![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 most common locations in the circle of Willis for an aneurysm |
ACommA and PCA
|
|
|
Acute tx of Hypercalcemia
|
IV fluids, THEN loop diuretic (but fluids first)
|
|
|
Acid-base disorder caused by aspirin overdose:
|
Mixed respiratory alkalosis and anion gap metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
WBC count in Synovial fluid analysis of
-Normal Joint -Osteoarthritis -Inflammatory condition joint -Septic arthritis |
Normal: 0-200/ml
-Osteoarthritis: 200 -- 2,000 -Inflammatory arthritis: 2,000 -- 50,000 -Septic arthritis: >50,000 |
|
|
Other name for ACTH stimulation test (in diagnosing Addison's)
|
Cosyntropin test
|
|
|
Acid-base and electrolyte abnormalities in Addison's disease
|
Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis with hyponatremia and hyperkalemia
(normally aldosterone causes reabsorption of Na+ and secretion of H+ & K+, so with addison's being a state of hypoaldosteronism you get the opposite, no Na reabsorbed and you keep all your H+ ions and K+ |
|
|
Electrolyte abnormalities in Cushing's syndrome
|
Hypernatremia and Hypokalemia (because corticosteroids have some mineralocorticoid activity)
*for explan of how aldosterone/mineralocorticoids cause electrolyte phys, see previous flashcard on Addison's) |
|
|
Scenarios/drugs that can result in Drug-induced Pancreatitis
|
1. Pt on diuretics--thiazides, furosemide
2. Pt with IBD--sulfasalazine, 5-ASA 3. Pt on immunosuppressive agents--azothioprine, L-asparaginase 4. Pt w/ hx of seizures or bipolar--valproic acid 5. AIDS pt--didanosine, pentamidine 6. Pt on Antibiotics--metronidazole, tetracycline |
|
|
Prolactin production is inhibited by ____________, but stimulated by ____________ and ____________.
|
Inhibited by dopamine.
Stimulated by Serotonin & Thyroid-releasing hormone |
|
|
Cancers that ↑ Erythropoeitin (& mnemonic)
|
"Potentially Really High Hematuria"
P- Pheochromoytoma R- Renal cell carcinoma H- Hepatocellular carcinoma H- Hemangioma |
|
|
HCM murmur increases when Preload ⬆ or ⬇?
And what maneuvers cause this increase in murmur intensity? |
⬇preload causes more murmur in HCM,
b/c this lessens the size of the ventricular cavity and causes increased outflow obstruction. VALSALVA INCREASES INTENSITY of HCM murmur b/c it causes ⬇ PRELOAD. Inspiration and Squatting, on the other hand, DECREASES INTENSITY of murmur b/c it ⬆ Preload Also Handgrip can DECREASE intensity because ⬆ Afterload, helping to maintain ventricular volume |
|
|
Most consistent reversible risk factor for pancreatitis:
|
Smoking
|
|
|
The most beneficial therapy to reduce the progression of diabetic nephropathy in the presence of renal insufficiency/azoetemia is:
|
Intensive BLOOD PRESSURE control--ACE inhibitors!
(to at least <130/80) |
|
|
Causes of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
and Mnemonic |
"STOP Making Thrombi"
-Sepsis -Trauma -Obstetric complications -Pancreatitis -Malignancy (esp gastric, breast, lung) -Transfusions |
|
|
Most common complication of Peptic Ulcer disease
|
Hemorrhage
|
|
|
Screening for colon cancer in pt's with Ulcerative Colitis
|
8 years after dx, then every 1-2 years after
|
|
|
Descriptive definitions of Osteomalacia vs Rickets vs Osteoporosis |
Osteomalacia and Rickets are both caused by Vitamin D deficiency, so both result in defective bone mineralization, but in kids it also has an effect on the growth plate cartilage, so...
Osteomalacia-defective mineralization of bone Rickets-defective mineralization of bone and cartilage Osteoporosis--normal bone mineralization, but low bone mass |
|
|
Windshield wiper fluid= what type of poisoning
|
likely ethylene glycol (if renal colic/stones) or methanol (if visual disturb's)
|
|
|
Supracondylar fracture can cause secondary injury to:
|
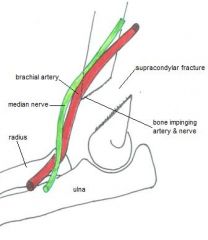
Brachial artery
(which would result in loss of radial pulse, so check it! |
|
|
Child has seizure a day after getting DTap. Can he get the vaccine again (next dose)?
|
The possible adverse rxn's to DTap are due to the pertussis component. If a CNS complication (like seizure, an encephalopathy, or an anaphylactic reaction occur within 7 days of its administration, then further admin of DTap is Contraindicated.
