.5 g/dL) - Hyperlipidemia - NORMAL C3 and C4*** |
|
|
Treatment for pediatric nephrotic syndrome
|
Oral prednisone (several weeks)
Supportive care (fluid and sodium restriction) Immunization against Pneumococcus and Varicella NB: If relapses occur on prednisone, try cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, high dose pulsed methyprednisolone. |
|
|
Possible complications of nephrotic syndrome
|
SBP
Other infections Clots |
|
|
When should you suspect congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
|
Setting: Infant
Presentation: - Vomiting - Dehydration - Salt wasting - Hyponatremia - Hypoglycemia - Hyperkalemia - Ambiguous genitalia (females) |
|
|
Diagnostic test for congenital adrenal hyperplasia
|
17-OH progesterone (increased in CAH)
NB: More definitive if performed before and after an IV bolus of ACTH |
|
|
When should you suspect Kawasaki disease?
|
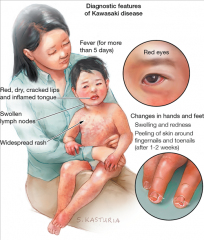
Setting: Child <5 yo
Presentation: - Fever for >=5 days AND (4 of the 5): - Bilateral conjunctivitis without exudate - Intraoral erythema, strawberry tongue, cracked lips - Nonvesicular rash - Erythema/swelling of hands and feet with desquamation - Nonsuppurative cervical lymphadenitis |
|
|
Workup for Kawasaki Disease
|
CLINICAL diagnosis
ESR/CRP (4-8 weeks) CBC (plts increase in weeks 2-3) Echo and EKG (baseline, 2-3 weeks and 6-8 weeks) |
|
|
Treatment for Kawasaki Disease
|

IVIG
High dose aspirin Add warfarin if platelet count is very high |
|
|
Complications of Kawasaki Disease
|

Early myocarditis
Pericarditis Coronary artery aneurysms (2nd-3rd week) Thrombosis |
|
|
When should you suspect Henoch Schonlein Purpura?
|
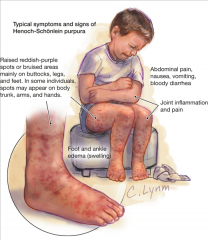
Setting: 2-8 yo with a recent upper respiratory illness
Presentation: - Palpable purpura on legs and buttocks - Fever - Abdominal pain - Arthritis - Glomerulonephritis/nephrosis - Intussusception |
|
|
Workup for Henoch Schonlein Purpura?
|
CLINICAL diagnosis
Supportive: - CBC (platelets up, WBC up, anemia) - ESR (up) - Anticardiolipin or antiphospholipid antibodies - UA: RBCs, WBCs, casts, albumin - Skin biopsy (IgA and C3 deposits) |
|
|
Treatment for Henoch Schonlein Purpura
|
Supportive:
- Steroids for GI and renal complications - Aspirin if positive anticardiolipin or antiphospholipid antibodies |
|
|
Is anemia ever physiologic in children?
|
Yes.
Term infants: Hgb nadir of 9-1 mg/dL at 12 weeks Premature infants: Hgb nadir 7-9 mg/dL at 3-6 weeks |
|
|
Treatment for pediatric iron deficiency anemia
|
Oral ferrous salts
Limit cow's milk Continue iron replacement for 8 weeks after lab values normalize to replete bone marrow |
|
|
When should you suspect pediatric lead poisoning?
|
Hyperactivity
Mental lethargy Aggression Learning disability Impaired growth Constipation |
|
|
Workup for lead poisoning
|
CBC with MCV (microcytic, hypochromic anemia)
Blood smear (basophilic stippling) Blood lead level (<10 mcg/dL is ok) X-rays of long bones (lead lines) |
|
|
Treatment for pediatric lead poisoning
|
If >=15 mcg/dL --> refer to department of health
If >45 mcg --> start chelation |
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for NF1
|
2 or more of the following:
- First degree relative with NF1 - >6 cafe-au-lait spots of 5 mm (if children) or 15 mm (if adult) - >2 neurofibromas - Lisch nodules - Optic glioma - Bone dysplasia - Axillary freckling |
|
|
Workup for a new pediatric diagnosis of NF1
|
Ophthalmology consult (Lisch nodules, optic glioma)
Derm consult NB: MRI not technically needed until there are eye or CNS abnormalities. |
|
|
What gastric abnormality is associated with Mallory-Weiss tears?
