![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A patient comes in with dysphagia…
• Best 1st test is a • Next best test is |
Best 1st test is a barium swallow
Next best test is endoscopy (can be dx and allow for bx of suspicious masses or tx in dilation of peptic strictures or injecting botox for achalasia). |
|
|
____________is the test of choice for achalasia.
|
Manometry
|
|
|
______________is the test of choice for
GERD. |
24 pH monitoring
|
|
|
If HIV+ (CD <100) or otherwise
immunocompromised- what gi?? |
remember candida,
CMV and HSV esophagitis |
|
|
Bad breath & snacks in
the AM Dx Tx |
Zenker’s diverticulum.
Tx w/ surgery |
|
|
Zenker is T or False Diverticulum?
|
False. Only contains mucosa
|
|
|
Dysphagia to liquids & solids.
Dx Tx Associated with |

|
|
|
Epigastric pain worse after
eating or when laying down cough, wheeze, hoarse. Dx Tests Tx |
GERD. Most sensitive test is 24-hr pH
monitoring. Do endoscopy if “danger signs” present. Tx w/ behav mod 1st, then antacids, H2 block, PPI. |
|
|
Indications for surgery? for gERD
|
bleeding, stricture, Barrett’s, incompetent LES,
max dose PPI w/ still sxs, or no want meds |
|
|
Dysphagia worse w/ hot &
cold liquids + chest pain that feels like MI w/ NO regurg |

|
|
|
If hematemesis (blood occurs
after vomiting, w/ subQ emphysema). Can see pleural effusion w/ ↑amylase Dx Next best test Tx |

|
|
|
If gross hematemesis
unprovoked in a cirrhotic w/ pHTN. Dx If Hypovolemic shock? Tx of choice? |

|
|
|
If progressive
dysphagia/wgt loss. Dx? (which kind?) Best first test? |
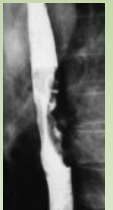
Esophageal Carcinoma
Squamous cell in smoker/drinkers in the middle 1/3. Adeno in ppl with long standing GERD in the distal 1/3. Best 1st test? barium swallow, then endoscopy w/ bx, then staging CT. |
|
|
A patient comes in with MEG pain…
• #1 cause is Tx |
#1 cause is non-ulcerative dyspepsia. Dx of
exclusion. Tx w/ H2 blocker and antacid. |
|
|
A patient comes in with MEG pain…
If GERD sxs predominate- Tx |
- tx empirically w/ PPI for
4 wks then re-evaluate. |
|
|
A patient comes in with MEG pain…
If biliary colic sxs predominate best test? |
RUQ sono
|
|
|
A patient comes in with MEG pain…
If hx of stones or drinking test? |
check amylase and
lipase and CT scan is best imaging for pancreas. |
|
|
A patient comes in with MEG pain…
Danger sxs warrant _________ work up- what are the danger sx? |
Danger sxs warrant endoscopic work up-
– >50 y/o, hx of smoking and drinking, recent unprovoked weight loss, odynophagia, Fe-def anemia or melena. |
|
|
Gastric Ulcers-
Sx Tests Tx |
Gastric Ulcers- MEG pain worse w/ eating. H.pylori, NSAIDs, ‘roids
– Double-contrast barium swallow shows punched out lesion w/ regular margins. EGD w/ bx can tell H. pylori, malign, benign. – Tx w/ sucralfate, H2-block, PPI. Surgery if ulcer remains s/p 12wks treatment. |
|
|
Duodenal Ulcers-
Sx Associated with Tx Tests |
MEG pain better w/ eating
– 95% assoc w/ H. pylori – Healthy pts < 45y/o can do trial of H2 block or PPI – Can do blood, stool or breath test for H. pylori but endoscopy w/ biopsy (CLO test) is best b/c it can also exclude cancer. – Tx H. pylori w/ PPI, clarithromycin & amoxicillin for 2wks. Breath or stool test can be test of cure. |
|
|
Acute Cholecystitis-
Sx Best 1st test Tx |