In these instances, DT should be substituted for DTaP (ie still get diptheria and tetanus, just not the pertussis component). |
|
|
Causes of widened mediastinum on CXr
|
-Aortic dissection
-Mediastinal tumors or mass (germ cell, lymphoma, tumors of thymus) -Mediastinitis -Lymphadenoapthy -anthrax -Esophageal rupture -Cardiac tamponade -Pericardial effusion |
|
|
Which type of pain (somatic or visceral) is poorly-localized, constant, and dull?
|
Visceral pain
vs somatic pain which is well-localized and more severe in intensity |
|
|
Potential dreaded complication of Compartment syndrome:
|
Volkmann's ischemic Contracture
(the final sequelae of compt syndrome in which the dead muscle has been replaced with fibrous tissue) |
|
|
Vague painful confution seen as a sequela of infection or trauma which may be minor, characterized by pain, hyperesthesia, and tenderness
|
Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
|
|
|
True or False:
Tightening of glycemic control will improve erectile dysfunction. |
False, it has not been shown to improve ED.
It is treated with phosphodisterase inhibitors (sildinafil) |
|
|
Most common causes of Acute Otitis Media (in order)
|
#1=Strep pneumo
#2=Hib #3=Moraxella |
|
|
What is Salvage therapy?
|
Treatment for a disease when standard therapy fails
(such as radiation therapy for PSA antigen recurrence after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer) |
|
|
Wilson's disease is also called:
|
Hepatolenticular degeneration
|
|
|
Mgmt of a pt with a liver mass who has traveled in an endemic area
|
-Evaluate for amoebic abscess with serologic testing for antibodies
-Empiric tx with Metronidazole |
|
|
The most significant risk factor for limb reduction defects associated with chorionic villus sampling:
|
Gestational age of the fetus
(CVS before 10 WGA is associated with greater risk) |
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for Rheumatic Fever
|
2 major or 1 major & 2 minor criteria
J♥NES criteria = Major criteria Joints (polyarthritis, hot/swollen joints) ♥ (carditis, valve damage) Nodules (subcutaneous) Erythema marginatum (painless rash) Sydenham chorea Minor crit = PEACE Previous Rheumatic fever ECG w/ PR prolonged Arthralgias CRP & ESR elevated Elevated temperatire |
|
|
Which baby milk (breast milk or formula) has an inadequate supply of Vit D
|
Breast milk
so exclusively beast fed infants need Vit D sup |
|
|
3 things GERD predisposes patients
|
Barrett's esophagus, Erosive Esophagitis, and Peptic Stricture formation
|
|
|
Most sensitive test to diagnose
-Acute Disseminated/diffuse Pulmonary Histoplasmosis -Chronic Disseminated Pulmonary Histoplasmosis |
-Acute: Antigen in the serum or urine
-Chronic: Fungal blood culture *Blood cultures can take up to 6 weeks to become positive in accute diffuse pulm histo so not the most sensitive in acute cases! |
|
|
Most severe consequences of methanol intoxication (2)
|
Vision loss and Coma
|
|
|
Causes of Foot drops (4)
|
#1=Peripheral neuropathy
-Trauma to the common peroneal nerve (common fibular nerve) -Radiculopathy to any of the spinal roots that contribute to the common peroneal nerve (L4, L5, S1, S2) Less commonly, can be congenital:Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease |
|
|
Only clotting factors not made by liver and hence not decreased in liver disease
|
vWF and Factor VIII
|
|
|
Causes of Dilated Cardiomyopathy:
|
1- Chronic CAD or ischemia
2 - ALCOHOL 3 - Doxorubicin 4 - MYOCARDITIS ✴ Viruses--COXSACKIE, Parvovirus B19, Enteroviruses, EBV, CMV, HHV-6 ✴ Parasites--Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas dz) ✴Bacteria ✴Fungi ✴ Drugs 5 - Pregnancy 6 - Hemochromatosis (usu restrictive CM) |
|
|
Hemochromatosis patient is at increased risk for:
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
Patients with uncontrolled hypertension are at greatest risk for what complication:
|
Myocardial infarction (CAD)
|
|
|
Normal MMSE score is:
|
27-30
|
|
|
Cause of Isolated Systolic Hypertension:
(ie systolic BP is elevated, but diastolic is normal) |
Decreased elasticity of arterial walls (rigidity of arterial walls...As a person ages, the elastic properties of the arterial wall diminish and the arteries become more rigid)
Note: Aortic regurg/insufficiency also caused Isolated Systolic hypertension....but on exam there would be a diastolic murmur) |
|
|
Caused of Hypertension with elevations in both systolic and diastolic
(systolic and diastolic hypertension) |
Increased plasma renin activity (like in RAS)
|
|
|
Which crosses suture lines: cephalohematoma or caput succedaneum?