|
Hiatal hernia (40-100%)
|
|
|
Treatment for acute seizure
|
ABCs and stabilize
Put in IVs Workup: Glucose, CBC, lytes, calcium, urine tox screen If still seizing --> benzos (1st line) or barbiturate (2nd) |
|
|
Most common pathogen in adult viral meningitis
|
Herpes simplex virus
|
|
|
Most common pathogens in pediatric viral meningitis
|
Enterovirus
Arbovirus (more common in rural areas bc zoonoses) |
|
|
When should you suspect nonallergic rhinitis?
|
Setting: > age 20
Presentation: - Onset after age 20 - Nasal Blockage - Rhinorrhea - Postnasal drip - No clear trigger - year long symptoms |
|
|
Treatment for nonallergic rhinitis
|
Intranasal glucocorticoids (fluticasone) or
Intranasal antihistamines (azelastine) |
|
|
When should you suspect allergic rhinitis?
|
Presents before age 20
Predominant eye symptoms Sneezing Nasal congestion Can usually identify a trigger Atopy Normal or blue nasal mucosa with pallor and occasional polyps |
|
|
Treatment for allergic rhinitis
|
Allergen avoidance
Intranasal glucocorticoids |
|
|
Additional treatment for patients on long term steroids
|
Long term= Greater than 3 months or greater than 6 months if dose is <10 mg/day
Baseline DEXA and then yearly Calcium and Vitamin D Add bisphoshonate only if risk of osteoporosis is very high |
|
|
How would you screen for HIV? What if the exposure was very recent?
|
Typical: ELISA --> Western blot for confirmation
Recent exposure: HIV RNA PCR or p24 antigen NB: PCR can also be used when ELISA is negative or indeterminate. |
|
|
Workup for a suspected HIV exposure
|
Antibody testing at 1st visit (ELISA)
Repeat at 6, 12 and 24 weeks |
|
|
What does an HIV ELISA test for?
|
Antibodies
So it will be negative if the patient hasn't seroconverted |
|
|
How often should CD4 count and HIV load be measured in an HIV patient?
|
Q3-4 months
|
|
|
Criteria for brain death
|
1) Irreversible absence of cerebral and brainstem reflexes
2) Absence of respiratory drive off the ventilator for a duration sufficient to produce hypercarbic drive (pCO2 50-60 or 10-20 minutes) 3) Body temp below 34 C 4) EEG isoelectric for 30 minutes at maximal gain 5) At least 24 hours observation in adults with anoxic brain damage with a negative drug screen NB: May still have purely spinal reflexes |
|
|
How do you diagnose C diff colitis?
|
1) Stool studies: PCR or EIA (PCR is more sensitive)
2) If negative and high clinical suspicion --> limited scope NB: Look for pseudomembranous colitis PCR looks for the toxin gene. EIA looks for the toxin itself. |
|
|
Which antibiotics are more likely to result in C diff?
|
Fluoroquinolones!
Enhanced spectrum penicillins Cephalosporins Clindamycin |
|
|
First Generation Cephalosporins
|
Cefazolin
Cephalexin Cefadroxil Cephalothin NB: Good for MSSA and strep |
|
|
What conditions can be associated with carpal tunnel?
|
Hypothyroidism
Wrist trauma Diabetes End stage renal disease RA Pregnancy Obesity Fibromyalgia |
|
|
Treatment for Barrett's Esophagus
|
Dependent on whether there's dysplasia
No dysplasia --> Yearly endoscopy Mild dysplasia -->Endoscopy Q6mo High grade dysplasia --> resection or ablation |
|
|
Modifiable risk factors in osteoporosis
|
Stop smoking (if >= 1 ppd)
Calcium + vitamin D Stop heparin Stop steroids Consider raloxifene.......be careful |
|
|
Primitive idealization
|
Defence mechanism where a pt views another person as perfect and cannot tolerate evidence to the contrary
|
|
|
Compensation (psych)
|
Defence mechanism
Pt overemphasizes achieves in one area bc of failures in another |
|
|
Projection
|
Defense mechanism
Pt attributes thoughts or desires to another person, especially those that are socially unacceptable |
|
|
Reaction Formation
|
Defense mechanism
Reaction to stress by substituting thoughts, behaviors or feelings that are the exact opposite Example: Gay man acting like a homophobe |
|
|
What kind of therapy works best in borderline patients?
