![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
defect in tyrosinase
accum? sx? path? |
albinism
accumulation of tyrosine (precursor to melanin) ungpigmented eyes and skin aa metabolism |
|
|
defect in phenlalanine hydroxylase or dehydrobiopterin reductase
accum? essential? sx? path? |
phenylalanine accum
tyrosine becomes essential (to produce Dopa, NE, Epi) sx: mental retardation, hypopigmentation, musty odor aa metabolism tx= decrease phenylalanine / aspartame in diet |
|
|
def of homogentisate oxidase
path? accum? sx? |
alkaptonuria
path = tyrosine breakdown accum of homegisic acid sx = dark pigment in cartilage, arthritis, urine darkens |
|
|
defect in cystathione synthetase
path? accum? sx? |
homocystinuria
sx = mental retardation, lens dislocation, DVT, athero (CV probs like marfans), caved in chest homocysteine accumulates aa metabolism |
|
|
deficient in branched chain decarboxylase
dz? sx? accum? tx? |
maple syrup urine dz
Valine, leucine, isoleucine accum = tx = lose these in the diet aa metabolism sx=hyperreflexia, sweet odor to urine |
|
|
defect in dibasic aa transporter in kidneys and intestinal epithelium
sx? what changes with excretion? tx? path? |
cystinuria
sx = urinary cystine stones aa metabolism path aa overexcreted = cystine, lysine, arginine, ornithine tx=acetozolamide |
|
|
defect in neutral aa transorter in kidneys and intestinal epith
|
Hartnup disease
increased excretion of neutral aa (tryptophan) sx=pellagra = dementia, dermatitis, diarrhea (tryp>niacin>pellagra) - can also be caused by niacin deficiency |
|
|
direct precursor to melanin?
Can pts with tyrosinase deficiency as with albinism still make NE and EPI? |
dopa
(tyrosine>dopa>melanin) dopa>dopamine>NE>Epi yes |
|
|
trypsin cleaves which aa from the NH3 terminal?
what about chymotrypsin? |
trypsin = Arg, lysine
chymotrypsin=phen, tyr, trp, leu |
|
|
do muscles release glc into circulatoin? why?
deficiency in this enzyme results in what sx and dz? |
no - no glc-6-phosphatase = only liver
type 1 Von Gierke glycogen storage disease = enlarged liver and kidney, fasting hypglycemia, acidosis, FTT |
|
|
a-glucosidase is an enzyme found where? action?
deficiency results in? |
lysomes of all cells - cell continuously degrade glycogen in lysosomes
deficiency = type II pompe glycogen storage disease sx = all organs with glycogen accum in lysosome - muscle hypotonia, cardiac failure, death before age 2 - no hypoglycemia here |
|
|
glycogen storage diseases all have similar sx what are they?
which does not have hypoglycemia? which is void of liver sx? |
lactic acidosis due to inability to mobilize glc stores (except Cori's Dz/III = debranching enzyme defect (a1,6 glucosidase) - can still make glc so no lactic acidosis)
increased TGs in the blood hepatomegaly (no liver sx in McArdles=V=glycogen phophorylase which is only in muscle = cleaves a1-4 bonds; fatty liver only with Von Gierkes where fasting hypoglycemia is severe = gluc 6 Pase defect) hypoglycemia (not in Pompe - type ii - glucosidase def in lysosomes) |
|
|
glycogen storage disease specific to liver enzyme? msucle enzyme?
|
g6Phosphatase = von gierkes/I = fatty liver with uricemia = liver only - muscle does not secrete glc into blood
muscle enzyem = glyc phosphorylase = McArdles/V = cleaves 1,4 bonds to form G1P = muscle pain, myoglobinuria, decreased exercise tolerancy |
|
|
glycogen storage dz with cardiomegaly, normal blood glkucose, death by age 2, lysosomal accumulation of glycogen?
|
pompe's dz/II = defect in a1,4 glucosidase in lysosomes
|
|
|
glycogen storage disease with normal lactate levels as gluconeogenesis is still in tact -- results in dextrin in the cytosol of cells and no fatty liver
|
Cori's dz/III
def=debranching enzyme (a1,6 glucosidase) |
|
|
corneal cloudin
mental retardation increased accum of heparin sulfate and dermatan sulfate enzyme def? d/o? genetics? |
Hurler's syndrome
defect in a-L iduronidase AR also with gargoylism (course facial hiar, macroglossia, micrognothia), recurring upper resp infection/airway obstruction mucopolysaccaridoses |
|
|
mental retardation
no corneal clouding accum of heparin sulfate and dermatin sulfate |
Hunters
iduronate sulfatase deficiency milder than hurlers X linked recessive may have abnormal facial appearance - pearly papules over arms and legs -- hyperactivity/aggressive behavoir mucopolysaccaridoses |
|
|
progressive paralysis
accum of sulfatides or cerebroside sulfate |
metochromatic leukodystrophy
enzyme def = arylsulfatase A AR central and peripheral demylination with ataxia, dementia |
|
|
blindness
deafness convulsions accum of glactocerebrosides d/o? enzyme? cell? |
Krabbe
def in B-glactaosidase AR globoid cells |
|
|
What accounts for gains in life expectancy?
|
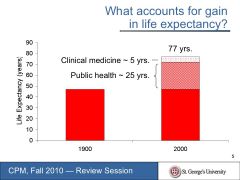
Clinical medicine ~ 5 years
Public Health ~ 25 years |
|
|
accum of sphingomyelin
liver and spleen enlargment foamy cells |
defect in sphingomyelinase
Neimann Pick AR |
|
|
accum of globosides (ceramide trihexoside)
reddish/puple skin rash kidney/heart failure angiokeratoma |
fabry dz
XR defect in a-galactosidase A |
|
|
accum of gangliosides (GM2)
blindness cherry red macula aschkenzi jews |
defect in hexosaminidase
tay sachs AR |
|
|
sphingolipidoses that are assoc with ashkenazi jews
|
Neimann pick (accum/def = shingomyelin/sphingomyelinase)
guacher (glucocerebroside/B-glucocerebrosidase) tay sachs (gm2 ganglioside/hexosaminidaseA) |