|
Caput suCCedaneum
(more C's than cephalohematoma--> multiple C's = Crosses suture lines = Caput seCCedaneum) cephalohematoma is subperiosteal hemorrhage and so is always limited to the surface on 1 bone)--presents few hours after birth and there is no discoloration of skin |
|
|
When should Abx be given to someone to prevent pulm complications
|
Only if they have severe lung disease or evid of infection...in which case surgery should only be done if emergent, otherwise elective surgeries should be postponed until no signs of infection
|
|
|
Typical/possible symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
|
abdominal pain, pain relief with bowel movements, looser and more frequent stools with the onset of pain, passage of mucous, a sense of incomplete emptying, or bloating
can also have extra intestinal...depression, sexual dysfunction, and urinary changes |
|
|
What drug class is contraindicated during a STEMI MI
|
Dihydropiridine CCB's (ie nifedipine)
b/c they cause vasodilation which leads to reflex tachycardia which worsens the heart ischemia non-dyhidropiridine CCBs like verapamil and diltiazem can be used for ongoing ischemic sx after beta blockers ave been administered, but they wont improve mortality |
|
|
-How can right heart failure/right ventricular infarction lead to hypotension?
-Why might a patient with a right ventricular infarct have a low heart rate in the face of hypotension? |
-Failure of the right ventricle leads o decreased preload, and therefore can result in decreased cardiac output and hypotension.
-that is suggestive of possible SA node ischemia (SA node is located in right ventricle) Pt's with RV infarcts require a high preload to maintain their BP and therefore are treated with IV fluids. You must avoid drugs that reduce preload such as nitro and diuretics! |
|
|
Kid needs treatment for ALL (non-emergent). Parents are divorced and have joint custody. What do you do when...
-One parent says yes, one parent says no. -Both parents object to treatment: |
-One says yes and other says no: Proceed with tx...if joint custody, only requires 1 parent to consent to treatment despite what the other says. If one parent has custody, then only what they say matters.
-If both parents object to a non-emergent treatment, you'd have to seek court approval before proceeding -If therapy is emergent or child will die, then proceed without consent if obtaining it would delay treatment |
|
|
How come patients with Hemophilia can get recurrent episodes of joint pain/swelling?
What would the most likely cause of this joint pain be? |
Recurrent hemarthroses--can lead to a joint injury called "hemophilic arthropathy." Exact mech not known, Iron deposition and synovial thickening with fibrosis are characterisitic.
-Cuaued by Hemosiderin (an iron-storage complex) deposition and fibrosis |
|
|
Gold standard for evaluating the cervix for possible cervical incompetence
|
Transvaginal Ultrasound
|
|
|
What does the sodium level tell you about Heart Failure:
|
🌟⬇Na = Severe Heart failure 🌟
The presence of HYPONAREMIA indicates the HEART FAILURE is SEVERE. Water retention and the associated reduction in the plasma Na concentration parallel the severity of heart dz; they reflect the degree of neurohumeral activation in pt's with heart failure. ⬇Na level is associated with ⬆Renin, Aldosterone, Vasopressin, and Norepinephrine. As a result, a pt's survival is significantly reduced if the serum Na is < 137. Mgmt included decreasing the intake of water to help control the electrolyte abnormalities. Uworld qID 4190 |
|
|
Both Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) and Hereditary Spherocytosis typically show spherocytes without central pallor on peripheral smear.