|
Dialectical behavior therapy
NB: Works on behavior modification and skill building |
|
|
What is interpersonal therapy?
|
Short term therapy that works well in depression
Focuses on relationships, reducing conflicts and building social support |
|
|
A tubular adenoma is found on colonoscopy. Now what?
|
Colonoscopy in 5 years
|
|
|
A hyperplastic polyp is found on colonoscopy. Now what?
|
No change in screening. Colonoscopy in 10 yrs.
|
|
|
Four adenomas are found on colonoscopy. Now what?
|
Colonscopy in 3 years
NB: Indicated for 3-10 adenomas, any adenoma >1 cm, villous features or high grade dysplasia |
|
|
A polyp with high grade dysplasia is found on colonoscopy. Now what?
|
Colonoscopy in 3 years.
NB: Indicated for 3-10 adenomas, any adenoma >1 cm, villous features or high grade dysplasia |
|
|
Do you ever need colon cancer screening more than every 3 years?
|
Only if:
1) Large (>2) sessile polyp that was removed piecemeal [2-6 mo] 2) Polyp with adenocarcinoma in situ and at least 2 mm margin [2-6 mo] 3) Patients with Familial Adenomatous Polpyposis [yearly beginning at 12] 4) HNPCC [yearly beginning at 25] |
|
|
Workup in fibromyalgia
|
Clinical diagnosis but should rule out other etiologies
TSH, T4 CBC ESR CK |
|
|
Which blood pressure meds can be used in bipolar disorder?
|
Lithium is exclusively renally excreted, so be aware of kidney function!
Amlodipine NB: Avoid furosemide, thiazides, ACEI and ARBs |
|
|
When should you suspect Vitamin D deficiency?
|
Setting: Gastric bypass or other malabsorption
Presentation: - Bone pain or resorption - Low phos - Calcium may be normal due to bone resorption - Hyperparathyroidism NB: Measure serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D to diagnose. |
|
|
Treatment for pelvic inflammatory disease
|
Severe: IV abx only, cover gonorrhea and chlamydia
- Doxycycline and cefoxitin or - Doxycycline and ceftriaxone Mild to moderate: Can consider PO or IM - Cover same bugs |
|
|
Antibiotics to treat gonorrhea
|
IM ceftriaxone (3rd gen)
PO cefixime (3rd gen) IV cefoxitin (2nd gen) |
|
|
Antibiotics for chlamydia
|
PO azithromycin
PO doxycycline |
|
|
What does mitral valve prolapse sound like?
|
Midsystolic click followed by a late systolic murmur
|
|
|
When should you suspect acute cholangitis?
|
Charcot's triad: Fever, jaundice, RUQ pain
Elevated direct bilirubin Elevated alk phos AST/ALT pretty normal |
|
|
Workup for acute cholangitis
|
LFTs
CBC Admit! Blood cultures Once controlled --> ERCP |
|
|
Treatment for acute cholangitis
|
Admit!
Strict vital sign monitoring Antibiotics (after blood cultures) IV fluids Once controlled, elective ERCP +/- biliary decompression |
|
|
When should you suspect iron deficiency anemia?
|
Microcytic
Hypochromic Anisocytosis Ferritin usually <15 NB: Anemia of chronic disease usually has normal or elevated ferritin (acute phase reactant). |
|
|
Pt has a high hemoglobin. How do you screen for polycythemia vera?
|
Serum erythropoetin level
- LOW in polycythemia vera - Elevated in compensatory polycythemia NB: JAK2 can be used as a confirmatory test for PV |
|
|
Workup of polycythemia
|
CBC
Serum erythropoetin level Carboxyhemoglobin (to rule out CO poisoning) Pulsox Consider sleep study if no obvious other etiology |
|
|
When should you suspect transverse myelitis?
