![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
140 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Goal Hgb in a pt who is on EPO due to CKD? |
11-12 |
|
|
Name the microcytic anemia (5): |
1. Iron deficiency 2. Pb poisoning 3. Chronic disease 4. Sideroblastic anemia 5. Thalasemias |
|
|
Name the Normocytic anemias (3): |
1. Hemolytic 2. Chronic disease 3. Hypovolemia
|
|
|
Name the macrocytic anemias (3): |
1. Folate deficiency 2. Vit B12 deficiency 3. Liver disease |
|
|
Low reticulocyte count in which type of anemias? |
Microcytic and macrocytic anemias |
|
|
1. Increased reticulocyte count, Increased indirect bill, Normal MCV, decreased haptoglobin. Dx? |
Hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Name the conditions associated with the following blood smear: a) Schistocytes b) Microcytic hypochromic RBC c) Hypochromic RBC with basophilic stippling d) Macrocytic RBC w/ hypersegmented neut. e) RBC surrounded by rings of iron granules f) Hypochromic RBC with target cells g) Bite cells and Heinz bodies
|
a) Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia b) Iron deficiency anemia c) Lead poisoning anemia = basophilic stipling also seen in thalasemia and alcohol use d) Vit B12 deficiency, Folate deficiency - No neurologic sx in folate deficiency e) Sideroblastic anemia f) alpha thalasemia g) G6PD deficiency |
|
|
What is the tx for hereditary spherocytosis? |
Folic acid 1mg qd Splenectomy in severe cases
- RBC infusion in severe anemia |
|
|
What drugs can cause hemolytic anemia in pts with G6PD deficiency? |
High Dose ASA sulfa drugs, Dapsone Primaquine Nitrofurantoin quinine and quinidine |
|
|
To Dx folate def definitely: |
Serum folate level and Red cell folate level |
|
|
1. Macrocytic anemia and peripheral neuropathy
2. Microcytic anemia and peripheral neuropathy
Dx =? |
1. Vit B12 deficiency
2. Lead poisoning |
|
|
Causes for sideroblastic anemia? |
Alcohol, INH, Lead poisoning |
|
|
10% of patients w/ sideroblastic anemia can progress to ______________ |
acute leukemia |
|
|
1. What vaccinations should be received by pts with sickle cell disease?
2. Aplastic crises in patients with SSD is a/w |
1. Hib, Influenza, Hep B, Pneumococcal
- Till age 5 pts should also get prophylactic Penicillin
2. Parvovirus B19 |
|
|
MCC of osteomyelitis in pts with Sickle cell disease? |
S. aureas is MCC in pts with SSD and healthy pts - consider Salmonella also in pts with SSD |
|
|
1. Monitor heparin anti-coat using _____
2. Monitor LMWH by checking ______
3. Monitor Warfarin by checking ____ |
1. PTT 2. Anti-Factor Xa - Pts with renal ds, elderly pts and obese patients might require it
3. INR |
|
|
What Rx to use to anti-coagulate a pt with HIT? |
1. Direct thrombin inhibitors (Lepirudo, argatroban)
Or 2. Direct Factor Xa inhibitors (Fondaparinux)
- B/c pts with HIT are hypercoagalable
|
|
|
Warfarin antagonizes which clotting factors? |
10, 9, 7, 2 and Protein C and S. |
|
|
What are the nutritional causes of Thrombocytopenia? |
1. Folate and Vit B12 deficiency 2. Alcohol
- Must rule out these two causes when presented with a patient having thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
What is the criteria for thrombocytopenia in HIT? |
Sudden decrease (50%) of platelets
|
|
|
What is the gold standard to diagnose HIT? What is commonly used?