So how do you differentiate the two. |
Hereditary Spherocytosis--strong family hx, (+) Osmotic fragility test, and (−) Coombs test,
AIHI-- (+) Direct Coombs test, negative fam hx, and (-) osm frag test |
|
|
Lab abnormalities that are an indication for thyroid function testing (4):
|
-Hyperlipidemia
-Unexplained hyponatremia (hypothyroidism can cause inappropriate ADH secretion) -High serum muscle enzymes (myopathy) -Anemia--typically is normocytic, normochromic |
|
|
Causes of arthritis:
|
◆ The biggies: Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Gout, Pseudogout, Septic arthritis
◆ Lupus & other collagen vascular diseases (SLE-symmetric & nonerosive) ◇ Mixed Connective Tissue Disorder ◇ Sjogren syndrome ◇ Scleroderma ◆ Psoriatic arthritis (psoriasis) ◆ Ankylosing Spondylitis ◆ Inflammatory Bowel disease ◆ Reactive arthritis (post-infection) ◆ Lyme disease (mono- or oligo-arthritis/migratory, late stage) ◆ Hemophilia (Hemophilic arthropathy) ◆ Paget disease ◆ Hemochromatosis ◆ Wilson's disease ◆ Neuropathy (Charcot joint) ◆ Prior trauma Others: ◇ Rheumatic fever (migratory arthritis/polyarthritis) ◇ Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP) (polyarticular arthritis) ◇ Sarcoidosis ◇ Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis ◇ Sickle cell disease (hip arthritis from avascular necrosis of the femoral head) |
|
|
Suspected prostatitis--most appropriate next step in mgmt:
|
Culture of Mid-stream urine sample
|
|
|
List the causes (many) of SIADH:
|
- Any CNS disorder (stroke, hemorrhage, trauma, psychosis, infection)
- Pulmonary diseases--esp. Pneumonia (viral, bacterial, tuberculous) - Tumor (small cell lung cancer) - Drugs (carbamazepine, NSAIDs, opiates, many more--list in drug adverse reactions flashcards) - Exogenous hormones (Vasopressin, Desmopressin-DDAVP, Oxytocin) - Endocrine d/o (Hypopituitarism & Hypothyroidism) -Symptomatic HIV infection -post-surgical procedure... |
|
|
What type of nerve injury causes diabetic neuropathy?
nerve compression, ischemia, or inflammation |
Nerve Ischemia cuases the various neuropathies seen in Diabetes Mellitus.
various pathophys factors result from the accum of sugar products in the bloodstream and lead to a resultant increase in oxidative stress on the nerve cell and an increase in vasoconstriction leading to ischemia, which will promote nerve cell injury and death. |
|
|
______ and _______ are both signs of increased cardiac filling pressures (congestive heart failure)
|
S3 and ⬆BNP
|
|
|
_____________________ should be suspected in any patient with pancytopenia following drug intake, exposure to toxins, or viral infections.
|
Acquired Aplastic Anemia
|
|
|
Earliest renal abnormality in diabetes:
|
Glomerular hyperfiltration (which creates intraglomerular hypertension leading to the further problems down the rd--glomerular BM thickening, and then mesangial expansion, and later nodular sclerosis
(this is why ACE inhibitors are so effective in diabetics, b/c of their ability to REDUCE THE INTRAGLOMERULAR HYPERTENSION) |
|
|
Osmotic diuresis occurs in patients with _______________, _____________, or _______________;
-And what will the urine and serum osmolalities be (normal, up, or down) |
Hyperglycemia, Glucosuria, or administration of mannitol
Both Serum & Urine Osmolality are ⬆, but Urine Osm > Serum Osm |
|
|
Which is associated with oral blisters/bullae: Pemphigoid vulgaris or Bullous Pemphigoid?
|
Pemphigoid vulgaris (these are also the ones that are more fragile with + Nikolfsky test
|
|
|
After US is done to rule out GB dz in patient with jaundice and abdominal pain, what labs/imaging/or test is next?
|
Abdominal CT
Abdom CT is a very sensitive and specific tool used in the dx of pancreatic cancer. Commonly, CT scan is effective in detecting bile and pancreatic duct dilitation, mass lesions w/in the pancreas, and indications of extrahepatic spread (eg. metastases or ascites) (not amylase/lipase or Ca-19-9) |
|
|
1st step in mgmt of an infant/newborn with suspected congenital diaphragmatic hernia
|
placement of an OROGASTRIC TUBE connected to continuous suction to prevent bowel distension causing further lung compression
|
|
|
________________ (PE finding) can be used to differentiate between heart-related vs liver-related causes of lower extremity edema. |
Hepato-jugular reflex
|
|
|
Diagnostic test for Pheochromocytoma |
24-hour fractionated urinary METANEPHRINES & CATECHOLAMINES (NOT VMA, less sensitive) |
|
|
Best diagnostic test for Endobronchial Obstructive Lesions:
|
Flexible Bronchoscopy (but if asks for best next step in mgmt, it would be high resolution CT scan) |
|
|
Management of Elevated Lead level |
First, confirm with Venous Lead level (if first sample was capillary). Then, chelation if Lead level > 45. Otherwise close observation, recheck in 1 month, and remove from the hazardous environment.
Chelation therapy: Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), and if >70, then DMSA + EDTA (calcium disodium edetate) |