|
Setting: Recent URI
Presentation: - Rapidly progressive lower extremity weakness - Sensory loss - Urinary retension - Dull back pain - Initial hypotonia and hyporeflexia -->spasticity later NB: Rule out compressive lesions |
|
|
When should you suspect temporal arteritis?
|
Tenderness of temporal area
Jaw claudication Headache |
|
|
Workup for temporal arteritis
|
ESR
Temporal artery biopsy |
|
|
Treatment for temporal arteritis
|
Emergent steroids
NB: Generally high dose prednisone for several weeks |
|
|
When should you suspect pseudotumor cerebri?
|
Setting: Obese young woman
Presentation: - Headache - Double vision (CN6 palsy) - Visual field loss - Pulsatile tinnitus - Papilledema - Normal imaging |
|
|
Workup for pseudotumor cerebri
|
LP with opening pressure (markedly elevated)
|
|
|
Treatment for pseudotumor cerebri
|
Weight loss
Acetazolamide Refractory --> shunt or optic nerve sheath fenestration |
|
|
When should you image a headache?
|
Sudden or severe
Onset after age 40 Focal neurological findings |
|
|
Treatment for migraines
|
Abortive therapy: sumatriptan or ergotamine
If >=4 headaches per month, add prophylaxis: - First choice: Propranolol - Alternatives: CCB, TCA or SSRI |
|
|
Abortive therapies for migraines
|
#1) Propranolol
Calcium channel blockers Tricyclic antidepressants SSRIs |
|
|
When should a patient with migraine headaches receive prophylaxis?
|
At least 4 headaches per month
|
|
|
When should you suspect cluster headaches?
|
Setting: Man
Presentation: - Exclusively unilateral - Redness and tearing of eye - Runny nose |
|
|
Treatment for cluster headaches
|
Abortive: Triptan, 100% oxygen or steroids
Prophylaxis: - CCB (verapamil) |
|
|
When should you suspect BPPV?
|
Vertigo, provoked by certain positions or maneuvers
NO ataxia NO tinnitus NO hearing loss Positive Dix-Hallpike maneuver |
|
|
Treatment for BPPV
|
Particle repositioning maneuvers (Epley, Semont)
Meclizine |
|
|
When should you suspect vestibular neuritis?
|
Vertigo unrelated to position
NO hearing loss NO tinnitus |
|
|
Treatment for vestibular neuritis
|
Meclizine
|
|
|
When should you suspect labyrinthitis?
|
Acute vertigo
Hearing loss Tinnitus |
|
|
Treatment for labyrinthitis
|
Self-limited
Meclizine |
|
|
When should you suspect Meniere's?
|
Chronic, remitting and relapsing
Vertigo Hearing loss Tinnitus |
|
|
Treatment for Meniere's
|
Setting: Middle aged
Salt restriction Diuretics |
|
|
When should you suspect acoustic neuroma?
|
Setting: Patient with NF2 (bilateral)
Presentation: - Vertigo - Hearing loss - Tinnitus - Ataxia** - May knock out CN 5 and/or 7, depending on size |
|
|
When should you suspect Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome?
|
Setting: Chronic alcoholic
Presentation: - Confusion with confabulation - Ataxia - Memory loss - Gaze palsy/ophthalmoplegia - Nystagmus |
|
|
Workup for Wernicke-Korsakoff
|
Head CT
B12 level TSH, T4 RPR or VDRL for syphilis |
|
|
Treatment for Wernicke-Korsakoff
|
Thiamine, then glucose
NB: Load with IV thiamine then PO |
|
|
When should you suspect Alzheimer's?
|
Setting: Older patient
Presentation: - Slowly progressive loss of memory - No focal deficits - Eventually develop apathy and imprecise speech - Diffuse symmetrical atrophy on CT/MRI |
|
|
Workup for memory loss
|
Head CT (not MRI)
B12 level TSH, T4 RPR or VDRL (rule out neurosyphilis) |
|
|
Treatments for Alzheimer's
|
Anticholinesterase meds (donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine)
Memantine NB: No benefit to combinations. |
|
|
When should you suspect frontotemporal dementia?
|
- Personality and behavior change first --> memory
- Focal atrophy of the frontotemporal lobes on imaging - No movement disorder |
|
|
Treatment of frontotemporal dementia
|
Anticholinesterase meds (donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine)
Memantine NB: Doesn't respond as well as Alzheimer's |
|
|
When should you suspect Creutzfeldt-Jakob?