|
1. Serotonin release assay - 14C-serotonin release assay (SRA)
- Very expensive (Gold Standard) Heparin induced platelet aggregation assay - Commonly used. - Very specific but not sensitive |
|
|
Whats the tx for HIT? |
Direct thrombin inhibitors - Lepirudin - Argatroban OR Direct Factor Xa inhibitors i.e. Fondaparinuxx
till the platelet level > 100K ==> Switch to Warfarin using bridging anticoag. with these agents. |
|
|
1. ITP usually has platelet levels < ________
2. Whats the pathophysiology 3. What's the tx? |
1. 50,000 2. Auto-immune. Antiplatelet ab 3. Children: Self limited Adults: steroids, splenectomy, plasmaphresis, immunoglobulin |
|
|
What's the triad of HUS? |
1. Hemolysis 2. Uremia - due to renal failure 3. Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Whats the pentad of TTP-HUS? |
1. Hemolysis 2. Uremia - due to renal failure 3. Thrombocytopenia 4. Fever, 5. AMS/ Neurological defects
|
|
|
Whats the tx for TTP-HUS? |
Steroids, Plasmapheresis, FFP |
|
|
What is the HELLP syndrome |
Hemolysis Elevated Liver enzymes Low Platelets
- During pregnancy, HTN, increased LFTs, decreased Hgb, Schistocytes on blood smear
2. Tx = Delivery if > 34 wks, Anti HTN Drugs, Steroids for surfactant prod if preterm |
|
|
von Willebrand disease |
1. Factor VIII and vWF 2. Increased PTT and Bleeding Time Decreased ristocetin cofactor activity |
|
|
What factors are not produced by the liver? |
VWF and Factor VIII |
|
|
Hemophilia 1. Hemophilia is _________ disorder 2. Hemophilia A is a Factor_____deficiency 3. Hemophilia B a Factor_____deficiency |
1. X-linked recessive 2. Factor VIII 3. Factor IX |
|
|
Uncontrolled bleeding after dental procedure, hemarthrosis, increased PTT, normal PT and normal bleeding time. Dx =? |
Hemophilia |
|
|
What are the labs a/w hemophilia |
Increased PTT Normal PT a Normal bleeding time Decreased factor VIII or IX |
|
|
What are the lab values for DIC? |
Decreased platelets --> increased Bleeding time Increased PT, PTT Decreased fibrinogen Increased fibrin split products Increased D-Dimer Decreased HCT
Schistocytes seen
|
|
|
Tx for DIC: |
Platelets FFP Cryoprecipitate Heparin - for chronic thrombi (Paradox)
|
|
|
Pt with sepsis. After giving IVF with no response + Pressors (norepi) also w/o much improvement. What is the next step? |
Give corticosteroids - suspecting adrenal insufficiency because a lot of times pts with septic shock also get adrenal insufficiency |
|
|
1) Sx of mono do not appear until _______ weeks after infection with EBV
2) When can pts return to contact sports? |
1) 2-5 weeks 2) One month after symptoms appear |
|
|
1) Medical student gets an accidental needle prick from an HIV infected patient. What prophylactic Rx should be given?
2) How often should the HIV antibody tests be carried out? |
1) Zidovudine Lamivudine
2) 6 weeks, 3 months 6 months |
|
|
At what CD4 level, there is a risk for
a) PCP infection? b) Bacterial pneumo c) Candida esophagitis d) TB e) AIDS dementia |
CD4 < 200 for all of them |
|
|
Which opportunistic infections occur at CD4 < 50? (3)
|
1. Cryptococcal meningitis
2. CMV 3. MAC |
|
|
Which opportunistic infections occur at CD4 < 100? (3)