|
|
|
Choledocothithiasis-
Sx Test |
– Same sxs + obstructive jaundice, high bili, alk phos
– U/S will show stones. Do cholecystectomy or ERCP to remove stone. |
|
|
Ascending Cholangitis-
Sx Tx |
– RUQ pain, fever, jaundice (+hypotension and AMS)
– Tx w/ fluids & broad spec abx. ERCP and stone removal. |
|
|
Cholangiocarcinoma-
Risk factors Tx |
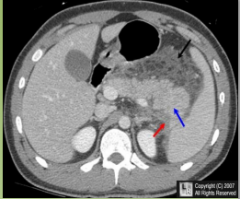
rare. RF are primary sclerosing
cholangitis (UC), liver flukes and thorothrast exposure. Tx w/ surgery. |
|
|
Chronic Pancreatitis-
Sx Can cause... |
– Chronic MEG pain, DM, malabsorption (steatorrhea)
– Can cause splenic vein thrombosis |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma- (of pancreas)
Sx Dx Tx |
– Usually don’t have sxs until advanced. If in head of pancreas
Courvoisier’s sign (large, nontender GB, itching and jaundice). Trousseau’s sign = migratory thrombophlebitis. – Dx w/ EUS and FNA biopsy – Tx w/ Whipple if: no mets outside abdomen, no extension into SMA or portal vein, no liver mets, no peritoineal mets |
|
|
A patient comes in with diarrhea… NEXTnext
|
next
|
|
|
If hypotensive, tachycardic
|
Give NS first!
|
|
|
# 1 cause of diarrhea
|
Viral is #1 cause --> rota in daycare kids, Norwalk on cruise
ships |
|
|
A patient comes in with diarrhea
what test?? |
Check fecal leukocytes --> tells invasion. Stool cx is best test
|
|
|
If bloody diarrhea
what bugs? |
consider EHEC, shigella, vibrio
parahaemolyticus, salmonella, entamoeba histolytica |
|
|
diarrhea + If hx of picnic
|
B. ceres, staph food poisoning. 1-6hrs
|
|
|
diarrhea + If hx of abx use
|
check stool for c. diff toxin antigen
|
|
|
diarrhea + If foul smelling, bulky, malnourished
|
consider Sprue,
chronic pancreatitis, Whipple’s dz, CF if young person. |
|
|
diarrhea + If accompanied by flushing, tachycardia/ hypotension
|
consider carcinoid syndrome (metastatic).
– *Can cause niacin deficiency! (2/2 using all the tryptophan to make 5HT) Dementia, Dermatitis, Diarrhea. |
|
|
A patient presents w/ fatigue, petechiae,
infection bone pain and HSM… NEXT |
nexxt
|
|
|
If >20% blasts?
|
Defines Acute Leukemia on Biopsy
|
|
|
CALLA or TdT?
|
ALL. Most common cancer in kids.
|
|
|
Auer Rods,
myeloperoxidase, esterase? |
AML. More common in adults. RF = rads
exposure, Down’s, myeloprolif. *M3 has Auer Rods and causes DIC upon tx |
|
|
Tartate resistant acid
phosphatase, ↓monos & CD11 and CD22+? |
Hairy Cell Leukemia. See enlarged
spleen but no adenopathy. Hairy Cells have numerous cytoplasmic projections on smear. Tx w/ cladribine 5-7day single course |
|
|
Tx of ALL?
|
Danorub, vincris, pred. Add intrathecal MTX for CNS
recurrence. BM transplant after 1st remission. |
|
|
Tx of AML?
|
Danorub + araC. If *M3 give all trans retinoic acid
|
|
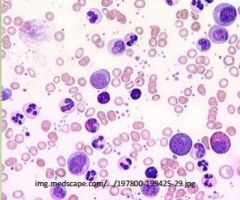
A patient presents w/
fatigue, night sweats, fever, splenomegaly and elevated WBCs w/ low LAP and basophilia? Dx Tx |
CML- 9:22 transloc tyrosine kinase
Tx w/ imantinib (Gleevec), inhibits tyrosine kinase. 2nd line is bone marrow transplant. |
|
|
Asymptomatic elevation
in WBCs found on routine exam – 80% lymphs. Dx? If Lymphadenopathy - If Splenomegaly If Anemia If Thrombocytopenia |
CLL
If Lymphadenopathy - Stage 0 or 1 need no tx- 12 yrs till death If Splenomegaly - Stage 2 tx w/ fludrabine If Anemia - blast crisis???? Tx??? If Thrombocytopenia - Stage 3 or 4 tx w/ steroids |
|
|
Enlarged, painless, rubbery
lymph nodes |
Think Lymphoma
|
|
|
Drenching night sweats,
fevers & 10% weight loss. |
“B-symptoms” = poor prognosis along w/
>40, ↑ESR and LDH, large mediastinal LND |
|
|
Best initial test?
|
Excisional lymph node biopsy
|
|
|
Next best test?
|
Staging Chest/Abdominal CT or MRI. If still unsure,
staging laparotomy is done. Bone marrow bx (esp for NHL |
|
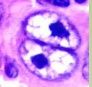
Orderly, centripetal spread
+ Reed Sternberg cells? |
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
|
|
|
Type w/ best prognosis?
|
Lymphocyte predominant
|
|
|
More likely to involve
extranodal sites? (spleen, BM) |
Non-hodgkin’s Lymphoma
|
|
|
Staging?
|
I = 1 node group, II = 2 groups, same side of diaphragm,
III = both sides of diaphragm, extension into organ. IV = BM or liver |
|
|
Treatment?
|
I/II get rads
III/IV get ABVD chemo |
|
|
Other hematologic randoms…
NEXT |
next
|
|
|
Bone pain, “punched out
lesions” on *x-ray*, hyper Ca – Best 1st test- – Confirmatory test- – Tx- |

|
|
|
Dizziness, HA, hearing/vision
problems and monoclonal IgM M-spike. |
Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia
|
|
|
No sxs, immunoglobulin
spike found on routine exam |
MGUS
|
|
|
Older pt w/ generalized
pruritis and flushing after hot bath. Hct of 60%. Dx Best 1st test Tx |
Polycythemia Vera
Check epo, make sure it isn’t secondary. (PSG, carboxy-Hb) Scheduled phlebotomy. Hydroxyurea can prevent thromboses |