|
Setting: Older patients (younger than in Alzheimers)
Presentation: - Rapidly progressive dementia - Myoclonus |
|
|
Workup for Creutzfeld-Jakob
|
EEG (abnormal)
MRI (normal) 14-3-3 protein on CSF NB: If 14-3-3 is negative, need brain biopsy! |
|
|
What is Lewy Body dementia?
|
Parkinson's disease + dementia
i.e. will have a gait disorder. |
|
|
When should you suspect normal pressure hydrocephalus?
|
Setting: Old men
Presentation: - Urinary incontinence - Dementia - Wide-based gait/ataxia |
|
|
Workup for normal pressure hydrocephalus
|
Head CT (hydrocephalus)
LP (normal opening pressure) |
|
|
Treatment of normal pressure hydrocephalus
|
Shunt
|
|
|
When should you suspect Huntington's?
|
Setting: 30ish with a family history
Presentation: - Dementia - Personality changes - Chorea |
|
|
Workup for Huntington's
|
Genetic testing
NB: Autosomal dominant |
|
|
When should you suspect MS?
|
Setting: Young woman from the northern latitudes
Presentation: Multiple CNS abnormalities at different times: - Optic neuritis - Bladder atony - Motor and sensory issues Fatigue Hyperreflexia Spasticity Scanning speech Depression Periventricular plaques on MRI (Dawson's fingers) |
|
|
Workup for MS
|
MRI
LP (oligoclonal bands) Visual evoked potentials (delayed conduction) NB: Do NOT order CT. Useless. |
|
|
Treatment for MS
|
Initial: Prednisone/methylprednisolone to speed resolution of acute exacerbations
Disease modifiers: - Beta interferon** - Glatiramer - Mitoxantrone - Natalizumab (causes PML) Symptom management: - Amantadine for fatigue - Baclofen or tizanidine for spasticity |
|
|
When should you suspect Parkinson's?
|
Setting: Older
Presentation: - Resting tremor - Slow, "festinating" gait - Orthostasis - "Cogwheel" rigidity - Micrographia - Hypomimia (underreactive face) |
|
|
Treatment for Parkinson's
|
#1: Mild or severe?
Mild: - Anticholinergic (benztropine or hydroxyzine) if <60 - Amantadine if >60 Severe: - Levodopa/carbidopa - Dopamine agonists (pramipexole, ropinirole, cabergoline) Adjuncts: - COMT inhibitors (tolcapone, entacapone) boost dopamine agents - MAOIs (selegine, rasagiline) - Deep brain stimulation |
|
|
Treatment for levodopa psychosis
|
Quetiapine
|
|
|
When should you suspect essential tremor?
|
Tremor both with intention and at rest
|
|
|
Treatment for essential tremor
|
Propranolol
|
|
|
Workup for new onset seizure
|
Sodium
Calcium Glucose O2 Creatinine Magnesium Head CT --> MRI if negative Urine tox screen If no etiology found, then --> EEG Neurology consult*** |
|
|
Treatment for status epilepticus (CCS style)
|
1) Lorazepam
--> move clock 10-20 min 2) If seizure persists, fosphenytoin --> move 10-20 min 3) If seizure persists, phenobarbital --> 10-20 minutes 4) If seizure persists, general anesthesia (pentobarbital, thiopental, midazolam, propofol) |
|
|
When should you treat a single seizure for epilepsy?
|
Strong family history of seizures
Abnormal EEG Status epilepticus that required benzos to stop Non-correctable etiology i.e. tumor |
|
|
Treatment for absence seizures
|
Ethosuximide
|
|
|
Treatment for petit mal seizures
|
Ethosuximide
|
|
|
First line drugs in epilepsy
|
Valproic acid
Levetiracetam Carbamazepine Phenytoin Lamotrigine (causes Stevens-Johnson and skin rxns) NB: All equally effective. Do NOT give valproate in pregnancy! |
|
|
Second line drugs in epilepsy
|
Gabapentin
Phenobarbital |
|
|
When should you suspect encephalitis?