|
1. Toxoplasmosis
2. Lymphoma (CNS or non-Hodgkin's) 3. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (JC virus) |
|
|
Whats the tx for cerebral toxoplasmosis |
1. Pyramethamine, Sulfadiazine, Clindamycin |
|
|
1. Whats the tx for cryptococcal meningitis?
2. How is it dx? |
1. Amphotericin B (Intrathecally b/c does not cross BBB) Flucanazole
2. Yeast seen w/ India ink stain of CSF Positive cryptococcal antigen |
|
|
1. Tx for CMV 2. What is the hallmark complication of CMV
3. How is dx? |
1. Ganciclovir, Foscarnet, Valganciclovir 2. Vision loss due to retinitis Bloody diarrhea
3. Viral titer Yellow infiltrates wi/ hemorrhage on fundoscopic exam |
|
|
- Fatigue, wt loss , fever - Diarrhea, abdominal pain - lymphadenopathy - hepatosplenomegaly
Presentation for which opportunistic infection? |
MAC |
|
|
What is the tx for MAC |
Clarithromycin, azithromycin |
|
|
Tx for PCP pneumonia |
TMP-SMX, Corticosteroids Other: Dapsone, Pentamidine, if allergic to Sulfa |
|
|
1. How is HIV diagnosed |
1. Eliza x2 + Western blot |
|
|
1. What is the main SE of zidovudine 2. What is the SE of abacavir
- Both of these are Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors |
1. Bone marrow toxicity 2. HSN |
|
|
What should prophylactic therapy for opportunistic infections started? |
When CD4 < 200 - TMP-SMX for PCP and Toxoplasmosis When CD < 100 - Clarithro or azithromycin for MAC - INH when close contacts have TB |
|
|
HIV pt is pregnant, what should be the tx? |
1. During labor: Zidovudine Newborn: Zidovudine for 6 weeks after birth
C-section indicated |
|
|
How is HIV in newborn dx =? |
Viral load |
|
|
Most common type of Hodgkin's lymphoma |
Nodular sclerosis |
|
|
Painless LAD of the neck if the most common finding of which lymphoma? |
Hodgkin's - also wt loss - pruritis - night sweats - fever - hepatosplenomegaly |
|
|
1. Auer rods seen in ____ 2. Smudge cells (fragile lymphocytes) seen in ____ 3. Reed-Sternberg cells seen in ______ 5. Starry sky pattern |
1. AML (myeloperoxidase +, no bone pain as seen in ALL) 2. CLL 3. Hodgkin's lymphoma (good prognosis) 4. ALL 5. Burkitt's lymphoma (EBV related) |
|
|
1. Philidelphia 9:22 chromosome 2. BCR:ABL 3. 14: 18 transformation 4. 8:14 transformation |
1. CML, in 15% of adult ALL cases 2. CML 3. Follicular lymphoma 4. Burkitt's lymphoma |
|
|
Most common non-hodgkin's lymphoma is: |
Diffuse large cell B-Cell lymphoma |
|
|
What is the difference in symptoms between hodgkin's and non-hodgkin's? |
1. Hodgkin's = Cervical LAD Non-Hodgkins = Generalized LAD |
|
|
1. ALL is a/w ____ 2. What are the sx of ALL |
1. Down syndrome 2. Young child (2-5 yrs old usually) Bone pain fatigue and dyspnea on exertion easy bruising frequent infections |
|
|
1. CLL usually in patients aged > ______ 2. What are the lab findings are: ___ |
1. 65 2. may get as high as 100,000 WBC
|
|
|
MCC of sideroblastic anemia? |
Alcohol |
|
|
Which anemia is most likely to have increased RDW (red cell Distribution Width) |
Iron deficiency anemia |
|
|
How to distinguish between different microcytic anemias? |
Iron studies |
|
|
Low MCV + Decreased Ferritin. Dx =? |
Iron deficiency anemia - Ferritin is an acute phase reactant that increases in response to stress - Therefore, to confirm the dx check TIBC. - Increased TIBC + Low Ferritin confirms the Diagnosis of Iron deficiency anemia |
|
|
Which anemia has a high circulating Fe++ level? |
Sideroblastic anemia |
|
|
Jehovah's witness with Iron deficiency anemia which is not responding to Oral FeSO4. Pt refuses blood transfusion. What's the next best step in management? |
1. IV or IM Iron |
|
|
________ stain looks for iron in ringed sideroblasts |
Prussian blue |
|
|
Microcytic anemia with a normal iron study. Dx=? |
Thalasemia - Electrophoresis distinguishes between alpha and beta |
|
|
70 yo alcoholic patient with tingling and numbness of hands and feet. a) Whats the first step in dx b) What's the next step? |
1) Blood smear to look for hypersegmented neutrophils - to differentiate from vit def vs alcohol induced
2) Check for Methylmalonic acid ---increased in Vit B12 deficiency |
|
|
1. Increased Reticulocytes, LDH, Bili Decreased haptoglobin Dx=? |
Hemolytic anemia - intravascular - Lowered haptoglobin means intravascular - Dark urine - free Hgb --> Hemoglobinuria - Hemoblobinura can cause ARF and ATN |
|
|
1. Whats the best initial test to dx sickle cell disease 2. Whats the indication for abx tx in a patient with sickle cell disease 3. Pt with sickle cell crises admitted in the hospital, the next day there is precipititous drop in HCT. Most likely cause? |
1. Blood smear 2. Fever, increased WBC 3. Parvovirus B19 - Dx with PCR or IgM Tx = Immunoglobulin |
|
|
1. Which SCD get exchange transfusion? 2. Whats the tx regimen for SCD (outpatient) |
1. Pts with CNS and eye issues, priapism 2. Hydroxurea Folate Pneumovax |
|
|
1. What is the test for PNH (Paroxysmal Noctural hemoglobinuria) ? 2. Whats the MCC of death in pts with PNH 3. Tx = ? 4. What conditions are a/w with PNH? |