|
Fever
Confusion NO meningismus or photophobia |
|
|
Most common pathogen in adult encephalitis
|
Herpes
|
|
|
Workup in encephalitis
|
Head CT
CSF PCR for HSV |
|
|
Treatment for adult encephalitis
|
Acyclovir
If resistant -->foscarnet |
|
|
When should you suspect brain abscess?
|
Fever
Headache Ring-enhancing lesion on CT NB: Consider HIV status |
|
|
Treatment for brain abscess
|
#1: HIV status
Negative: Brain biopsy Positive: Empirically treat for toxo with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine x 2 weeks --> reimage with CT |
|
|
When should you suspect progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy?
|
Setting: HIV positive patient
Presentation: - Brain lesions without ring enhancement or mass effect |
|
|
Treatment for PML
|
Nothing specific
Raise CD4 count |
|
|
When should you suspect neurocysticercosis?
|
Setting: Mexican with a seizure
Presentation: - Seizures - Multiple small cystic lesions on CT (may be calcified) |
|
|
Treatment for neurocysticercosis
|
Are the lesions calcified or active?
Active: Albendazole - Give steroids to prevent a reaction to the dying parasites |
|
|
When should a head CT be performed before an LP?
|
History of CNS disease
Focal neurologic deficit Papilledema Seizures AMS Significant delay in ability to perform an LP |
|
|
Workup for suspected meningitis
|
Do they have any signs of hydrocephalus?
Yes --> Blood cultures, abx, head CT No --> LP and blood cultures, abx |
|
|
What should you look for in an LP for meningitis?
|
Gram stain
Protein (if normal --> NOT bacterial) Glucose (<60% of serum for bacterial) CSF cell count (thousands of neutrophils if bacterial) Culture |
|
|
Gram positive diplococci in CSF
|
Pneumococcus
|
|
|
Gram negative diplococci in CSF
|
Neisseria
|
|
|
Gram negative, pleomorphic coccobacilli
|
Haemophilus
|
|
|
Gram positive bacilli in CSF
|
Listeria
|
|
|
What is the best initial test for meningitis?
|
CSF cell count
NB: Thousands of neutrophils = bacterial meningitis until proven otherwise |
|
|
What do you expect in the CSF with bacterial meningitis?
|
Elevated protein
Positive gram stain (does not rule out if neg) Glucose <60% of serum Elevated cell count |
|
|
When should you suspect cryptococcal meningitis?
|
Setting: HIV positive patient with CD4 <100
Presentation: - Slower onset - Meningeal signs may be more subtle or asynchronous |
|
|
Diagnostic test(s) for cryptococcal meningitis
|
India ink (on gram stain)
Cryptococcal antigen (CSF) |
|
|
A lesion affects CN 3 and/or 4? Where is it?
|
Midbrain
|
|
|
A lesions affects CN 5-8. Where is it?
|
Pons
|
|
|
A lesion affects CN 9-12. Where is it?
|
Medulla
|
|
|
Third Generation Cephalosporins
|
Ceftriaxone
Cefotaxime Ceftazidime Cefpodoxime Cefixime Ceftibuten NB: Ceftazidime has Pseudomonal activity. All 3rd gen have an association with C diff. |
|
|
Treatment for cryptococccal meningitis
|
Amphotericin and 5-flucytosine
Follow with PO fluconazole - Continue until CD4 rises above 100 |
|
|
Empiric treatment for bacterial meningitis
|
IV ceftriaxone
Vancomycin Ampicillin (covers Listeria) Dexamethasone NB: Dex can be stopped later if it's not S. pneumoniae |
|
|
When should you suspect Lyme Disease?
|
Setting: Recent outdoor activity, camping, hiking
Presentation: Stage 1 - Target lesion, fever, joint pain, muscle pain, LAD Stage 2 - Myocarditis, AV block, Bell's palsy, peripheral neuropathy, meningitis Stage 3: Arthritis, Chronic neurologic symptoms |
|
|
Treatment for Lyme meningitis
|
IV ceftriaxone or
Penicillin |
|
|
Diagnostic test for Lyme Disease
|
Western blot or PCR
|
|
|
Treatment for Lyme Disease (no CNS or CV sx)
|
Doxycycline or
Amoxicillin |
|
|
When should you suspect Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
|
Setting: Hiker, camper
Presentation: - Fever - headache - Malaise - Rash starting on the wrists and ankles and moves inward |
|
|
Diagnostic test for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
|
Serology for R. ricketsii
NB: Must start tx empirically before this comes back |
|
|
Treatment for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
|
Doxycycline
|
|
|
When should you suspect TB meningitis?
|
Setting: Immigrant, history of lung TB
Presentation: - Very slow onset - Very high CSF protein level - Positive AFB culture (<10%) |
|
|
Treatment for TB meningitis
|
Same as lung TB + steroids
Rifampin Isoniazid Ethambutol Pyrazinamide |
|
|
When should you suspect viral meningitis?
|
CSF:
- Lymphocytes predominance - Normal glucose - Normal protein NB: Diagnosis of exclusion |
|
|
When should you suspect Neisseria meningitis?
|
Setting: Young person, teenager, military, asplenic
Presentation: - Meningismus - Petechial rash*** |
|
|
Treatment for N. meningitidis meningitis?
|
Empiric ceftriaxone and vancomycin
Put in respiratory isolation Treat close contacts with rifampin *** NB: Medical staff do NOT count as close contacts. Ciprofloxacin or ceftriaxone can also be used prophylactically. |
|
|
When should you suspect Listeria meningitis?
|
Setting: Elderly, neonates, HIV, asplenic, immunocomprised
|
|
|
When should you get a head CT in trauma?
|
LOC
AMS |
|
|
CT findings with subdural hematoma
|
Crescent shaped collection
|
|
|
Ct findings with a cerebral contusion
|
Bruising (intraparenchymal)
|
|
|
CT findings with epidural hematoma
|
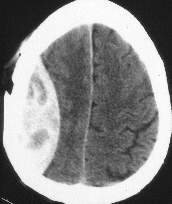
Lens shaped collection
|
|
|
Treatment for concussion
|
Nothing specific
|
|
|
Treatment for cerebral contusion
|
Admit for observation
Most get no additional treatment |
|
|
Treatment for subdural and epidural hematomas
|
Small: Let it resorb
Large; Evacuate |
|
|
Treatment for a large intracranial hemorrhage with mass effect
|
Mannitol
Intubation/hyperventilation to pCO2 of 25-30 Evacuate |
|
|
When should you suspect subarachnoid hemorrhage?
|
Sudden, severe headache
Photophobia Stiff neck LOC (50%) NO fever Focal neurologic deficits (30%) |
|
|
Workup for subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
Noncontrast head CT
- Negative --> LP - Positive is diagnostic Do angiography to determine site of bleeding |
|
|
Treatment for subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
Hydrocephalus?
- If yes, --> shunt Angiography to determine site of bleeding Embolize PO nimodipine to prevent vasospasm and stroke |
|
|
When should you suspect syringomelia?
|
Loss of sensation (pain and temperature) in the upper extremities bilaterally
Capelike distribution (neck, shoulders, arms) |
|
|
When should you suspect spinal epidural abscess?
|
Back pain
Tenderness Fever |
|
|
Treatment for spinal epidural abscess
|
Dx: MRI
Antibiotics against staph (oxacillin, nafcillin) Decompress, if large |
|
|
When should you suspect spinal stenosis?
|
Leg pain on walking
Pulses intact Pain is worse when walking downhill, better when leaning forward |
|
|
When should you suspect an anteiror spinal artery infarction?
|
Loss of all sensation exception proprioception and vibration
|
|
|
When should you suspect Brown-Sequard Syndrome?
|
Setting: Trauma to the spine
Presentation: - Loss of ipsilateral proprioception and vibration - Loss of contralateral pain and temperature |
|
|
When should you suspect ALS?
|
Upper motor neuron signs?