1. CD55 and CD59 levels 2. Large vessel thrombosis 3. Tx = Steroids 4. AML, Aplastic anemia, G6PD def |
|
|
Which subtype of leukemia presents with DIC? |
AML M3 - Tx==> All-trans retenoic acid |
|
|
1. Tx for ALL?
2. Pt has a relapse of Acute leukemia. What is the treatment? |
1. Danorubicin Vincristin Prednisone
2. Bone marrow transplant
|
|
|
ALL recurs in the __________, and to tx it ________ is given via ________ |
Spinal cord, Methotrexate Intrathecally (injected directly in the spinal cord) |
|
|
Treatment for Severe leukocytosis which causes symptomatic sludging of blood? |
Leukophresis |
|
|
1. Huge spleen, abdominal pain and early satiety is a feature of this leukemia?
2. Tx for this disease? What is the absolute cure? |
1. CML (9:22 Philidelphia chromosomes)
2. Imatinib 3. Bone marrow transplant |
|
|
What is the treatment for CLL? |
Fludarabine |
|
|
For an allogenic bone graft, what is the age limit? |
< 50 year old
- < 70 yo for an autologous stem cells |
|
|
What is the decision tree for diagnosing CML |
High WBC --> Check diff. for elevated Neutrophil --> if neutrophil elevated (~90%) ---> check LAP ( low LAP score in CML)
if Low LAP --> due to CML; otherwise reactive ds.
***LAP = Leukocyte alkaline phophatase score |
|
|
1. What is the most accurate diagnostic test for Multiple myeloma? |
1. > 10% plasma cells
|
|
|
What is the treatment for Multiple Myeloma |
If < 70 year old ==> Autologous stem cell implant Rx: Vincristine, Adriamycin, Dexamethasone - used to prepare the marrow for the transplantation
If > 70 and Healthy ==> Thalidomide
If > 70 and Fragile ==> Melphelane (does not cure, just lowers the cell count) |
|
|
Which stages of lymphoma get: a) Radiation b) Chemo |
a) Stage I and II, Any stage with "B" symptoms - B Sx= Fever, Wt loss, Night sweats
b) Stage III and IV
* Excisional biopsy 1st and then must get CT and bone marrow biopsy before radiating |
|
|
Hodgkin's disease mostly presents as Stage ____
NHL mostly presents in Stages___ and ____ |
Stage I and II (~90%) - Thats why mostly treated with radiation
Stage III and IV - Therefore mostly get chemo |
|
|
CD20 is expressed by |
NHL |
|
|
What is the chemo tx for NHL: + SE
|
CHOP:
Cyclophosphamide: SE Hemorrhagic cystitis Hydroxy-Adriamycin: Cardiotoxicity O: Oncavin/Vincrystine - SE = Peripheral neuropathy P: Prednisone |
|
|
What is the chemo tx for Hodgkins and their SE? |
ABVD:
Adriamycin: Cardiotoxicity Bleomycin: Lung fibrosis Vincristine: Peripheral neuropathy Dacarbazine: Pro-emetic |
|
|
Healthy patient + Isolated Low Platelets + Normal spleen (exam + U/S). Dx =? |
ITP |
|
|
22 yo F presents to the ED with epistaxis, and petichiae. PT: Normal PTT: High Platelets: Normal
Most likely dx =? |
1. von Willebrand's disease.
Note: Thalasemia will also have the same labs but almost NEVER occurs in women |
|
|
1) What's the most sensitive test for ITP
2) What's the treatment for ITP |
1. Anti-platelet ab 2. Steroids If multiple episodes of recurrence after stopping steroids ==> Splenectomy |
|
|
Pt with ITP with life-threatening bleeding (e.g. SDH, Melana, etc). Whats the tx? |
IVIg / Rhogam - Stops macrophages from consuming platelets |
|
|
1. What are the two conditions that make up microangiopathic hemolytic anemia?
2. What is the pathophysiology behind it? |
1. HUS TTP
2. Deficiency of metaloproteinase - need to dissolve the platelet plug - removes vWF from the platelet plug |
|
|
What is the treatment for HUS and TTP |
Plasmapheresis - Provides the metaloprotienases which wash away the platelet plugs responsible for causing microangiopathy hemolytis |
|
|
What are the labs for Hemophilia? |
PT: Normal PTT: High Platelets: Normal
- causes delayed hemarthrosis - VWF will have these same labs. - Therefore differentiate btw the two by the nature of the bleeding. - Platelet bleeding more superficial + GI + CNS + epistaxis |
|
|
What is ristocetin test? |
Test for the function of vWF |
|
|
1. Treatment for Uremia induced platelet dysfxn? 2. Treatment for VWD ? 3. Treatment for mild Hemophilia |
1. DDAVP i.e. Desmopressin 2. DDAVP i.e. Desmopressin as well 3. DDAVP i.e. Desmopressin as well
|
|
|
1. What conditions increase both the PT and PTT with normal Platelets?(3)
|
1. Liver disease (shows greater elevation of PT than PTT)
Vit K deficiency (shows greater elevation of PT than PTT) DIC |
|
|
1. The only condition that gives elevated PTT only (no other abnormalities)? |
Lupus anticoagulant |
|
|
Most common cause of coagulopathy in a pt with normal PT, PTT and Platelets? |
Factor V leiden mutation |
|
|
1. What is pathophysiology of Glanzmann thrombosthenia
2. What tests are done for dx?
3. Tx=? |
1. Deficient or dysfunction Gp IIb/IIIa - leading to defective platelet aggregation
2. Platelet agonist ADP, Epi, Collagen - show decreased response Ristocetin - Normal
3. Platelet transfusion |
|
|
1. What is pathophysiology of Bernard Soulier Syndrome
2. What tests are done for dx? 3. Tx=? |
1. AR disorder: Thrombocytopenia and large Plateletsv
2. Pronlonged Bleeding time ADP, Epi, Collagen - normal aggregation Ristocetin - Platelets do not aggregate |
|
|
What is Diamond-Blackfan syndrome |
Congenital Macrocytic anemia |
|
|
Sudden onset of dark urine, Jaundice, increased indirect Hgb, Spherocytes on peripheral smear, increased LDH. Most likely dx? |
Autoimmune hemolysis - recent hx of infection or drug exposure is helpful in diagnosis - positive Coomb's |
|
|
TTP Pentad?
Whats the treatment |
1. Uremia (renal failure) Fever Thrombocytopenia microangiopathic hemolytic anemia CNS/AMS
2. Plasmapheresis |
|
|
Normocytic anemia with teardrop cells |
Myelophthistic anemia e.g. myelofibrosis |
|
|
Reticulocytosis causes _______ anemia |
Macrocytic anemia |
|
|
1. Elevated methylmalonic acid is seen in ?
2. Elevated homocysteine is seen in ? |
1. Vit B12 deficiency
2. Folate and Vit B12 deficiency |
|
|
______ is an infectious cause of Vit B12 deficiency |
Diphyllobothrium datum (fish tapeworm) |
|
|
RDW is ______ in thalasema and ____ in Iron def. anemia |
1. Close to normal, Increased |
|
|
Autoimmune hemolysis causes ______ (extravascular, intravascular) hemolysis |
Extravascular |
|
|
Marked Leukocytosis, Low LAP, Marked splenomegaly, +ve phillidelphia chromosome |
CML |
|
|
Whats the differentiating feature between myelodysplasia and myelofibrosis |
1. In Myelodysplasia, there is - Absence of splenomegaly - rapid clinical course |
|
|
What are the values for PT and PTT in TTP (low, high, normal) ? |
Normal |
|
|
What Rx can be given to prevent renal failure due to tumor lysis syndrome (2)
|
1. Allopurinol OR
Rasburicase - lowers uric acid by degradation of uric acid and by catalyzing oxidation of uric acid Aggressive IVF |
|
|
What is the gold standard for dx of CML? |
Cytogenic studies for phillidelphia chromosome (9:22) Detection bcr-abl in peripheral blood by FISH |
|
|