- Hyperreflexia - Babinski - Spasticity - Weakness Lower Motor Neuron signs: - Muscle wasting - Fasciculations - Weakness |
|
|
Treatment for ALS
|
Riluzole
NB: Blocks accumulation of glutamate |
|
|
Treatment for diabetic neuropathy
|
Gabapentin
Pregabalin Last choice: TCA |
|
|
Treatment for carpal tunnel
|
1) Splint
2) If sx persist, steroid injxn 3) If sx persist, surgery |
|
|
What should you suspect radial nerve palsy?
|
"Saturday night palsy"
Wrist drop |
|
|
When should you suspect peroneal nerve palsy?
|
Setting: Wearing high boots
Presentation: - Foot drop - Inability to evert foot |
|
|
When should you suspect Bell's Palsy?
|
Presentation:
- Hemifacial paralysis, upper and lower - Loss of taste on anterior 2/3 of tongue - Hyperacusis - Inability to close eye |
|
|
Treatment for Bell's Palsy
|
Steroids
|
|
|
When should you suspect reflex sympathetic dystrophy?
|
Setting: Previous injury to the extremity
Presentation: - Extreme pain resulting from light touch - Burning quality |
|
|
Treatment for Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy
|
NSAIDs
Gabapentin Consider nerve block Extreme cases: surgical sympathectomy |
|
|
Treatment for restless leg syndrome
|
Ropinirole or Pramipexole
|
|
|
When should you suspect Guillain Barre?
|
Setting: Antecedent infection several weeks before
Presentation: - Bilateral, symmetric leg weakness (ascending) - Loss of deep tendon reflexes (areflexia) - Elevated CSF protein withOUT cells - Mild sensory changes - Eventually CN involvement, respiratory compromise |
|
|
Treatment for Guillain Barre
|
Admit!
Peak inspiratory pressure (predicts respiratory failure) IVIG or plasmapheresis - Check IgA levels before giving IVIG NB: Do NOT use steroids! |
|
|
Workup for Guillain Barre
|
Peak inspiratory level (spirometry)
LP (elevated CSF protein after first 48 hours) ESR CBC Lyme titer (to rule out) Nerve conduction study (shows demyelination) |
|
|
When should you suspect myasthenia gravis?
|
Setting: middle-aged woman or older man
Presentation: - Weakness and fatiguability of muscles - Ptosis/diplopia - Dysarthria - Dysphagia - Respiratory failure |
|
|
Workup of myasthenia gravis
|
Anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies
Tensilon test (edrophonium chloride) --> improved strength |
|
|
Treatment for myasthenia gravis
|
Pyridostigmine or neostigmine
Refractory and <60 yo --> thymectomy Refractory --> Prednisone, azathioprine or cyclosporine |
|
|
When should you suspect an ACA stroke?
|
Profound lower extremity weakness
Mild upper extremity weakness Personality changes Urinary incontinence |
|
|
When should you suspect MCA stroke?
|
Profound arm weakness
Aphasia Apraxia/neglect Eyes deviate toward lesion Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia with macular sparing |
|
|
When should you suspect PCA stroke?
|
Inability to recognize faces
|
|
|
When should you suspect vertebrobasilar artery stroke?
|
Vertigo
Nausea/vomiting "Drop attack" Vertical nystagmus Dysarthria Ataxia Labile blood pressure |
|
|
When should you suspect PICA stroke?
|
Ipsilateral face
Contralateral body Vertigo Horner's Syndrome |
|
|
Treatment for ischemic stroke
|
1)Noncontrast head CT
2) Thrombolytics (if <3 hrs since onset and not contraindicated) 3) Aspirin or clopidogrel or aspirin/dipyridamole 4) Look for etiology: Echo, carotid duplex, EKG/Holter monitor - If <50 without risk factors, add ESR, RPR or VDRL, ANA, ds-DNA, Protein C, protein S, factor V Leiden mutation, antiphospholipid abx On Discharge: Manage BP (<130/80), glucose and lipids (LDL<100) |
|
|
Absolute contraindications to thrombolytics
|
History of hemorrhagic stroke
Intracranial mass Surgery within 6 weeks Bleedign disorder Traumatic CPR within 3 weeks Suspicion of aortic dissection Stroke in the last year Brain injury or surgery in last 6 months |
|
|
Cervical Cancer Screening
|
Start at age 21
Paps every 2-3 years Stop at age 65 |
|
|
Colon Cancer Screening
|
General population:
- Start at 50 - Colonoscopy every 10 yrs 1st degree relative: - Age 40 or 10 yrs before dx HNPCC: - Start at age 25 - Colonsocopy every 1-2 years |
|
|
Criterica for HNPCC
|
3 family members
2 generations 1 before age 50 |