In Tumor lysis syndrome, what labs are seen? (3) |
Serum Uric acid: High Ca: Low PO4: High |
|
|
Treatment of hereditary Spherocytosis |
Folate |
|
|
Serum ferritin < _______ may reflect Iron deficiency in patients with inflammatory states. |
100-120 ng/L
Normal Ferritin Range: 20-200 |
|
|
What are the features of aplastic anemia? |
- Pancytopenia, - Low reticulocyte count - Hypoplastic bone marrow (<20% cellularity) with normal maturation of all cell lines |
|
|
Erythrocytes show hypochromia, anisocytosis (changes in size), and poikilocytosis (changes in shape) . Likely dx? |
Iron deficiency anemia |
|
|
Aplastic crises in pts with chronic hemolytic anemia is usually due to ________ |
Parvovirus B19 - Diagnosed by finding serum IgM antibodies against parvovirus B19 |
|
|
The presentation of _______ is characterized by right-sided heart failure with peripheral edema, abnormal venous waveforms, fixed splitting of S2, loud or palpable pulmonic valve closure, tricuspid regurgitation, a right ventricular heave, and clear lungs. |
pulmonary hypertension |
|
|
Laboratory findings suggestive of ___________ include: microangiopathic hemolysis with prominent schistocytes on peripheral blood smear, decreased haptoglobin, elevated serum LDH, and thrombocytopenia. |
TTP-HUS syndrome |
|
|
__________ is a condition in which platelets agglutinate and the clumped platelets are not recognized as such by automated blood counters. The diagnosis is suspected by finding large platelet clumps on the stained blood film |
Pseudothrombocytopenia |
|
|
_______ is the first line treatment for immune thrombocytopenic purpura? What's the indication?
|
Corticosteroids
- Corticosteroids are generally indicated in patients with ITP who have symptomatic bleeding and platelet counts < 50,000/µL or in those with severe thrombocytopenia and platelet counts < 15,000/µL |
|
|
A 42-year-old woman is evaluated for swelling and discomfort of the right leg without an obvious precipitating event. She also has a history of two spontaneous abortions. Persistent lupus anticoagulant or persistently elevated levels of IgG anticardiolipin or β2-glycoprotein I antibodies
a) Dx b) Tx |
a) Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
b) Life long anticoagulation |
|
|
How is lupus anticoagulant tested? |
Test with PTT. - If prolonged, perform a mixing study; - mixing with normal plasma will not correct the study if lupus anticoagulant is present. |
|
|
Pt has hypercalcemia, diffuse osteopenia, anemia, leukopenia, renal insufficiency, and a history of encapsulated organism–related pneumonia, which is a characteristic presentation of _______________ |
Multiple myeloma |
|
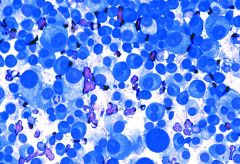
Identify? |
Multiple Myeloma |
|

|
AML - myeloblast with Auer rods. - Auer rods are clumps of azurophilic, needle-shaped crystals made from primary cytoplasmic granules. |
|
|
TOC for nephrogenic DI? |
Amiloride or Thiazides |
|
|
No increase in osmolarity or suboptimal increase after water deprivation? |
DI
Intranasal or SubQ Desmopressin next - If Urine (osm) --> Increases Then Central DI otherwise nephrogenic |
|
|
Bone aspirate showing peritrabecular bone marrow aspirates |
NHL |
|
|
In Polycythemia Vera, ___ is given to pts who are at increased risk for thrombosis (>60 yr old, prior thrombosis, CV risk factors) |
Hydroxyurea
Tx= phlebotomy |
|
|
Fatty marrow. Most likely dx? |
Aplastic anemia |
|
|
What electrolyte imbalance is seen in Tumor Lysis syndrome (4) ? |
Hypocalcemia Hyperuricemia Hyperphosphatemia Hyperkalemia |
|
|
Pt with bruising and isolated elevated PTT. Whats the next step in management |
1:1 mixing studies |
|
|
ALL is characterized by the presence of these two markers? |
CALLA - Common ALL antigen TdT - terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase |
|
|
Seborrheic dermatitis, glossitis, angular cheilitis, peripheral neuropathy, confusion, and seizures
can be a result of Vitamin _____ deficiency? |
Vit B6
Causes include: Malabsorption, Alcohol and drugs -INH, Chloramphenicol, pyrazinamide |
|
|
Prolonged PTT, a defect in ______ pathway |
Intrinsic |

